
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
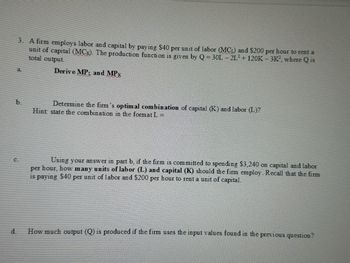
Transcribed Image Text:3. A firm employs labor and capital by paying $40 per unit of labor (MCL) and $200 per hour to rent a
unit of capital (MC). The production function is given by Q = 30L-2L2+ 120K-3K2, where Q is
total output.
a.
Derive MPL and MPK
b.
Determine the firm's optimal combination of capital (K) and labor (L)?
Hint state the combination in the format L =
Using your answer in part b, if the firm is committed to spending $3,240 on capital and labor
per hour, how many units of labor (L) and capital (K) should the firm employ. Recall that the firm
is paying $40 per unit of labor and $200 per hour to rent a unit of capital.
d.
How much output (Q) is produced if the firm uses the input values found in the previous question?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?I. If labor and capital are perfect substitutes in production, the isoquant is a downward-sloping line.II. If a company needs to use inputs in fixed proportion such that the capital to labor ratio is always 2, the firm's isoquants are L-shaped.III. If the production function is given by Q = min(14, 7), the firm can produce, at minimum, 21 units of output. IIII, II, and IIIII and II Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardQuestion 2: Consider the following production function that depends only on labor:Q = 2L+6L² - 3L³ 1. Compute the APL (average product of labor). 2. Compute the MPL (marginal product of labor). 3. What is the value of L* at which APL is the highest? 4. For L > L*, which one is bigger, APL or MPL? How about when I < L* and L = L* ? 5. Draw APL and MPL on the y-axis as a function of L on the x-axis. Label the point of the intersection of APL and MPL.arrow_forwardplease show graphs and table thank youarrow_forward
- Company Z has the following data corresponding to the production function. Where (L) is the amount of the labor factor and (K) capital. Q=K0.4 L 0.6 a) Calculate the amount of production, applying the production function for each of the respective values of K and L. K L Q 10 80 30 160 50 320 70 640 90 1200 a) Graph the amount of production obtained on the Y axis, and with the labor input on the Х аxis b) Draw isoquant lines for each level of production, placing capital on the Y axis and labor on the X axis, to better appreciate the displacement.arrow_forwardQUESTION 39 The folllowing table shows data for a simple production function. Capital (K). Labor (L) 10 0 10 1 10 2 3 4 5 6 10 10 10 10 TP or Q AP MP 6 14 20 14 8 Assume that the cost of capital, PK, is $50 per unit, and the cost of labor, PL, is $100 per unit. Marginal cost, MC, is at minimum when labor, L, is equal to O2 units. O4 units. O 3 units. 5 units.arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm has production function F(L, K) = L^2/3 K^1/3 for producing widgets, thewage rate for labor is w = $400, and the rental rate of capital is r = $25.a) Suppose that the firm has received an order for Q = 120 units of output. Neatly specify this firm’s costminimization problem, using the particulars associated with this problem.b) Give two equations that an interior solution satisfies, tailoring your equations to the particulars of thisproblem.c) Solve the two equations for the firm’s optimal choice. Show your work.d) Determine this firm’s minimum cost of producing 120 units.e) Now suppose that the firm’s production goal is left as the variable Q. Come up with the firm’s costfunction C(Q). Show your work.arrow_forward
- ***QUESTION HAS FOUR PARTS - ALL PARTS MUST BE ANSWERED TOGETHER AS THEY ARE DEPENDENT ON EACH OTHER*** 1. A farmer raises apples using land (K) and labor (L), and has an output of ? (?,?) = ? 0.5 ? 0.5 bushels of apples. a. Find several input combinations that give the farmer 6 bushels of apples. Sketch the associated isoquant on a graph, with L on the x-axis and K on the y-axis. b. In the short run, the farmer only has 4 units of land. What is his short-run production function? Graph it for values of L from 0 to 16, with L on the x-axis and output on the y-axis. What is the name of the slope of this curve? c. Assuming the farmer still only has 4 units of land, how much extra output does he get from adding 1 extra unit of labor if he is already using only 1 unit of labor? How much extra output does he get from adding 1 extra unit of labor if he is already using 4 units of labor? d. In the long run, the farmer can change both his amount of land and his amount of labor. Suppose…arrow_forwardCobb Douglas production function..? Solve this I'll Upvote your workarrow_forwardGrease Tech produces oil changes. The production of oil changes reles on both capital (K) and labor (L) and is combined in the following production function F (K, L) = KILL Take the derivative of this production function with respect to capital. What is the marginal product of capital evaluated at (le. just plug in the numbers) 64 units of capital used and 16 units of labor?arrow_forward
- Digging calms by hand in Sunset Bay requires only labor input. The total number of calms obtained per hour (q) is given by :Q = 100√LWhere L is labor input per hour. A. Graph the relationship between q an LB. What the average productivity of labor in Sunset Bay? Graph this relationship and show that output per unit of labor input diminishes for increase in labor input. C. It can be shown that the marginal productivity of labor in Sunset By is given by:MPL =50√LGraph this relationship and show that labor’s marginal productivity is less than average productivity for all values of L . Explain why this is do.D. Explain the concept of diminishing returns to labor and how this concept related to increasing marginal costs.arrow_forwardPlease Solve the answer can u see in option im needed max in 15-20 minutes thank uarrow_forwardCould you please help me with this question? Thank you!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education