
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
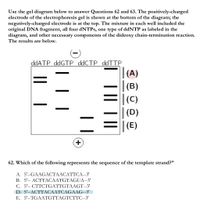
Transcribed Image Text:Use the gel diagram below to answer Questions 62 and 63. The positively-charged
electrode of the electrophoresis gel is shown at the bottom of the diagram; the
negatively-charged electrode is at the top. The mixture in each well included the
original DNA fragment, all four dNTPs, one type of ddNTP as labeled in the
diagram, and other necessary components of the dideoxy chain-termination reaction.
The results are below.
ddATP ddGTP ddCTP ddTTP
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
+.
62. Which of the following represents the sequence of the template strand?"
A. 5'--GAAGACTAACATTCA--3'
B. 5'-- ACTTACAATGTAGUA--3'
C. 5'-- CTTCTGATTGTAAGT--3'
D. 5'--ACTTACAATCAGAAG--3'
E. 5'--TGAATGTTAGTCTTC--3'
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Provide the sequences of the template and coding strands of a DNA double helix that was used toproduce this RNA: 5’-GUUACCGACUAU. Be sure to label the 5’ and 3’ ends.arrow_forward17. Complete the following Central Dogma Grid Puzzles: First determine which DNA strand is the template (look at provided nucleotides). Label template and coding/sense (non-template) strand in first column. In the second column, label the 5' and 3' ends of DNA and RNA sequences and the amino (N) and carboxyl (C) ends of the polypeptide. The last four columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments (reading frame). This is from within a coding region so you don't have to find a start codon. Fill in all nucleotides and amino acids using the mRNA code table on the last page. a. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA strand C DNA strand G mRNA codon A U TRNA anticodon A polypeptide TRParrow_forward2b) What anticodon would a suppressor tRNA have to have to suppress a 5'UAA3' stop codon?arrow_forward
- For each of the following sequences, place a check mark in the appropriate space to indicate the process most immediately affected by deleting the sequence. Choose only one process for each sequence (i.e., one check mark per sequence). Process most immediately affected by deletion RNA Sequence deleted Replication Transcription Translation processing a. ori site b. 3' splice site consensus c. Poly(A) tail d. Terminator e. Start codon f. -10 consensus g. Shine-Dalgarnoarrow_forward17arrow_forward2. H. Gobind Khorana deciphered the genetic code by (1) chemically synthesizing DNA molecules of known sequence, (2) using this synthetic DNA as a template to produce RNA in a reaction involving RNA polymerase and dNTPs, then finally (3) using this RNA in an in vitro translation experiment with the ribosome and amino acyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) building blocks to produce peptides. For each single-stranded deoxyribonucleotide sequence Khorana synthesized (shown below), a single polypeptide was produced in the in vitro translation step (3): (1) Synthetic DNA d(TTT)n d(CCC)n d(AAA)n d(GGG)n d(AAACCC)n d(AC)n d(ACA)n a. (2) RNA encoded by synthetic DNA (3) Peptide product composition polylysine polyglycine polyphenylalanine polyproline Equal F and G Equal C and V polycysteine Fill in the RNA sequences that were produced by RNA polymerase in column (2). b. When Khorana conducted this work, one looming question in the field was whether or not the genetic code is overlapping or non-overlapping. In a…arrow_forward
- b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA strand C DNA strand T G A MRNA codon C|A U TRNA anticodon G A polypeptide TRParrow_forward(11) If you design a gRNA with the sequence, GGU AUC AUU GCA CUG ACC AG, in theory which position of the nucleotide in the genomic DNA sequence below will be cut by Cas9 protein, which may lead to a knockout due to an error in DNA repair? The starting and the end coordinate positions of the DNA fragment on the chromosome are indicated at the beginning and end of the sequence, respectively. 110,001 ATC GGT ATC ATT GCA CTG ACC AGA GGC TAC 110,030 A) Between 110,023 (G) and 110,024 (A) B) Between 110,021 (C) and 110,022 (A) C) Between 110,020 (C) and 110,021 (C) D) Between 110,009 (C) and 110,010 (A)arrow_forwardA. Diagram a short single strand of DNA 5’ -AA-GG- 3’. Show the chemical structure of the phosphoribosyl backbone and the attachment point for nucleotides added as “A” or “G”. B. Diagram the product of digestion was a restriction enzyme to cut this sequence between the A and G.arrow_forward
- A mutation has occurred to a wild type mRNA sequence: Wild Type: 5’-AUG-UUG-CAA-GCG-3’ The new mutated sequence: 5’-AUG-UUG-UAA-GCG-3’ What kind of mutation has occurred? a)Silent mutation b)Missense mutation c)Nonsense mutation d)Frameshift mutationarrow_forward36.Start with two exons and an intervening intron. Include the cap and poly-A tail in your starting pre-mRNA. Show 2’-OH, 3’-OH, O-P-O phosphodiester bonds for the two transesterification reactions that splice exon 1 and exon 2. Be sure to include the branchpoint A and intron consensus sequences. You will need to show where the incoming -OH attacks the O-P-O bond to allow correct splicing in the lariat and between exons. Make your arrows precise. Show the lariat with the consensus sequences. Whenever possible, show 5’ and 3’ ends. Explain the fate of the lariat after it forms?arrow_forwardI. The DNA template, 3'–CGTTACCCGAGCOCGTACGATTAGG–5', was exposed to a mutagen, resulting in the following three templates. 2. A. 3'–CGTTACCCGAGCCGTAACGATTAGG-5' nserti on leuding to frame shift B. 3-CGTTACCCGATCCGTACGATTAGG–5' Point - Transversin C. 3'-CGTTACCCGAGCCGTTCGATTAGG–5' Transition I. Transcribe and translate each template and write down the primary sequence of the resulting polypeptide/protein. Describe how each of the mutations will affect the final protein product from the corresponding template. N met -gla - Ser- Ala -cys -Stup-d Predict whether gene expression (from initiation of transcription to final protein product) would be faster in a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. Explain your answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education