
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
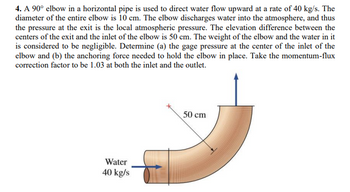
Transcribed Image Text:4. A 90° elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to direct water flow upward at a rate of 40 kg/s. The
diameter of the entire elbow is 10 cm. The elbow discharges water into the atmosphere, and thus
the pressure at the exit is the local atmospheric pressure. The elevation difference between the
centers of the exit and the inlet of the elbow is 50 cm. The weight of the elbow and the water in it
is considered to be negligible. Determine (a) the gage pressure at the center of the inlet of the
elbow and (b) the anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place. Take the momentum-flux
correction factor to be 1.03 at both the inlet and the outlet.
Water
40 kg/s
50 cm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider water flow through a horizontal, short garden hose at a rate of 30 kg/min. The velocity at the inlet is 1.3 m/s and that at the outlet is 11.75 m/s. The hose makes a 180° turn before the water is discharged. Disregard the weight of the hose and water. Taking the momentum-flux correction factor to be 1.08 at both the inlet and the outlet, the anchoring force (in N; hint: the answer is a negative number) required to hold the hose in place is ?arrow_forwardIn a horizontal pipe water flows at a rate of 9.1 L/s. Here, the pipe has two sections, one with a diameter of 10.16 cm and the other with a diameter of 5.08 cm, with a gradual smooth reducing section. In this case, a mercury manometer is used to measure the pressure difference. If friction is negligible how would I find the differential height of mercury between the two sections? If the manometer on the 5.08cm pipe section was replaced with a pitot tube how would the reading change? any help would be deeply appreciatedarrow_forwardA cylindrical tank with a radius of 3ft is filled with water which has a weight density of 62.4 lb/ft^3. The water is to be pumped to a point 2ft above the top of the tank. (a) How much work is performed in pumping all the water from the tank? (B) How much work is performed in pumping 3ft of water from the tank? (C) At what point is 1/2 of the total work done?arrow_forward
- not an assingment or assesed question its a tutorialarrow_forwardBEER with a density of 789 kg/m3 from a non-elevated open reservoir (P1=0 bars) flows before the pump at 0.75 m/s. The beer is pumped at a rate of 15 m/s to a 5 meter elevated tank with a pressure reading of 0.69 Bars. assuming zero Friction losses, Calculate the actual work if the pump's efficiency is just 44%. Calculate the theoretical and actual power in hp for a mass of 100 kg and a time of 1 minute of Beer.arrow_forwardProblem 5: A pressurized tank of water has a 10-cm-diameter nozzle at the bottom, where the liquid discharges to the atmosphere. The liquid level is 2.5 m above the outlet and the tank diameter can be assumed to be much larger than the diameter of the discharge nozzle. The air pressure in the space above the liquid is 250 kPa (absolute) while the atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. Neglecting frictional effects, determine the rate of discharge (kg/sec) of liquid from the tank when the liquid level is 2.5m Air 250 kPa 25m 10 cmarrow_forward
- In the jet impact experiment, water jet impacts on a curved vane in the vertical direction. As shown in the figure below, the exit has an angle with respect to the vertical direction. The distance from the nozzle to the vane surface at the exit is h. The water volume flow rate is measured to be Q, the density of water is p, and the cross section area of the nozzle is A₁. Assume that the flow has reached the steady state. (1) Use the Bernoulli's equation to determine the velocity Vout at the exit of the vane. Assume that friction between water and the curved vane can be neglected. (2) Apply the Reynolds transport theorem to derive the expression of the impact force F, on the curved vane (neglect the jet weight). (3) Under the condition of a fixed volume flow rate Q, determine the maximum impact force Fr,max that can be obtained when the angle varies (e.g. in different vane designs). Va out 9 Ao Vout harrow_forwardA cylindrical container with a massless and frictionless piston is filled with water up to a height h, as shown in the schematic. What mass m should be placed on the piston so that the water flow rate through the opened valve doubles? Consider that piston area A₁ = 0.05 m², valve area A₂ = A1/8, h = 0.9 m, Pwater = 1000 kg/m³, and g = 9.80 m/s². piston area: A₁ m = ? Т h/5 valve area: A₂arrow_forwardSolve it fast.arrow_forward
- Water flows through a garden hose at a rate of 1 l/s. The upstream diameter of the hose is 2.5 cm, and the nozzle outlet has a diameter of 1 cm. Determine the upstream pressure (gage pressure).arrow_forwardA large, open-topped water tank is being filled from above by a 1.0-cm-diameter hose. The water in the hose has a uniform speed of 11 cm/s. Meanwhile, the tank springs a leak at the bottom. The hole has a diameter of 0.70 cm. Determine the equilibrium level heq of the water in the tank, O measured relative to the bottom, if water continues flowing into the tank at the same rate. heq 1.26 X10-3 Incorrect marrow_forwardIf you have a flat tire and need to pump up the tire on your car with a hand pump, what force do you have to apply to the pump handle? Assume the air pressure in your tire will be 20 lb/in2, that is 1.1 KPa (138,0000 N/m2). Let the air pump have a cross-section that is 5 cm in diameter. It depends on the weight of the car. About 270 N when the tire is full, not much when you start pumping on the empty tire. About 270 N for as long as it takes from the beginning. Just a few newtons until you are satisfied with how full the tire is because of the hand pump.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY