
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
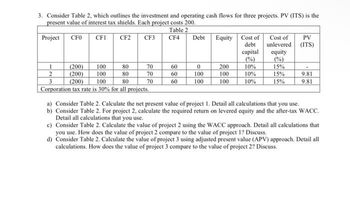
Transcribed Image Text:3. Consider Table 2, which outlines the investment and operating cash flows for three projects. PV (ITS) is the
present value of interest tax shields. Each project costs 200.
Table 2
Project CF0
CF1 CF2
CF3
CF4
1
2
3
(200)
100
80
(200)
100
80
(200) 100
80
Corporation tax rate is 30% for all projects.
70
70
70
60
60
60
Debt
0
100
100
Equity Cost of
debt
200
100
100
Cost of
unlevered
capital equity
(%)
(%)
10%
15%
10%
15%
10%
15%
PV
(ITS)
9.81
9.81
a) Consider Table 2. Calculate the net present value of project 1. Detail all calculations that you use.
b) Consider Table 2. For project 2, calculate the required return on levered equity and the after-tax WACC.
Detail all calculations that you use.
c) Consider Table 2. Calculate the value of project 2 using the WACC approach. Detail all calculations that
you use. How does the value of project 2 compare to the value of project 1? Discuss.
d) Consider Table 2. Calculate the value of project 3 using adjusted present value (APV) approach. Detail all
calculations. How does the value of project 3 compare to the value of project 2? Discuss.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Eddie Corporation is considering the following three investment projects (Ignore income taxes.): Project D $ 65,600 $ 76,096 Multiple Choice Investment required Present value of cash inflows Rank the projects according to the profitability index, from most profitable to least profitable. O E, C, D E, D, C D, C, E Project C $ 57,600 $ 63,936 C, E, D. Project E $ 136,000 $ 148,240arrow_forwardman.6 Crenshaw Enterprises has gathered projected cash flows for two projects. Year Project I Project J 0 −$ 266,000 −$ 266,000 1 113,400 94,600 2 106,200 100,600 3 90,200 102,600 4 79,200 109,600 At what interest rate would the company be indifferent between the two projects? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. Which project is better if the required return is above this interest rate?arrow_forward\table[[, Net Cash Flows ($)], [Year, Project T, Project F], [0, -100,000, -100,000 0 1 Net Cash Flows (S) Year Project T Project F -100,000 -100,000 60,000 33,500 60,000 33,500 33,500 33,500 2 3 4 Project T has a life of two years and project F has a life of four years. The cost of capital is 10% for both projects. Assume that both projects will be needed in future, and they can be repeated forever without any changes in their cash flows. Use the above information to answer questions 17-19. 17. Over a common life of 4 years, what is the NPV of project T [ (NPV (T, 2)]? a. $8264.46 b. $6190.49 c. $4132.23 d. $7547.30 s e. $7428.96 18. What is the Equivalent Annual Annuity (EAA) of project F? a. $2103.98 b. $1898.12 c. $1952.92 d. $2088.12 e. $1924.76 19. Which project should be accepted? a. Project T b. Project F c. None of the projectsarrow_forward
- Look at the cash flows for projects F and G given below. Cash Flows($) Project C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 IRR (%) NPV at 10% F (8,000 ) 5,200 5,200 5,200 0 0 0 0 0 42.6 4,932 G (8,000 ) 2,600 2,600 2,600 2,600 2,600 2,600 2,600 2,600 28.0 5,871 The cost of capital was assumed to be 10%. Assume that the forecasted cash flows for projects of this type are overstated by 8% on average. That is, the forecast for each cash flow from each project should be reduced by 8%. But a lazy financial manager, unwilling to take the time to argue with the projects’ sponsors, instructs them to use a discount rate of 18%.arrow_forwardConsider a project with the following cash flows: Time 0 1 2 3 4 5 CF -$5,000 $5,000 $4,000 $2,000 $1,000 -$6,000 Please round your answer to two decimal places. (e.g. 12345.67 for $12,345.67; 12.34 for 12.34%) a) What is the NPV of this project if the cost of capital is 10%? b) To calculate the MIRR, find the modified cash flow at year 0 c) What is the MIRR of this project?arrow_forwardNn1. Accountarrow_forward
- The following are a project's cash flows. Its cost of capital is 10% . What is the project's discounted payback? Year 0 1 2 3 Cash flows −$900 $500 $500 $500arrow_forwardson.3arrow_forwardCompute the NPV for Project X and accept or reject the project with the cash flows shown below if the appropriate cost of capital is 10 percent. Time: 1 2 4 Cash flow: -150 -150 250 225 200arrow_forward
- 1. Consider the below three investment projects generating cash flows as follows: Project 1 2 3 4 -500,000 -500,000 -500,000 А 1,000,000 -500,000 -500,000 -500,000 -500,000 B 550,000 750,000 -500,000 1,000,000 1,000,000 -500,000 Assume that the cost of capital is 10%. Use this cost of capital to discount (or inflate) all negative cash flows to the present time and all positive cash flows to period 1 in the below table. Then, calculate the IRR based on the cash flows of period 0 and 1. Project 1 IRR А B Using the above modified IRR, make investment decision for each project. Dose the modified IRR deliver correct decisions?arrow_forwardConsider the following information: Cash Flows ($) Project C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 A –5,300 1,300 1,300 2,700 0 B –700 0 600 2,300 3,300 C –5,200 3,400 1,700 800 300 a. What is the payback period on each of the above projects? (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardA project has the cash flows shown in the following table. If the cost of capital is 9%, what is the NPV of the project? Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Incremental Free Cash Flow -913 281 281 281 281 281 191 Question 5Answer a. $294 b. $272 c. $312 d. $325arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education