
Curren'S Math For Meds: Dosages & Sol
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305143531
Author: CURREN
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
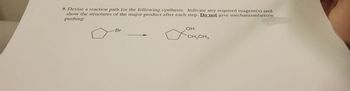
Transcribed Image Text:9. Devise a reaction path for the following synthesis. Indicate any required reagent(s) and
show the structures of the major product after each step. Do not give mechanism/arrow
pushing.
Br
OH
CH2CH3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Which of the following statements about the allosteric site is true? a. The allosteric site is a second active site on a substrate in a metabolic pathway. b. The allosteric site on an enzyme can allow the product of a metabolic pathway to inhibit that enzyme and stop the pathway. c. When the allosteric site of an enzyme is occupied, the reaction is irreversible and the enzyme cannot react again. d. An allosteric activator prevents binding at the active site. e. An enzyme that possesses allosteric sites does not possess an active site.arrow_forwardWhich Is “Better: NMR or MS? Compare and contrast mass spectrometry and NMR. in terms of their potential advantages and disadvantages for metabolomic analysis.arrow_forwardWhich of the following analogies best describes the induced-fit model of enzyme-substrate binding? a hug between two people a key fitting into a lock a square peg fitting through the square bole and a round peg fitting through the round hole of a children’s toy the fitting together of two jigsaw puzzle piecesarrow_forward
- The synthetic process by which monomers are covalently linked is (a) hydrolysis (b) isomerization (c) condensation (d) glycosidic linkage (e) ester linkagearrow_forwardb. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be intermediates in the pathway for production of protein E. To determine where the block in protein-E production occurred in each individual, the various intermediates were given to each individuals cel Is in culture. After a few weeks of growth with the intermediate, the cells were assayed for the production of protein E. The results for each individuals cells are given in the following table. A plus sign means that protein E was produced after the cells were given the intermediate listed at the top of the column. A minus sign means that the cells still could not produce protein E even after being exposed to the intermediate at the top of the column. Denote the point in the pathway in which each individual is blocked.arrow_forwarda. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be intermediates in the pathway for production of protein E. To determine where the block in protein-E production occurred in each individual, the various intermediates were given to each individuals cel Is in culture. After a few weeks of growth with the intermediate, the cells were assayed for the production of protein E. The results for each individuals cells are given in the following table. A plus sign means that protein E was produced after the cells were given the intermediate listed at the top of the column. A minus sign means that the cells still could not produce protein E even after being exposed to the intermediate at the top of the column. Draw the pathway leading to the production of protein E.arrow_forward
- MATHEMATICAL Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide about 107 times faster than the uncatalyzed reaction. If the latter required one year, how much time would be needed by the catalase- catalyzed reaction?arrow_forwardEnergetic of Fructose-1 ,6-bis P Hydrolysis (Integrates with Chapter 3.) The standard free energy change (G) for hydrolysis of fructose-1. 6-bisphosphate (FBP) to fructose-S-phosphate (F-6-P) and P: is -16.7 KJ/mol: FBP + H2O fructose-6-P + Pi The standard free energy change (G) for ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 KJ/mol: ATP + H2O ADP + Pj What is the standard free energy change for the phosphofructokinase reaction: ATP + fructose-6-P ADP + FBP b. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? c. Assuming the intracellular concentrations of [ATP] and (ADP] are maintained constant at 4 mM and 1.6 mM, respectively, in a rat liver cell, what will be the ratio of [FBP]/[fructose-6-P] when the phosphofructokinase reaction reaches equilibrium?arrow_forwardAllosteric Regulation of Ribonucleotide Reductase by ATP and Deoxynucleotides Describe the underlying rationale for the regulatory effects exerted on ribonucleotide reductase by ATP, dATP, dTTP, and dGTP.arrow_forward
- What is the primary difference between a circular pathway and a linear pathway?arrow_forwardGTP or ATP is produced during the conversion of isocitrate into ketoglutarate succinyl CoA into succinate fumarate into malate malate into oxaloacetatearrow_forwardExamine the ActiveModel for alcohol dehydrogenase and describe the structure and function of the catalytic zinc center.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College


Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College