
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
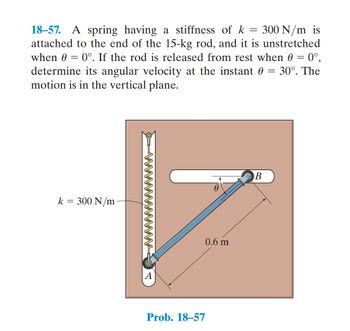
Transcribed Image Text:### Problem 18-57: Angular Velocity of a Rod Attached to a Spring
**Description:**
A spring with a stiffness of \( k = 300 \, \text{N/m} \) is connected to the end of a 15-kg rod. The rod is positioned vertically and the spring is unstretched when the angle \( \theta = 0^\circ \). The rod is released from rest at this position. The objective is to find the angular velocity of the rod when the angle \( \theta = 30^\circ \). The motion of the rod is confined to a vertical plane.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a rod of length \( 0.6 \, \text{m} \), pinned at point \( A \) and free to rotate. A spring of stiffness \( k = 300 \, \text{N/m} \) is attached at one end to point \( A \) and at the other end to point \( B \), which is also attached to the rod. The spring is vertical when the rod is horizontal.
- **Points A and B:**
- \( A \) is the pivot point where the rod is fixed.
- \( B \) is the point on the rod where the spring is attached.
- **Spring:**
- The spring is unstretched when \( \theta = 0^\circ \) (horizontal position).
- The spring's stiffness is \( k = 300 \, \text{N/m} \).
- **Rod Length:**
- The length of the rod from point \( A \) to point \( B \) is \( 0.6 \, \text{m} \).
- **Angle \( \theta \):**
- The rod makes an angle \( \theta \) with the horizontal.
**Problem Statement:**
Given that the rod is released from rest at \( \theta = 0^\circ \), determine the angular velocity when \( \theta = 30^\circ \).
**Concepts Involved:**
- **Potential Energy in the Spring:** When the rod is released and starts to rotate, the spring stretches, storing potential energy.
- **Kinetic Energy of the Rod:** As the rod moves, it gains kinetic energy which includes rotational kinetic energy due to its mass and angular velocity.
- **Conservation of Energy:** The total mechanical energy (sum of potential energy and
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- F17-14. The 100-kg cylinder rolls without slipping on the horizontal plane. Determine the acceleration of its mass center and its angular acceleration. 0.3 m P = 200 Narrow_forward19-23. The hoop (thin ring) has a mass of 5 kg and is released down the inclined plane such that it has a backspin w = 8 rad/s and its center has a velocity vg = 3 m/s as shown. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the hoop and the plane is µr = 0.6, determine how long the hoop rolls before it stops slipping. w = 8 rad/s vG = 3 m/s 0.5 m 30°arrow_forwardThe wheel has a mass of 25 kg and a radius of gyration kb = 0.15m. It is originally spinning at @=40 rad/s. If it is placed on the ground, for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is uc = 0.5, determine the time required for the motion to stop. What are the horizontal and vertical components of reaction which the pin at A exerts on AB during this time? Neglect the mass of -0.4 m AB. 0.2 m- B 0.3 m Iarrow_forward
- R19-1. The cable is subjected to a force of P = (10r) Ib. where t is in seconds. Determine the angular velocity of the spool 3 s after Pis applied, starting from rest. The spool has a weight of 150 lb and a radius of gyration of 1.25 ft about its center, O. P= (10) lb 1 ftarrow_forwardSOLVE USING PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGYarrow_forward16-34. For a short time a motor of the random-orbit sander drives the gear A with an angular velocity of VA = 40(t3 + 6t) rad/s, where t is in seconds. This gear is connected to gear B, which is fixed connected to the shaft CD. The end of this shaft is connected to the eccentric spindle EF and pad P, which causes the pad to orbit around shaft CD at a radius of 15 mm. Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and the tangential and normal components of acceleration of the spindle EF when t = 2 s after starting from rest. B D 40 mm 10 mm A -15 mm -Ε F WA Parrow_forward
- 18–37. The spool has a mass of 20 kg and a radius of gyration of 200 mm ko = 160 mm. If the 15-kg block A is released from rest, determine the velocity of the block when it descends 600 mm. Aarrow_forwardThis is a dynamics question. Answer: t = 0.6125 sarrow_forwardThe uniform 80 kg slender rod is at rest in the position shown when P = 450 N is applied. Determine the value of angular velocity, w2 the rod if L1 = 5.5 m and L2 = 6.5 m. A L L2 L1 Barrow_forward
- 13-85. The spring-held follower AB has a weight of 0.75 lb and moves back and forth as its end rolls on the contoured surface of the cam, where r= 0.2 ft and z = (0.1 sin 20) ft. If the cam is rotating at a constant rate of 6 rad/s, determine the force at the end A of the follower when 0 = 45°. In this position the spring is compressed 0.4 ft. Neglect friction at the bearing C. z = 0.1 sin 20 0.2 ft B ở = 6 rad/s A k= 12 lb/ftarrow_forward17-110. The 15-lb disk rests on the 5-lb plate. A cord is wrapped around the periphery of the disk and attached to the wall at B. If a torque M = 40 lb - ft is applied to the disk, determine the angular acceleration of the disk and the time needed for the end C of the plate to travel 3 ft and strike the wall. Assume the disk does not slip on the plate and the plate rests on the surface at D having a coefficient of kinetic friction of 4, = 0.2. Neglect the mass of the cord. M = 40 lb · ft -3 ft-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY