
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
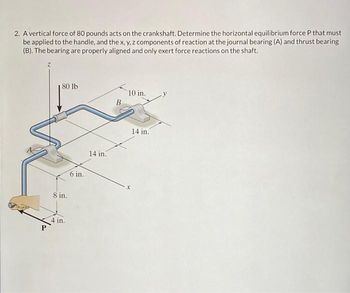
Transcribed Image Text:2. A vertical force of 80 pounds acts on the crankshaft. Determine the horizontal equilibrium force P that must
be applied to the handle, and the x, y, z components of reaction at the journal bearing (A) and thrust bearing
(B). The bearing are properly aligned and only exert force reactions on the shaft.
80 lb
8 in.
4 in.
6 in.
14 in.
B
10 in.
14 in.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 33arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Neglecting the weights of the bar and the pulley and assuming the weight of the ball B to be 1057N calculate the reaction at the pin at A in N. (X,XX,XXX represents the last digits number of your IC). 4/0% A 3.5 m D Barrow_forwardQ.4) The rod is supported by journal bearings at A, B and C and subjected to a force of 500 N (in y-z plane) and a couple moment of 400 N-m as shown below. The bearings are in proper alignment and exert only force reactions on the rod. Derive the static equilibrium equations for the rod shown and find the force reactions at the bearings. 500 N 0.3 m 0.4 m 42° 400 N.m B 0.1 m 0.2 marrow_forward
- A) The axially loaded bar is fixed at A and loaded as shown. Draw a free-body diagram and determine the support reaction at A. On paper, draw a free-body diagram of the bar and determine the reaction at A for the bar to be in equilibrium. Assume that the unknown reaction at A acts in the negative x direction. B)Using the answer from Part A, draw free-body diagrams or a load diagram and determine the internal axial forces in segments AB, BC, and CD. C)Using the internal axial forces determined in Part B, calculate the bar's maximum average normal stress. Using your free-body diagrams or load diagram from Part B and the axial stress equation, calculate the bar's maximum average normal stress.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the reaction at support A, in lb. If: P = 330 lb, h = 19 in., A = 22 in. b = 8 in.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the reaction at support A, in lb. If: P = 314 lb, h = 13 in., A = 27 in. b = 8 in.arrow_forward
- A 20-kg cover for a roof opening is hinged at corners A and B . The roof forms an angle of 30° with the horizontal, and the cover is maintained in a horizontal position by the brace CE . Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the magnitude of the force exerted by the brace and the reactions at the hinges. Assume that the hinge at A does not exert any axial thrust.arrow_forwardThe drop gate at the end of the trailer has a mass of 1.24 Mg and mass center at G. It is supported by the cable AB and hinge at C. (Eigure 1) Submit Previous Answers Correct Part B What are the z and y components of reaction at the hinge C? Figure ( Express your answers using three significant figures separated by a comma. vO AZO vec 6 C.. C, = kN 1m 1.5m Submit Previous Answers Request Answerarrow_forwardTo determine the reaction forces at supports on a horizontal beam by using the equations of equilibrium for a static application. As shown, beam ABC is supported by the roller at A and pin at C. The geometry of the beam is given by a=2.0a=2.0 ftft, b=7.0b=7.0 ftft, and c=12.0c=12.0 ftft. The applied forces are F1=1.50F1=1.50 kipkip and F2=2.00F2=2.00 kipkip. Force F1F1 is applied at an angle θ=60∘θ=60∘ with the horizontal. Neglect the weight of the beam.(Figure 1)arrow_forward
- Question 4 What are the reaction forces at point A? A TOTALA 1.5 m B G 20 kN 1.5 m C -1.5 m- D F 10 kN 1.5 m 2 m ELarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .... The shaft is supported by three smooth journal bearings at A, B, and C. Determine the components of reaction at these bearings.arrow_forwardAnswer the following question: 1. What is the magnitude and direction of the vertical component of the reaction of the support at point A? 2. What is the magnitude and direction horizontal component of the reaction of the support at point A? 3. What is the magnitude and direction of the reaction of the support at point G?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY