
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
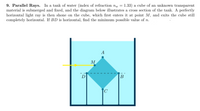
Transcribed Image Text:9. Parallel Rays. In a tank of water (index of refraction nw =
material is submerged and fixed, and the diagram below illustrates a cross section of the tank. A perfectly
horizontal light ray is then shone on the cube, which first enters it at point M, and exits the cube still
completely horizontal. If BD is horizontal, find the minimum possible value of n.
1.33) a cube of an unknown transparent
A
М
D
В
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer the following questions A. The critical angle for total internal reflection at a diamond-air interface is 25 degrees. Suppose the light falls at an angle to the normal. Then, total internal reflection will occur if the incident medium is: a) air and angle < 25 degrees b) air and angle > 25 degrees c) air and angle = 25 degrees d) diameter and angle > 25 degrees e) diamond and angle < 25 degrees B. A ray of light in water (index n1) hits its surface (with air) at a critical angle for total internal reflection. Now some oil (index n2) floats in the water. The angle between the ray in the oil and the normal is: note: sin -1 (1.00), it is read as the inverse sine of one. a) sin -1 (1/n1) b) sin -1 (1/n2) c) sin -1 (1.00) d) sin -1 (n1/n2) e) sin -1 (n2/n1) C. A ray of light passes obliquely (non-zero angle) through a glass plate that has parallel faces. The emerging ray: a) it leans more towards the normal than the incident ray b) is reflected internally toatl c) tilts…arrow_forward1) What is the speed of light in a glass(n=1.5)? 2) A man 1.80 m tall stands in front of a vertical plane mirror. What is the minimum height of the mirror, if he is to see his whole body? Assume his eyes are 10 cm below the top of his head.arrow_forwardA goldfish is swimming inside a spherical bowl of water having an index of refraction n = 1.333. Suppose the goldfish is p 10.4 cm from the wall of a bowl of radius |R| = 15.8 cm, as in the figure below. Neglecting the refraction of light caused by the wall of the bowl, determine the apparent distance of the goldfish from the wall according to an observer outside the bowl. 1.07 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm behind the glassarrow_forward
- In the figure, a 2.1-m-long vertical pole extends from the bottom of a swimming pool to a point 50.0 cm above the water. Sunlight is incident at angle = 51.0°. What is the length in meters of the shadow of the pole on the level bottom of the pool? The water has an index of refraction of 1.33. A Blocked sunraysarrow_forwardTwo light beams are incident normal to one surface of a triangular prism with refractive index n = 1.4 surrounded by air. What is the value of the angle between the two emerging beams, shown as a in the figure? d a 90° d 45° O 70.4° 73.7° O 61.8° 60.0° O 65.8° ..... ......arrow_forwardAssume that a material is composed of 3 layers in descending order: air (nair = 1.00), water (nwater = 1.33), and glass (nglass= 1.52). Then, assume that a monochromatic light ray in the air passes through the surface of water with an angle of incidence 0₁ = 40 degrees. A. Find the angle of refraction in glass after it passes completely through the water layer. B. Find how fast is the light ray moving in the glass?arrow_forward
- Optical fibers are a central part of technology for rapid information transmission with a high level of efficiency. A new type of optical fiber is crafted with an index of refraction n = less than that of water in the vicinity of room temperature, where NH2O fact that n < nH20 potentially problematic if the fiber should be submerged? 1.25 = 1.33. Why is the O A. Total internal reflection would be frustrated, allowing loss of signal. O B. Internal reflection would actually be enhanced, so there is no problem. C. Electric eels might have free internet access.arrow_forwardw9-10 A diamond in air is illuminated with white light. On one particular facet, the angle of incidence is 25.70°. Inside the diamond, red light (λ = 660.0 nm in vacuum) is refracted at 10.88° with respect to the normal; blue light (λ = 470.0 nm in vacuum) is refracted at 10.13°. How would a diamond look if there were no dispersion? a. The diamond would look white. b. The diamond would look red. c. The diamond would look blue. d. The diamond would be clear.arrow_forwardSuppose you have an unknown clear substance immersed in water, and you wish to identify it by finding its index of refraction. You arrange to have a beam of light enter it at an angle of 45.0° with respect to the normal, and you observe the angle of refraction to be 40.3°. A. What is the index of refraction of the substance? B. What is its likely identity?arrow_forward
- You are using a transparent tube as an optical fiber in open air (n air=1.00) you have calculated that the critical angle for the fiber is 34.5. a) what is the index of refraction of your optical fiber? b)to make your fiber more durable, you encase it in a cladding with an index of refraction equal to 1.35. Will the beam be reflected into the fiber or will it leak into the cladding when the incident angle inside the fiber is 50.arrow_forwarda. A ray of light enters a fiber optic cable with index of refraction n from air at an angle e as shown below. Let the angle 0 be 69°. For total internal reflection to occur at the cable-air interface, what must be the value of n? Dair - 1 n = Ꮎ θα ec narrow_forwardStephen is given a large crystal and needs to verify whether it is a diamond or cubic zirconia. He shines a beam of light at a 48.8 ° angle upon the face of the crystal and measures the refraction angle. What is the refraction angle if the crystal is a diamond? refraction angle for diamond - What is the refraction angle if the crystal is a cubic zirconia? refraction angle for cubic zirconia =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON