
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
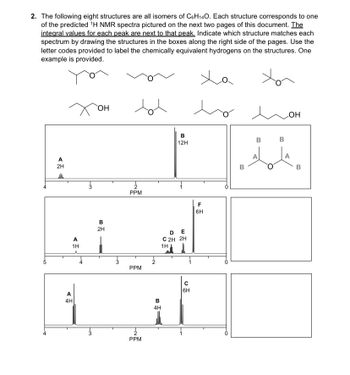
Transcribed Image Text:2. The following eight structures are all isomers of C6H14O. Each structure corresponds to one
of the predicted ¹H NMR spectra pictured on the next two pages of this document. The
integral values for each peak are next to that peak. Indicate which structure matches each
spectrum by drawing the structures in the boxes along the right side of the pages. Use the
letter codes provided to label the chemically equivalent hydrogens on the structures. One
example is provided.
Xor
A
2H
1H
<-
A
4H
-3₂₂
OH
B
2H
tot
2
PPM
PPM
-N
2
PPM
N-
-~
B
12H
DE
C 2H 2H
1H
B
4H
6H
ха
по мон
F
6H
B
B
B
w

Transcribed Image Text:5
A
2H
A
2H
B
2H
2H
Н
A
1Н
A
2H
B
3H
B
3H
F3
B
2H
-3
з
PPM
PPM
PPM
PPM
2
PPM
1Н
ми
0 1
1Н
N-
C
2H
М.
D
2H
elle
B
3H
9H
D
3H
с
9H
i
E
E
6H
6H
D
6H
H
E
ЗН
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7) A molecule has a chemical formula of C6H1202 and produces the spectrum below. Determine its structure. Any labile protons, if they exist, might be present in this 1H NMR spectrum. All signals are singlets. 11 10 HSP-00-610 9 8 7 6 5 ppm 1H 4 -M 3 2H 3H - N 2 6H 1arrow_forwardSpectroscopy H H .co,H -OCH,CH3 CH3CHCH2CI ČH3 NO2 For each of the above compounds, do the following: 1. List the wave numbers of all the IR bands in the 1350- 4000 cm-1 region. For each one, state what bond or group it represents. 2. Label equivalent sets of protons with lower-case letters. Then, for each 1H NMR signal, give the I value, the type of splitting (singlet, doublet etc.), and the number of protons it represents. Label the signals with lower-case letters that match the letters used to label the protons.arrow_forwardAs a pioneer in Organic Chemistry you test out a potential new catalyst for the reaction of Br2 with the compound below. After isolating a major product, analysis reveals one Br has been added substituting one H. You take an 1H NMR (shown below) to help decide if an EAS, benzylic substitution or non-benzylic substitution has occurred. Draw the product. Then assign each proton in the product with a letter corresponding to the labels shown in the spectrum below.arrow_forward
- need help with the first box please explain well I do not understand thank you.arrow_forwardUse the spectral information given below to derive a structural formula for unknown II. Its molecular formula is C4H100. LO0 IR Spectrum of Unknown II 80 %T 60 40 20 2000 Wavenumbers (cm-1) 4000 3000 1500 1000 400 HNMR Spectrum of Unknown II 9H S S 1H 5 3 2 PPM C13NMR Spectrum of Unknown II 70 60 50 40 PPM 30 20 10arrow_forwardFrom the 13C spectrum of a compound, one can assign signals to specific carbon atoms of the compound and determine the number of protons on each of those carbon atoms. Such information in conjunction with the DEPT C-13 chart will allow the appearance of the corresponding DEPT spectrum of the compound to be predicted. There are five signals (I – V) in the 13C spectrum of compound A as shown below. At the exactly same location of each of these five signals, "a peak", "no peak", or "an inverted peak" may appear in the corresponding DEPT-135 spectrum. Predict the DEPT-135 spectrum of compound A by selecting the expected signal appearance at each of these five locations in the DEPT-135 spectrum. - II II IV V in HO A 100 PPM 180 160 140 120 80 60 40 20 v At the location of signal I A. no peak v At the location of signal IIl В. а рeak v At the location of signal IIl C. an inverted peak v At the location of signal IV v A the location of signal Varrow_forward
- Part A Draw C4HgBr₂ that has the following ¹H NMR spectrum: 1.97 (s, 3H), 3.89 (s, 1H). Hint: Draw C4H₁0 (there are two isomers), and then replace two H atoms with Br atoms. NOTE NOTE! C4H8Br2 has 8 H's! But the integral is 3H and 1H!!! How will you fix that? Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds), Atoms, and Advanced Template toolbars. The single bond is active by default. H 12D EXP L CONT 1arrow_forwardYou measured the carbon-carbon bond lengths of four different compounds in Experiment 8 (Molecular Modeling and IR spectroscopy). Which of the following compounds has the shortest average C-C bond length? Benzene Cyclohexene Cyclohexane O Cyclohexadiene Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true? Select all that apply: When two atoms are bonded together, the distance between atoms is the same all the time. In the IR spectrum, carbonyl groups (C=O) have strong sharp peaks ranging from 1700 cm 1 to 1750 cm-1. When a molecule absorbs an IR radiation, electrons are excited within the molecule and each absorbed electron creates a band in the molecules IR spectrum. IR spectroscopy is useful in confirming the structure of the analyzed compound. Molecule N2 does not absorb IR radiationarrow_forward. Deduce the structure of an unknown compound with the molecular formula of C5H₁2O using the information given by its infrared spectrum. ANSWER A) НО. B) D) Intensity Frequency (peak): (cm): 3300 m EEEEE m m m m m 2900 2800 1465 1450 1375arrow_forward
- a) Shown below is the 1H NMR (CDCl3 is the solvent) of butanal. The splitting pattern of each of the four peaks is provided. For each of the four peaks determine the number of hydrogens that belongs to each peak from the red integral line. Provide the number of the hydrogens in the order A, B, C, D. b) What happens when the radiofrequncy pulse in the NMR instrument matches the Larmor Frequncy of an NMR active nucleus? A. The electrons transition to the LUMO B. The nuclei undergoes a spin flip C. Nothing D. The bonds in the molecule stretch and vibratearrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is incorrect regarding IR spectroscopy? options: The diagnostic region contain all signals that arise from double bonds, triple bonds and X-H bonds The fingerprint region contains signals resulting from the vibrational excitation of most single bonds (stretching and bending) The intensity of a signal is dependent on the dipole moment of bond giving rise to the signal A conjugated C=O bond produce a high energy signal than an unconjugated C=O bond The wavenumber of each signal is determined primarily by bond strength and the masses of the atoms sharing the bondsarrow_forwardI need help with thisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY