
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
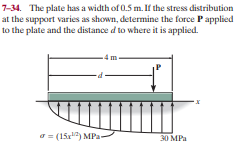
Transcribed Image Text:7-34. The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress distribution
at the support varies as shown, determine the force P applied
to the plate and the distance d to where it is applied.
4 m
a = (15r") MPa-
30 MPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- R8-6. The head H is connected to the cylinder of a compressor using six steel bolts. If the clamping force in each bolt is 4 kN, determine the normal strain in the bolts. Each bolt has a diameter of 5 mm. If ay = 280 MPa and E - 200 GPa, what is the strain in each bolt when the nut is unscrewed so that the clamping force is released?arrow_forward9-55. Determine the equivalent state of stress for an element oriented 60° counterclockwise from the element shown. Show the result on the element. 400 MPa 250 MPa 560 MPaarrow_forwardIf the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the force P is applied, determine the magnitude of P. The wire is A-36 steel and has a diameter of 3 mm.arrow_forward
- 7-30. The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional area of 780 mm². Determine the average normal stress in each member due to the loading P = 40 kN. State whether the stress is tensile or compressive. a9m -1.2m -1.2 m- 0.75 Parrow_forward1-103. The bar is supported by the pin. If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is (o)allow = 150 MPa, and the allowable shear stress for the pin is Tallow = 85 MPa, determine the diameter of the pin for which the load P will be a maximum. What is this maximum load? Assume the hole in the bar has the same diameter d as the pin. Take 1 = 6 mm and w = 50 mm.arrow_forward*7-36. The pedestal has a triangular cross section as shown. If it is subjected to a compressive force of 2250 N, specify the x and y coordinates for the location of point P(x, y), where the load must be applied on the cross section, so that the average normal stress is uniform. Compute the stress and sketch its distribution acting on the cross section at a location removed from the point of load application. X 75 mm 300 mm 150 mm 2250 N Prob. 7-36 P(x,y) yarrow_forward
- *7-56. The steel swivel bushing in the clevator control of an airplane is held in place using a nut and washer as shown in Fig. (a). Failure of the washer A can cause the push rod to separate as shown in Fig. (b). If the average shear stress is Tng = 145 MPa, determine the force F that must be applied to the bushing that will cause this to happen. The washer is 15 mm thick. 20 mm - (a) (b)arrow_forwardThe plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress distribution at the support varies as shown, determine the force P applied to the plate and the distance d to where it is applied.arrow_forwardThe 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at point G. If it is suspended from cables AB and AC, determine the diameter of cable AB so that the average normal stress in this cable is the same as in the 10-mm-diameter cable AC.arrow_forward
- 7-67. If the allowable shear stress for each of the 10-mm-diameter steel pins at A, B, and Cis Tllo - 90 MPa, and the allowable normal stress for the 13-mm-diameter rod is oalon - 150 MPa, determine the largest intensity w of the uniform distributed load that can be suspended from the beam. 1.2 m 0.3marrow_forwardR7-5. Determine the average punching shear stress the circular shaft creates in the metal plate through section AC and BD. Also, what is the bearing stress developed on the surface of the plate under the shaft? 40 kN - 50 mm - Ti0 mm -60 mm -120 mmarrow_forwardDetermine the maximum normal stress (in MPa) developed in the bar when it is subjected to a tension of P = 12 kN.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY