
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
See attached picture
Question.) Below are the NMR spectra and molecular formulas of three molecules. Draw the complete structure in the boxes below. All the atoms in each molecule are closed shell (octets) and uncharged. Lack of IR data does not mean that a specific
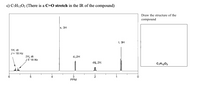
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription and Explanation of NMR Spectrum for C₇H₁₂O₂**
This image presents an NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectrum of the compound with the molecular formula C₇H₁₂O₂. The spectrum is labeled to indicate different chemical shifts and splitting patterns. Notably, there is a reference to a C=O stretch in the IR spectrum, suggesting the presence of a carbonyl group.
### Spectrum Details:
- **Chemical Shifts (δ, ppm)**:
- Around 6.0 ppm: Two doublet of triplets (dt), each signifying 1H, with a coupling constant (J) of 18 Hz, indicating a possible alkene proton.
- Around 3.4 ppm: A singlet (s), corresponding to 3H, likely indicating a methyl group adjacent to an electronegative atom such as oxygen.
- Around 2.3 ppm: A doublet (d), representing 2H, potentially an indication of methylene protons adjacent to a carbonyl group.
- Around 1.2 ppm: A doublet of quartets (dq), representing 2H, suggesting coupling between a CH2 group and adjacent methyl groups.
- Around 0.9 ppm: A triplet (t), representing 3H, most likely a terminal methyl group.
### Graph Description:
- **X-Axis**: Represents chemical shift in parts per million (PPM), which indicates the environment of protons within the molecule.
- **Y-Axis**: Indicates the intensity of the signals, corresponding to the number of hydrogen atoms contributing to each signal.
### Structural Considerations:
- The combination of chemical shifts and splitting patterns provides insights into the molecular structure, suggesting the presence of aliphatic and potentially unsaturated structures.
- The presence of a singlet at 3.4 ppm is characteristic of protons adjacent to an oxygen atom, possibly indicating that the compound contains an ester group.
- The C=O stretch (indicated by IR data mentioned in text) complements the NMR data by suggesting an ester or carbonyl functionality in the structure.
Since the structure is to be drawn based on this data, the attributes such as the C=O stretch and NMR signals guide the deduction of the exact structural formula of C₇H₁₂O₂.
**Note**: The structure should be drawn based on these
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Also, highlight each bond in this structure that is cis but which could be trans in a different cis/trans isomer. If there are no such bonds, check the No bonds to highlight box under the drawing area. Note: be careful not to highlight a bond just because it's cis in this drawing! It also needs to be a bond that would create a different cis/trans isomer if it were changed to trans. This molecule has cis/trans isomers in all. G Carrow_forwardWrite the condensed structure of a compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms and that has. please help with al partsarrow_forwardPlease see attachedarrow_forward
- Examine the molecule below, and select the statements that apply. If it can lose H, draw its conjugate base. If it can gain H, draw its conjugate acid. Show all lone pairs and non-zero formal charges. OH This molecule will not lose an H This molecule could lose an H™. Its conjugate base is: This molecule will not gain an H™ This molecule could gain an H". Its conjugate acid is: doarrow_forwardCan u help with the last four rows of this chart. Atoms number 4,5, and 6arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- What’s the total number of VSEPR groups in HCN?arrow_forwardDraw an equivalent resonance structure that minimizes charge. Include all lone pairs in your structure. Give detailed Solution with explanation needed. don't give Handwritten answer CH2arrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY