Question
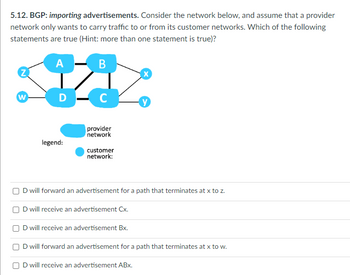
Transcribed Image Text:**5.12. BGP: Importing Advertisements**
Consider the network diagram below, assuming that a provider network only wants to carry traffic to or from its customer networks. Examine the network structure and determine which of the following statements are true (Hint: more than one statement is true).
**Diagram Explanation:**
- **Nodes**:
- **Provider Nodes (Blue):** A, B, C, D (central nodes representing a provider network).
- **Customer Nodes (Black):** w, x, y, z (peripheral nodes connected as customer networks).
- **Connections**:
- **Provider Network Connections:**
- Node A is connected to Nodes Z, B.
- Node B is connected to Nodes A, D, X.
- Node D is connected to Nodes W, C, Y, X.
- **Customer Network Connections:**
- Node W is connected to Node D.
- Node X is connected to Node B.
- Node Y is connected to Node D.
- Node Z is connected to Node A.
**Legend**:
- Provider networks are indicated by blue nodes.
- Customer networks are indicated by black nodes.
**Statements:**
1. □ D will forward an advertisement for a path that terminates at x to z.
2. □ D will receive an advertisement Cx.
3. □ D will receive an advertisement Bx.
4. □ D will forward an advertisement for a path that terminates at x to w.
5. □ D will receive an advertisement ABx.
In the context of BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), consider the rule that provider networks prefer not to forward advertisements to other providers, only to customers. Analyze the paths and select the statements that abide by this principle.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Using BGP path advertisements to implement routing policy. Consider the network below with interconnected provider networks and customer networks. Assume that provider network D only wants to carry traffic that originates in one of its customer networks (w, z) or is destined to one of its customer networks. It specifically does not want to forward datagrams between two other provider networks, since that transit traffic is neither sourced from, nor destined to, a customer network of D. W Oz à X customer network: Given these policies, to which other networks will network D advertise the path Dw? ПА П В Oy A DC legend: B provider networkarrow_forwardIn Cisco Packet Tracer, I have three routers (A, B, and C). B and C should be in a cluster; this cluster should have one IP address: 205.128.216.18. A, which should have an IP address of 172.167.5.8, should only use one cable to connect to the cluster.arrow_forwardAssume a company has three offices: Central, East, and West. The company is granted a block of 64 addresses with the beginning address 70.12.100.128/26. The management has decided to allocate 30 addresses for the Central office and divides the rest of addressesbetween the two other offices equally. Design the subnets. (Find: Mask, Network and Broadcast address, First and last address, number of usable addresses in each network).arrow_forward
- 3.3-4a. What is a checksum? Which of the following statements are true about a checksum? Hint: more than one statement is true. A checksum is computed at a sender by considering each byte within a packet as a number, and then adding these numbers (each number representing a bytes) together to compute a sum (which is known as a checksum). The sender-computed checksum value is often included in a checksum field within a packet header. The receiver of a packet with a checksum field will add up the received bytes, just as the sender did, and compare this locally-computed checksum with the checksum value in the packet header. If these two values are different then the receiver knows that one of the bits in the received packet has been changed during transmission from sender to receiver. The receiver of a packet with a checksum will add up the received bytes, just as the sender did, and compare this locally-computed checksum with the checksum value in the packet header. If these two values…arrow_forwardBridge Self Learning Algorithm. Five LANs are connected by four bridges. Each bridge maintains two tables that describe what stations are in each LAN. Initially, all the tables are empty. Show how the tables of the four bridges change after each of the following events happen in sequence. A sends a frame to B B sends a frame to A C sends a frame to A G sends a frame to Barrow_forwardComputer Network LAN Network Topology Image. the image below Use the image as a reference, if the values are A, B, C and D (3rd octet) with the following conditions: Value A = 29 Value B = A + 1 Value C = A + 2 Value D = A + 3 x1, y1, z1 are the interfaces for the router gateway, while x2, x3, y2, y3, z2, z3 are for the router interface a. Find the Routing Table R1, R2, and R3 using the following table! Destination Next hop Interface b. With the Routing Table that you have specified in point a, which path will PC1B take when communicating with PC2B and PC3B c. In theory there is a routing table for Network Address 0.0.0.0 with a Subnet Mask of 0.0.0.0, explain the function of this routing table?arrow_forward
- Consider a wireless network with the following parameters. There are three Access Points operating with both bands (2.4G and 5G) enabled. The three Access Points are operating with the identical configuration. The 2.4G radios are each configured with 2 VAPS where SSID1-Printer and SSID2-Contractor. The 5G radios are each configured with 1 VAP where SSID-VolP. All SSIDS have connected users. Answer the following questions. Only enter a number without units (i.e. 5) How many unique BSSIDS are required? How many ESSIDS are configured? How many VAPS or SSIDS are configured? The three Access Points are connected to the same network. How many Distribution Systems are there?arrow_forward13). F = Suppose you are distributing a 10 Gbit file to N number of files. Server us = 20 MbpsIt has upload speed and each es di = 1 Mbps download speed and upload speed. N = 10,Both client-server distribution and P2P for 100 and 1000 and u = 200 Kbps, 600 Kbps and 1 MbpsA chart that gives the minimum distribution time for each combination of the N and u values for the distributionprepare.arrow_forwardSMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the standard protocol for transferring mail between hosts. A TCP connection is set up between a user agent and a server program. The server listens on TCP port 25 for incoming connection requests. The user end of the connection is on a TCP port number above 1023. You have defined the packet filter rule set shown in the table below. These rules permit and/or deny inbound and outbound traffic between the user agent and the mail server. Describe the purpose of each packet filter rule in the table. Rule Direction Source Address Destination Address Protocol Destination Port Action A2 In External Internal TCP 25 Permit B2 Out Internal External TCP > 1023 Permit C2 Out Internal External TCP 25 Permit D2 In External Internal TCP > 1023 Permit E2 Either Any Any Any Any Denyarrow_forward
- Make a map → from source to destination there are many routes that can be taken within the map. Connect the 5 routers → name it A (has 3 connections), B (has 2 connections), C (has 2 connections), D (has 2 connections), and E (has 1 connection). IP addressing: LAN A1 A2 A3 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2 E1 Network Address 192.168.1.0 192.168.2.0 192.168.3.0 192.168.10.0 192.168.11.0 192.168.20.0 192.168.21.0 192.168.32.0 192.168.33.0 192.168.40.0 Subnet Mask /24arrow_forward0. AS1 has the following routing table, draw the network of AS’s that these paths imply: prefix path P1 AS2 P2 AS4 AS5 AS3 P1 AS4 AS2 P2 AS5 AS3 P1 AS5 AS2 Assuming AS 1 accepted all the paths advertised to it, what paths does AS4 advertise to AS1? What AS is P1 in? What about P2? AS5 no longer wants to forward packets destined for prefix P1 on behalf of AS1, but it is ok forwarding prefix P2, how would it change the paths it advertises to AS1? If AS1 sends a packet to AS4 destined for P1, what path will it take? How do we know AS4 won’t forward it back to AS1? If AS1 gets the following advertisement from AS4, P1 AS4 AS1 AS2 how would it update its table? Why?arrow_forwardQuestion 7: An ISP has the following block of addresses 132.204.192/20. The manager of this ISP hired you to help him assign IP block of addresses to the following subnets. • Subnet A should have enough addresses to support at least 850 interfaces; • Subnet B should have enough addresses to support at least 55 interfaces; • Subnet C should have enough addresses to support at least 46 interfaces; • Subnet D should have enough addresses to support at least 40 interfaces; • Subnet E should have enough addresses to support at least 20 interfaces. • Subnet F should have enough addresses to support at least 28 interfaces. Give the range of addresses (in binary) assigned to each subnet. Show your work.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios