
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Explain this in simple terms and de
Transcribed Image Text:1:42 PM Mon Apr 3
<
42
43
44
45
46
47
5
af
D
O
6. Plant...1 copy
stele
cambs
Photopols
d
adid
tofa
ufuk
ce
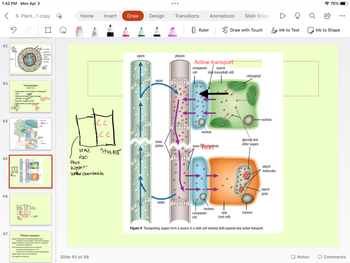
Transpiration
(water loss)
• Evaporation of H₂O films on mesophyll
cells
• Diffusion of water vapor through
stomata
Tension created in leaf
Pulls water up xylem from soil
fansion dow
koks, brama, and Lommen
root hair
epidermis
endodermis
xylem
pericycle
phloem
Phloem transport
Sugar transferred from photosynthetic cell to
Sugar leaves sieve cell via diffusion
H₂O leaves via osmosis
cortex
433
when shampts are
an get cle
in the f
companion cell by passive and active transport
Sugar transferred to sieve tube cell from companion
cell (passive transport)
H₂O enters sieve element cell via osmosis
increases water pressure in cell
pushes H₂O and dissolved sugar along phloem
Home
10 Mil
H₂C
A
Slide 45 of 48
Insert Draw Design
асс
cl
Have
higger
welter concentration
9999.993
xylem
BE
water
sieve
plates
water
●●●
Transitions
phloem
Ruler
Animations
Active transport
companion
source
cell
(leaf mesophyll cell)
nucleus
sieve tilberements
BI
nudeus
Draw with Touch
Slide Show
sink
(root cell)
chloroplast
glucose and
other sugars
nucleus
nucleus
starch
molecules
starch
grain
companion
cell
Figure 9 Transporting sugars from a source to a sink cell involves both passive and active transport.
Ink to Text
Notes
76%
Ink to Shape
Comments
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- . Cycloheximide is a drug that inhibits protein synthesis.Predict what effect cycloheximide would have onde-etiolationarrow_forwardA. Many, but not all, of the electron transfer reactions involve metal ions. Say if it is true or false justify only if it is falsearrow_forwardWhich of the terms in the Gibbs free energy equation denotes enthalpyarrow_forward
- Please discuss the connection of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) and dioxin.arrow_forwardUse ATP and ADP to illustrate the release or input ofenergy in chemical reactionsarrow_forwardExplain the following term, be sure to include energy requirements for each process and a biological example of each process: Facilitated diffusionarrow_forward
- Explain about the EPO experiments.arrow_forwardYou are a drop of water that your instructor has taken. For this assignment you will write the pathway you would follow will the limitations are written below. START with the name of the structure where you would first be absorbed. END with the name of the structure where you would leave your instructor's body. Name EVERY structure through which you must pass between the start and endpoints. If you get stuck, write something to indicate (such as ....) then continue on the latter part of the pathway.arrow_forwardA. Briefly explain the factors that could affect enzyme activityB. How can these factors influence the enzyme reaction?arrow_forward
- Explain about contact inhibition.arrow_forwardH1. Estimate the TKN associated with a sample having 50 mg/L of cell tissue and 10 mg/L of ammonia. Assume cell tissue has a molecular composition of C5H7O2N.arrow_forwardDescribe the C4 Pathway and Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) reactions, and when they occurarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education