
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
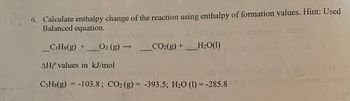
Transcribed Image Text:210
6. Calculate enthalpy change of the reaction using enthalpy of formation values. Hint: Used
Balanced equation.
-
C3H8(g) +
O₂ (g) →
AH values in kJ/mol
CO₂(g) + H₂O(1)
C3H8(g) = -103.8; CO₂ (g) = -393.5; H₂O (1) = -285.8
Slonel'i
34 140m² p vrl=3
odtyd enab how to £25031
odi to ondo verons lamotri
Lar
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me solve this question, i keep getting it wrong everytimearrow_forwardSubstance AH (kJ/mol) MgCl2(aq) -785.1 kJ/mol HCl(aq) -167.2 kJ/mol Given the enthalpy of formation data in the table, what is the enthalpy of reaction for the reaction you performed in this lab? To calculate the enthalpy of reaction, use the following formula. AHrxn =ΣAH(products) - ΣAH; (reactants) Note that you will need the balanced chemical equation for the reaction performed in the lab. Also, note that AH; for the standard state elements is 0 kJ/mol. AHrxn = Is the calculated result simliar to the experimentally determined result? yes no kJ/molarrow_forwardConsider the following reactions: AH = -393.5 kJ (graphite) + 2 AH = -285.8 kJ 2(g) CH,OH + 3/2 0, +2H,0 AH = -726.4 k (1) Choose... Choose... -48.25 Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction: 188.7 + 2 H29) CH,OH -37.6 C (graphite) + V½ 0, 10.7 -238.7 39.0 268 11.85 Given the following information: N, bond energy = 941 kJ/mol, F, bond energy = 154 kJ/mol 2 N + 3/2 F AH = -103 kJ/mol 2(g) Choose... Calculate the N-F bond energy (kJ/mol) A ballon originally had a volume of 8.68 L at 258 K and a pressure of 575 mmHg. To what temperature (in K) must the balloon be cooled to reduce its volume to 5.00 L at a pressure of 730 mmHg? Choose... Varrow_forward
- 10. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of N₂O5 from the following data: kJ mol kJ 2NO(g) + O₂(g) →2NO₂(g) 4NO2(g) + O₂(g)→2N205(g) N₂(g) + O₂(g) →2NO(g) 4,H☺ = -114.1 = -110.2- 'mol kJ mol AH AH = + 180.5,arrow_forward2 E6L14(s) + 19 A2(g) → 12 MA2(g) + 7 L₂A(g) AH = 1300 kJ/molrxn 21. What is the enthalpy of formation, AH, for the substance E6L14 shown in the reaction above? AH (kJ/mol) ??? со How Substance E6L14(S) A₂(g) De MA₂(g) L₂A (g) 0 100 50 Barrow_forwardFind the enthapy change for the reaction below in kJ . 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) --> 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) ΔH= ? Given : (NH3(g)) = -46.1, (NO(g)) = + 90.3 kJ/mol and (H2O(g)) = -241.8 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- Using standard heats of formation, calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction. 2HBr(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl(g) + Br₂(g) AH (HBr(g)) = -36.3 kJ/mol AH (Cl₂ (9)) = 0.0 kJ/mol AH (HCl(g)) = -92.3 kJ/mol AH (Br₂ (9)) = 30.9 kJ/mol AH rxn = kJarrow_forwardThe combustion of 0.1566 g benzoic acid increases the temperature of a bomb calorimeter by 2.51°C. Calculate the heat capacity of this calorimeter. (The energy released by combustion of benzoic acid is 26.42 kJ/g.) Heat capacity = kJ/°C A 0.2195-g sample of vanillin (Cg H3 O3) is then burned in the same calorimeter, and the temperature increases by 3.21°C. What is the energy of combustion per gram of vanillin? Energy = kJ/g Per mole of vanillin? Energy = kJ/molarrow_forwardA student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1100. g of water (see sketch at right). thermometer stirrer First, a 5.500 g tablet of benzoic acid (C,H,CO, H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of water oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is observed insulation to rise from 15.00 °C to 42.56 °C over a time of 10.3 minutes. Next, 5.720 g of acetaldehyde (C2H,O} are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 15.00 °C to 40.53 °C. chemical reaction "bomb" Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: A "bomb" calorimeter. 2C,H,0(g) + 50, (g) 4CO, (g) + 4H,0 (g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note…arrow_forward
- The balanced thermochemical equation for the combustion of exactly one mole of propane is: C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 3 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O(l) ΔH = -2220 kJ/mol What is the enthalpy change for the reaction: 1.5 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) → 0.5 C3H8 (g) + 2.5 O2 (g) ΔH = ?arrow_forwardHow much heat is produced when 0.480 mol of methane is burned under standard conditions. Enthalpy of combustion of methane = -891 kJ/mol. - A) -891 kJ B 428 kJ -222 kJ -644 kJ -428 kJarrow_forward2 C,H,0(g) + 50,(8) 4 CO2(g) + 4 H,0(g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced students: it's possible the student did not do these experiments sufficiently carefully, and the values you calculate may not exactly match published values for this reaction. exothermic Is this reaction exothermic, endothermic, or neither? endothermic O neither If you said the reaction was exothermic or endothermic, calculate the amount of heat that was released or absorbed by the reaction in the second experiment. kJ kJ Calculate the reaction enthalpy AH, per mole of C,H¸0. rxn molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY