
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
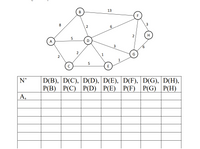
Transcribed Image Text:B
13
F
8
2
6.
2
H
5
A
D
3
9.
2
1
G
1
5
|D(B), D(C), D(D), D(E), | D(F), D(G), D(H),
P(B) |P(C) P(D) P(E) P(F) P(G) P(H)
N'
А,

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following network. With the indicated link costs, use Djikstra’s shortest-
path algorithm to compute the table of shortest paths from A to all other network nodes.
Show how the algorithm works by filling out the table below. Use column “N" for “all
visited nodes in current step", and each row for "distance and predecessor of each
destination node once a new node is visited".
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I have spent hours on internet to find an example of iterative lengthening search algorithm but found nothing. I need it ASAP. Can anyone help me? Please. It is its definition: Iterative lengthening search is an iterative analogue of uniform-cost search. The basic idea is to use increasing limits on path cost. If a node is generated whose path cost exceeds the current limit, it is immediately discarded. For each new iteration, the limit is set to the lowest path cost of any node discarded in the previous iteration. I dont understand many things in this definition. 1-What is the first limit before we start? 2-Do we delete the discarded node from the graph or what? 3-What is the generated node? Is it expanded or is it just found as neigbor? 4-What is "lowest path cost of any node discarded"?? Path from where to where?? From start to that node or what? 5-What does path cost mean in this problem? Is it from source to the new node or between current node and next chosen node? I am literally…arrow_forwardSubject : Algorithm and Data Structurearrow_forward5.04-4. Bellman Ford Algorithm - a change in DV (1, part 4). Consider the network below, and suppose that at t=0, the link between nodes b and c goes down. And so at t=0, node b recomputes its distance vector (DV) and sends out its new DV (as needed). At t=1 this new DV is received at b's neighbors, who then perform their calculation and send out their new DVs (as needed); these new DVs arrive at their neighbors at t=2, and so on. What is the last time in this network at which a DV calculation will take place as a result of the link change at t=0? U O O o 1 1 3 2 at t=0 the link (with a cost of 1) between nodes b and c goes down A 8 1 6 compute 1 1 1 1 an essentially infinite amount of time; this is the count-to-infinity problem 1 Secondarrow_forward
- 5.01-3. Dijkstra's Algorithm (1, part 3). Consider the network shown below, and Dijkstra's link-state algorithm to find the least cost path from source node U to all other destinations. Using the algorithm statement and its visual representation used in the textbook,complete the third row in the table below showing the link state algorithm's execution by matching the table entries (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e) with their values. Write down your final [correct] answer, as you'll need it for the next question; the *s shown correspond to your answers to earlier parts of this question. [Note: You can find more examples of problems similar to this here B.) (a) 3 (b) 8 ·V- 2 X Step 0 u 11 1 2 (a) 4 * 2 6 -W 3 W X y Z N' D(v),p(v) D(w).p(w) D(x),p(x) D(y).p(y) D(z).p(z) 00 1 (b) Z (c) [Choose ] [Choose 1 (d) (e)arrow_forwardAfter how many time ticks, will L's distance vector (i.e., its DV that it exchanges with its neighbor) reflect this change in topology?arrow_forward5.04-3. Bellman Ford Algorithm - a change in DV (1, part 3). Consider the network below, and suppose that at t=0, the link between nodes g and h goes down. And so at t=0, nodes g and h recompute their DVs. Following this recomputation, to which nodes will h send its new distance vector? (Note: to answer this question, you’ll need to know some of the DV entries at g and h at t=0, but hopefully they’ll be obvious by inspection).arrow_forward
- Mark Zuckerberg, the CEO of Facebook, has hired you to lead the Facebook Algorithms Group. He has asked you to use various graph algorithms to analyze the world's largest social network. The Facebook Graph has 2.8 billion vertices, with each vertex being a Facebook user. Two vertices are connected provided those two users are "friends". The first decision you need to make is how you want to model the Facebook graph. Determine whether you should use an adjacency-list representation or an adjacency-matrix representation.arrow_forwardDescribe an efficient algorithm for finding a maximum spanning tree in G, which would maximize the bandwidth between two switching centers. Describe the problem in terms of input and expected output clearly. Develop a program that accepts a network G of switching centers and the bandwidth between them (not all are connected directly with each other) and two switching centers a and b; it will output the maximum bandwidth between any two switches a and b. Please give solution in Java/C/Python languagearrow_forward5. For the graph below: 7 5 9 20 3. 1 1 1 3 (Route length is the sum of the weights of the edges in the route. When no weight is assigned to an edge the weight is assumed to be 1.) What is the shortest route from 5 to 5 to 2?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education