
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:3. For the reaction SO2(g) + NO2(g) 2 NO(g) + SO3(g), Ko = 85.0 at 4.60 x 102 °C. A
reaction is started with 0.0500 M of both reactants (Note, initially no products).
a) Calculate the equilibrium concentration in M of all species. (If you correctly set-up the ICE
chart for this problem, you will see the equilibrium constant expression is a perfect square & so
the quadratic formula is not needed. If yours is not a perfect square, check your work.)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Equilibrium concentration is the concentration in a chemical reaction when the concentration of reactant and products becomes equal and does not change with time. That condition is called the equilibrium state of a chemical reaction.
Hence it is represented by the equation as shown below:
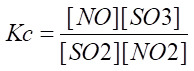
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.7 mol of Br,, 1.4 mol of OCl, and 1.6 mol of BrCl. The following reaction becomes possible: Br, (g) +OCl, (g)- BROC1(g)+BrC1(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.645 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of OCl,. Round your answer to two decimal places. olo ? Ar G Explanation Check © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. AIL Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: N(g)+3 H,(9) - 2 NH;(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.0016. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with nitrogen and hydrogen, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction compound pressure expected change in pressure vessel 11.39 atm Of increase O I decrease O (no change) H. 25.28 atm O t increase OI decrease O (no change) A NH, 16.95 atm O t increase OI decrease O (no change) 12.82 atm O t increase OI decrease O (no change) 28.45 atm O f increase OI decrease O (no change) B NH, 21.46 atm O f increase O I decrease O (no change) N 10.92 atm O f increase OI decrease O (no change) O I decrease O (no change) H. 23.86…arrow_forward||| = Using the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 193.: CO(g) + H₂O(g) - CO₂(g) + H₂(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 23. L reaction vessel is filled with 1.2 mol of CO₂ and 1.2 mol of H₂. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. CO₂(g)+H₂(g) 2 CO(g) + H₂O(g) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 2 CO(g)+2H₂O(g) - 2 CO₂(g) + 2H₂(g) Exmlanation Check Q Search O There will be very little CO and H₂O. O There will be very little CO₂ and H₂. O Neither of the above is true. K = 0 K = 0 X W Ⓒ2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce ? S HHarrow_forward
- Consider the decomposition reaction: X(g) + 2 Y(g) XY2(s) where X and Y are some chemical groups. At a certain temperature the equilibrium constant for this reaction is Ke= 0.108. If you start with a large amount of XY2 (s), c= what will be the concentration of Y(g) once the system reaches equilibrium? (HINT: Draw an ICE table or you will likely get this wrong!) (A) 0.108 M (B) 0.216 M (C) 0.300 M (D) 0.600 M (E) 1.08 Marrow_forwardA chemist is studying the following equilibirum, which has the given equilibrium constant at a certain temperature: N2 (g) + 2 H,0(g) =2H,(g) + 2 NO (g) 8. :4. × 10 He fills a reaction vessel at this temperature with 9.0 atm of nitrogen gas and 7.8 atm of water vapor. Use this data to answer the questions in the table below. O yes Can you predict the equilibrium pressure of NO, using only the tools available to you within ALEKS? x10 no If you said yes, then enter the equilibrium pressure of NO at right. O Round your answer to 1 significant digit. atmarrow_forwardMethanol liquid burns readily in air. One way to represent this equilibrium is: 2 CH3ОН(1) + 3 02(9)+ 2 CO2(g) + 4 H20(g) We could also write this reaction three other ways, listed below. The equilibrium constants for all of the reactions are related. Write the equilibrium constant for each new reaction in terms of K, the equilibrium constant for the reaction above. 1) CНH3ОН(1) + 3/2 02(9)+ =cO2(g) + 2 H20(g) K1 = %D 2) 2 CO2(9) + 4 H20(g) 2 CH3ОН (1) + 3 02(9) K2 = 3) СO2(g) + 2 H20(g) еснзон (1) + 3/2 02(g) K3 : %3D Drag and drop your selection from the following list to complete the answer: к1/2 1/K (1/K)!/2arrow_forward
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.8 mol of CO, 0.20 mol of H2O and 1.0 mol of H2. The following reaction becomes possible: CO(g)+H,O()-CO,(z)+H.() The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 2.64 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H2O. Round your answer to two decimal places. Ом 5arrow_forwardSulfur dioxide and oxygen react to form sulfur trioxide during one of the key steps in sulfuric acid synthesis. An industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 1.7 atm of sulfur dioxide gas and 4.7 atm of oxygen gas, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of sulfur trioxide gas to be 1.0 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the reaction of sulfur dioxide and oxygen at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = [|arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution.....arrow_forward
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.9 mol of Br,, 1.8 mol of BrOCl and 1.6 mol of BrCl. The following reaction becomes possible: Br, (g) + OC1, (g) = BIOC1(g) + BrC1(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 4.15 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of Br,. Round your answer to two decimal places. 0.53 M ?arrow_forward6. A quantity of liquid methanol, CH3OH, is introduced into a rigid 3.00-L vessel, the vessel is sealed, and the temperature is raised to 500K. At this temperature, the methanol vaporizes and decomposes according to the reaction CH3OH(g) → CO(g) + 2 H2(g), Ke= 6.90×10-². If the concentration of H₂ in the equilibrium mixture is 0.426M, what mass of methanol was initially introduced into the vessel?arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.90 mol of NO, 1.6 mol of NO and 1.4 mol of CO,. The following reaction becomes possible: NO,(g) + CO (g) = NO (g)+ CO,(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 3.12 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO. Round your answer to two decimal places. IMarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY