
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
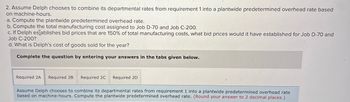
Transcribed Image Text:2. Assume Delph chooses to combine its departmental rates from requirement 1 into a plantwide predetermined overhead rate based
on machine-hours.
a. Compute the plantwide predetermined overhead rate.
b. Compute the total manufacturing cost assigned to Job D-70 and Job C-200.
c. If Delph establishes bid prices that are 150% of total manufacturing costs, what bid prices would it have established for Job D-70 and
Job C-200?
d. What is Delph's cost of goods sold for the year?
Complete the question by entering your answers in the tabs given below.
Required 2A Required 2B Required 2C Required 2D
Assume Delph chooses to combine its departmental rates from requirement 1 into a plantwide predetermined overhead rate
based on machine-hours. Compute the plantwide predetermined overhead rate. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
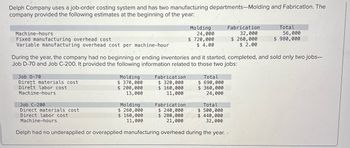
Transcribed Image Text:Delph Company uses a job-order costing system and has two manufacturing departments-Molding and Fabrication. The
company provided the following estimates at the beginning of the year:
Machine-hours
Fixed manufacturing overhead cost
Variable manufacturing overhead cost per machine-hour
Molding
24,000
$ 720,000
$ 4.00
Fabrication
32,000
$ 260,000
$ 2.00
Total
56,000
$ 980,000
During the year, the company had no beginning or ending inventories and it started, completed, and sold only two jobs-
Job D-70 and Job C-200. It provided the following information related to those two jobs:
Total
$ 690,000
$ 360,000
24,000
Job D-70
Dirert materials cost
Direct labor cost
Machine-hours
Molding
$ 370,000
$ 200,000
13,000
Fabrication
$ 320,000
$ 160,000
11,000
Job C-200
Direct materials cost
Molding
$ 260,000
Direct labor cost
Machine-hours
$ 160,000
11,000
Fabrication
$ 240,000
$ 280,000
21,000
$ 500,000
$ 440,000
32,000
Total
Delph had no underapplied or overapplied manufacturing overhead during the year..
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Required:1. Using the traditional approach to assigning overhead costs to academic programs:a. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate.b. Assign the overhead costs to each academic program using the predetermined rate.c. Calculate the total cost per student (direct costs plus overhead) of operating each academic program.2. Using ABC, complete the following requirements:a. Complete the first-stage allocation of overhead costs to academic programs.b. Calculate the activity rates for each of the activity cost pools.c. Using the activity rates calculated in (b), complete the second-stage allocation of overhead to academic programs.3. Based on the results of (2), calculate the total cost per student (direct costs plus overhead) of operating each academic program.4. Draft a memo to Maple explaining the key reasons for differences in the total cost per student of operating each academic program that arise between traditional costing approach and ABC.arrow_forwardDO NOT GIVE SOLUTION IN IMAGEarrow_forwardSingle Plantwide Rate and Activity-Based Costing Whirlpool Corporation (WHR) conducted an activity-based costing study of its Evansville, Indiana, plant in order to identify its most profitable products. Assume that we select three representative refrigerators (out of 333): one low-, one medium-, and one high-volume refrigerator. Additionally, we assume the following activity-base information for each of the three refrigerators: Three Representative Number of Machine Number of Number of Sales Number of Refrigerators Hours Setups Orders Units Refrigerator-Low Volume 24 14 38 160 Refrigerator-Medium Volume 225 13 88 1,500 Refrigerator-High Volume 900 120 6,000 Prior to conducting the study, the factory overhead allocation was based on a single machine hour rate. The machine hour rate was $200 per hour. After conducting the activity-based costing study, assume that three activities were used to allocate the factory overhead. The new activity rate information is assumed to be as follows:…arrow_forward
- Chrzan, Incorporated, manufactures and sells two products: Product EO and Product NO. Data concerning the expected production of each product and the expected total direct labor-hours (DLHs) required to produce that output appear below: Product E0 Product Ne Total direct labor-hours Activity Cost Pools Labor-related Production orders Order size The company is considering adopting an activity-based costing system with the following activity cost pools, activity measures, and expected activity: Estimated Overhead Cost Multiple Choice $33.94 per MH $54.20 per MH Direct Expected Labor-Hours Production Per Unit 10.1 410 1,550 9.1 $51.98 per MH $21.40 per MH Activity Measures DLHS orders MHs Total Direct Labor- Hours $ 301,890 61,087 585,366 $948,343 The activity rate for the Order Size activity cost pool under activity-based costing is closest to: 4,141 14, 105 18,246 Product E 4,141 850 5,550 Expected Activity Product NO 14, 105 950 5,250 Total 18,246 1,800 10,800arrow_forwardWhich one is the correct answer?arrow_forwardPredetermined overhead rates are calculated: a. first and then multiplied by total actual units of the allocation base to compute the applied manufacturing overhead costs. b. based on actual total manufacturing overhead costs C. by dividing total estimated manufacturing overhead cost by total actual units of the allocation base. d. none of the given answers is correct. e. at the end of the accounting period once the actual amount of manufacturing overhead is known.arrow_forward
- Concepts and Terminology From the choices presented in parentheses, choose the appropriate term for completing each of the following sentences: Sentence a. An example of factory overhead is b. Direct materials costs combined with direct labor costs are called c. Long-term plans are called d. Advertising costs are usually viewed as plans. costs. costs. e. The management process by which management monitors operations by comparing actual and expected results is f. The plant manager's salary would be considered to the product. g. The salaries of factory supervisors are normally considered a cost.arrow_forwardLarge, Inc., manufactures and sells two products: Product G8 and Product 00. Historically, the firm has used a traditional costing system, with direct laborurs as an activity base, to allocated manufaturing overhead to products. Data concerning the expected production of each product and the expected total direct labor-hours (DLHS) required to produce that output appear below: Product GS Product 00 Total direct labor-hours Product G8 Product 00 Activity Cost Pools Labor-related Expected Production 780 380 The direct labor rate is $22.90 per DLH. The direct materials cost per unit for each product is given below: Direct Materials Cost per Unit $121.10 $121.50 Machine setups Order size Activity Measures DLHS setups MHS Direct Labor-Hours Per Unit The company is considering adopting an activity-based costing system with the following activity cost pools, activity measures, and expected activity: 5.8 2.8 Estimated Overhead Cost $ 59,555 58,390 369,508 $487,453 Total Direct Labor- Hours…arrow_forwardplease asnzwer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is incorrect? O A. If MOH is overallocated to a job that has been sold, and the company calculates sales price by marking up job costs, the job will likely be underpriced. O B. The formula to arrive at the POHR is total budgeted manufacturing overhead divided by total estimated allocation base. O C. To calculate the increase to WIP for allocated MOH costs, the POHR is multiplied by the actual amount of the allocation based used by the cost object. D. "Number of units" is typically not an appropriate allocation base for MOH because the company's products do not consume equal overhead resources. If the over/underallocated MOH is fairly large and the majority of the units have not been sold, the balance in MOH should be prorated between WIP, FG, and COGS. O E.arrow_forwardDoede Corporation uses activity-based costing to compute product margins. In the first stage, the activity-based costing system allocates two overhead accounts--equipment depreciation and supervisory expense--to three activity cost pools--Machining, Order Filling, and Other--based on resource consumption. Data to perform these allocations appear below: Overhead costs: Equipment depreciation $ 91,000 Supervisory expense $ 12,300 Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools: Activity Cost Pools Machining Order Filling Other Equipment depreciation 0.60 0.30 0.10 Supervisory expense 0.60 0.20 0.20 In the second stage, Machining costs are assigned to products using machine-hours (MHs) and Order Filling costs are assigned to products using the number of orders. The costs in the Other activity cost pool are not assigned to products. Activity: MHs (Machining) Orders (Order Filling) Product W1 6,050 198 Product M0 21,800 999 Total…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education