
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
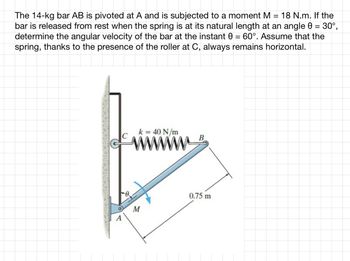
Transcribed Image Text:The 14-kg bar AB is pivoted at A and is subjected to a moment M = 18 N.m. If the
bar is released from rest when the spring is at its natural length at an angle 0 = 30°,
determine the angular velocity of the bar at the instant 0 = 60°. Assume that the
spring, thanks to the presence of the roller at C, always remains horizontal.
k = 40 N/m
M
B
0.75 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The circular disk of mass m and radius r, is rolling through the bottom of the circular path of radius R. If the disk has an angular velocity determine the force N exerted by the path on the disk.arrow_forwardThe 18-kg rod AB is pin-connected at A and subjected to a couple moment of M =15 N- m The rod is released from rest when the spring is unstretched at 0 = 30°. As the rod rotates, the spring always remains horizontal, because of the roller support at C. (Figure 1) Determine the rod' s angular velocity, measured clockwise, at the instant 0 = 60°. Express your answer using three significant figures. Enter positive value if the angular velocity is clockwise and negative value if the angular velocity is counterclockwise. vec rad/s k = 40 N/m 0.75 m M = 15 N- marrow_forward*19-12. The 40-kg roll of paper rests along the wall where the coefficient of kinetic friction is µz = 0.2. If a vertical force of P = 40 N is applied to the paper, determine the angular velocity of the roll when 1 = 6 s starting from rest. Neglect the mass of the unraveled paper and take the radius of gyration of the spool about the axle O to be ko = 80 mm. P= 40 N 13 12 PO 120 mmarrow_forward
- 18-6. A force of P=20 N is applied to the cable, which causes the 175-kg reel to turn without slipping on the two rollers A and B of the dispenser. Determine the angular velocity of the reel after it has made two revolutions starting from rest. Neglect the mass of the cable. Each roller can be considered as an 18-kg cylinder, having a radius of 0.1 m. The radius of gyration of the reel about its center axis is kg=0.42 m. 307 250 mm OG 500 mm 400 mm-arrow_forwardThe 2.28-kg uniform slender bar rotates freely about a horizontal axis through O. The system is released from rest when it is in the horizontal position 0 = 0 where the spring is unstretched. If the bar is observed to momentarily stop in the position 0 = 66°, determine the spring constant k. For your computed value of k, what is magnitude of the angular velocity of the bar when 0 = 48°. B 0.85 m 0.85 m 2.28 kg 0.29 my Answers: k = i N/m ω- rad/s 1arrow_forwardSOLVE USING PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGYarrow_forward
- At the instant shown, link CD rotates with an angular velocity of W = 9.0 rad/s. If it is subjected to a couple moment M= 320 N-m, determine the magnitude of the vertical reaction force developed on pin D. The block has a mass of 50 kg and center of mass at G. Neglect the mass of links AB and CD. (Hint, since the mass of link AB or CD is negligible, the external force or moment acting on it sums up to 0.) Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². 0.1 m 0.6 m В А 0.4 m' G 0.4 m D C M Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forwardThe uniform 80 kg slender rod is at rest in the position shown when P = 450 N is applied. Determine the value of angular velocity, w2 the rod if L1 = 5.5 m and L2 = 6.5 m. A L L2 L1 Barrow_forward0₁ Oy || 5 Kronk is asked to pull the lever. He applies a force of 20 N, causing the 8 kg lever to have an angular rad velocity of 3 || 6 8 . Determine the angular acceleration of the lever and the reaction forces at O. Assume the lever is a slender rod and that the lever was originally propped up to be level horizontally. The prop was removed at the instant Kronk applied the force. α = 5 Kronk applies the force at a length 7 and the lever has length 1 = 0.2 m. Use negative if CW 1 N N 1 rad 8² F (0) -CCWarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY