
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The spring-held follower AB has a mass of 0.5 kg and moves back and
forth as its end rolls on the contoured surface of the cam, where r = 0.15 m and z =
(0.02 cos 2θ) m. If the cam is rotating at a constant rate of 30 rad/s, determine the
force component Fz at the end A of the follower when θ = 30°. The spring is
uncompressed when θ = 90°. Neglect friction at the bearing C.
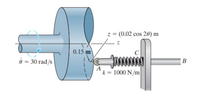
Transcribed Image Text:z = (0.02 cos 20) m
0.15 m
C
è = 30 rad/s
B
A
k = 1000 N/m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The small object m is placed on the inner surface of theconical dish that rotates about the vertical axis as shown.If μs = 0.3. Determine the range of velocities of m to keepthe motion on a horizontal plane without slipping.arrow_forwardThe particle of mass m = 2.5 kg is attached to the light rigid rod of length L = 1.27 m, and the assembly rotates about a horizontal axis through O with a constant angular velocity = w = 3.2 rad/s. Determine the force T in the rod when 0 = 36°. The force Tis positive if in tension, negative if in compression. Part 1 Answers: Calculate the r- and 0-components of acceleration. a₁ = de = i i L 6 m m m/s² m/s²arrow_forwardThe platform AB when empty has a mass of 400 kg centre of mass at G1 and natural period of oscillation t1=3.82 s. If a car, having a mass of 1.2 Mg and centre of mass at G2 is placed on the platform, the natural period of oscillation becomes t1=4.58 s. Determine the moment of inertia of the car about an axis passing through G2.arrow_forward
- of stion The man stands on the platform at O and runs out toward the edge such that when he is at A, y = 5 ft, his mass center has a velocity of 2 ft/s and an acceleration of 3 ft/s², both measured relative to the platform and directed along the positive y axis. If the platform has an angular velocity of 0.4 rd/s and angular acceleration of 0.2 rad/s² as shown in the figure below, determine the following: Note that i, j represent the unit vectors of x and y axes, respectively. Z The velocity of his mass center at this instant is The acceleration of his mass center at this instant is 00 # ft/s. W # ft/s². Aarrow_forwardThe helical path is wound around the circular cylinder with radiusR . The step h= 2*pi*R. The object A is sliding through the path guide under gravity (acting in the negative zdirection). There is no air resistance 1)Draw the force diagrams in (theta ,Z ) plane (tangent to the cylinder) and in( r,theta ) plane. 2) If the initial speed is 0, find the speed after 3 full circles. Given: R, g, m, u.[Hint: Use the work-energy principle.]arrow_forwardP= 900 N 4) The uniform 40 kg slender rod is being pulled by a cable that passes over the small smooth peg at A, and a vertical force F is applied at the edge 0.8 m as shown. If the rod has an angular velocity of w=6 rad/s 6 rad/s at the instant, determine the tangential and normal components of reaction forces at the F=150 N pin 0, and the angular acceleration of the rod. tosmt 0.6 m 0.3 marrow_forward
- The clock pendulum consists of the slender rod of length I and mass m and the bob of mass 7m. Neglect the effects of the radius of the bob and determine lo in terms of the bob position x. Calculate the ratio R of Io evaluated for x = ³/1 to Io evaluated for x = 1. 7m x m 1arrow_forward3. The uniform bar has a mass m and length 7. If it is released from rest when 0 = 0°, determine its angular velocity as a function of the angle before it slips. 3 23arrow_forwardIn the figure, rod AB has a mass of 10 kg, and must slide within the slots as shown. If the spring is unstretched when θ = 0°, determine the angular velocity of the bar when it reaches that angle after being released from θ = 30°.arrow_forward
- *13=108. The collar, which has a weight of 3 lb, slides along the smooth rod lying in the horizontal plane and having the shape of a parabola r = 4/(1 – cos 0), where 0 is in radians and r is in feet. If the collar's angular rate is constant and equals ò = 4 rad/s, determine the tangential retarding force P needed to cause the motion and the normal force that the collar exerts on the rod at the instant 0 = 90°.arrow_forwardWhen in the mode of adsorbing, the vertical shaft is rotating with an angular velocity of 3 rad/s at 0 = 0°. When picking up trashes, a force F needs to be applied to the collar so that 0 = 90°. Help students determine the angular velocity of the shaft at 0 = 90°. Also, find the work done by force F from 0 = 0° to 0 = 90°. Neglect the mass of rods GH and EF and the collars I and J. The rods AB and CD each have a mass of 10 kg. 0.3 m E 0.3 m 0.1 m 0.3 m A 0.1 m H F 0 0.3 m Barrow_forwardThe cylinder is at rest supported by the spring of stiffness 205 N/m when a torque of 78 Nm is applied as shown. The mass of the cylinder is 2.5 kg and its radius is 205 mm. If the wheel rolls without slipping, find the velocity of the centre of the wheel when it has moved a distance 352 mm up the slope with the angle ẞ= 25°.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY