
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
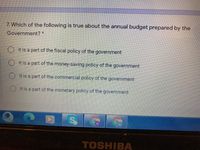
Transcribed Image Text:7. Which of the following is true about the annual budget prepared by the
Government? *
It is a part of the fiscal policy of the government
O It is a part of the money-saving policy of the government
O It is a part of the commercial policy of the government
It is a part of the monetary policy of the government
TOSHIBA
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Deficits in new classical economics Felix lives in the fictional country of Lindelof, which raises government revenue by taxing everyone the same amount. The government of Lindelof has just implemented a tax cut that reduces annual taxes by $3,500 per person. However, government spending has not changed, nor is it likely change in the future. The tax cut has raised Felix's income by $3,500. If Felix acts according to the prediction of new classical economics (and doesn't plan to leave Lindelof), his consumption is likely to increase by Suppose that instead of cutting taxes while keeping its spending the same, the government did the opposite: it increased its spending by $3,500 per person while keeping taxes the same. If everyone in Lindelof acted like Felix, the likely increase in aggregate demand would be per person.arrow_forwardConsider the following picture. c' A D B E F Suppose that the government changes government spending: it increases G and decreases G', but leaves T and T' unchanged. The interest rates in the economy are also unchanged. What happens to the budget line of the consumer? O It expands to the right: the consumer will be able to consume more in the present, and less in the future It contracts to the left: the consumer will be able to consume less in the present, and more in the future O It's unchanged O Impossible to tell!arrow_forwardD₂ Which of the following movements would be consistent with the government budget going from deficit to surplus and the simultaneous enactment of an investment tax credit? O a movement from Point A to Point C a movement from Point B to Point A O a movement from Point B to Point F a movement from Point C to Point Barrow_forward
- The following graph shows the aggregate demand curve ( AD1) for this economy before the change in government spending. Use the green line (triangle symbol) to plot the new aggregate demand curve ( AD2) after the multiplier effect takes place. For simplicity, assume that there is no "crowding out." Hint: Be sure that the new aggregate demand curve (AD2) is parallel to the initial aggregate demand curve ( AD1 ). You can see the slope of AD1 by selecting it on the graph. 140 AD, 135 AD, 130 125 120 115 110 105 100 3 4 OUTPUT (Trillions of dollars) PRICE LEVELarrow_forward6. Use the following table to answer these questions: Y C I G X $ 500 $ 500 $ 10 $ 20 $ 60 $ 600 $ 590 $ 10 $ 20 $ 40 $ 700 $ 680 $ 10 $ 20 $ 20 $ 800 $ 770 $ 10 $ 20 $ 0 $ 900 $ 860 $ 10 $ 20 - $ 20 $ 1,000 $ 950 $ 10 $ 20 - $ 40 a.What is the Marginal Propensity to Import? b.What is the Marginal Propensity to Invetst? c.What the difference between both of…arrow_forwardE4arrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward14) What could explain what is happening in the graph to the right? a. The government has given investors an investment tax credit, increasing investors appetite for savings. b. The government has removed the tax protected status of IRA accounts, increasing savings. c. The government balances the interest rate Το r1 Eo E1 So $1 budget reducing its debt, and the "crowding out" effect disappears. business desire to obtain funds. 90 91 quantity of loanable funds d. A new technology makes industry much more productive, therefore increasing e. There are many things that could explain what the graph shows us, but we don't have enough information to decide on any of a. thru d. above.arrow_forward2arrow_forward
- 1. The government expenditure multiplier is the effect of a change in government expenditure (G) on goods and services: a. An increase in aggregate expenditure increases aggregate demand (AD), which increases real GDP, which induces an increase in consumption expenditure (C), and which further increases aggregate demand (AD). b. An increase in aggregate expenditure increases aggregate supply (AS), which increases real GDP, which induces an increase in consumption expenditure (C), and which further increases aggregate supply (AS). c. An increase in aggregate expenditure decreases aggregate demand (AD), which decreases real GDP, which induces an decrease in consumption expenditure (C), and which further decreases aggregate demand (AD). d. An increase in aggregate expenditure decreases aggregate supply (AS), which decreases real GDP, which induces an decrease in consumption expenditure (C), and which further decreases aggregate supply (AS). 2. How do banks create money? Group of…arrow_forward2arrow_forward2. Assume a given economy has an equilibrium GDP of $360 billion. A. If government spending and taxes both increase by $40 billion, determine the new equilibrium GDP. B. If both G and taxes increase by $40 billion, what impact will these two changes happening at the same time have on the budget? In other words, will these two changes cause a surplus, a deficit, or a balanced budget? C. Solve for the numerical value of the balanced budget multiplier.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education