
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:T-Mobile Wi-Fi ?
1 9:56 AM
77%
Done
19 of 22
UMIT
FOU FO
9 9I FOU FO : a FJU
FOU I FOU
adent.desmes.com/activitybuilder/student/6087417008264d0cbd495700screenld=b6bbeebc-a5df-4575-a585-f32a107db362
A E FO, F O O ( New
e Cennec.
Clara Destiry sho
O Employment Center
(Up
a Login Session Expiration.
sson 13: Experimenting
b Selling Associate-.
E Sign in
P View Portrait Prog.
O Nursing: Tradition.
10 of 13
Nex
50
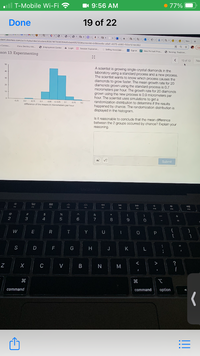
A scientist is growing single-crystal diamonds in the
laboratory using a standard process and a new process.
The scientist wants to know which process causes the
diamonds to grow faster. The mean growth rate for 20
diamonds grown using the standard process is 0.7
micrometers per hour. The growth rate for 20 diamonds
grown using the new process is 0.9 micrometers per
hour. The scientist uses simulations to get a
randomization distribution to determine if the results
happened by chance. The randomization distribution is
displayed in the histogram.
40
30
20
10
0.25
0.2
-0.1
0.05 0. 0.05
difference of the means in micrometers per hour
0.15
0.1
0,15
0.2
Is it reasonable to conclude that the mean difference
between the 2 groups occurred by chance? Explain your
reasoning.
Submit
MacBook Air
80
F3
Fd
23
&
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
W
E R
T Y U
:
S
F
G
H J
K L
>
?
C
V B N
command
command
option
+ I|
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The number of employed persons in Mexico between 2009 and 2019 can be modeled as a random variable with mean 52269218 employed persons and variance of 7607951381613.1 persons2.The mean of the X-bar sample will be obtained from a random sample of 44 data.What is the probability that X-bar will fall between 51,559,018 and 53,539,565?arrow_forwardshow step by step The bacterium tropical have diameters that are normally distributed with mean 9 nm and standard deivation 3.8 nm. A researcher does not know these parameters and measures a tropical to have a diameter of 11 nm. What is the probability a randomly-chosen bacterium of this species has a diameter of under 11 nm? To learn what the parameters are for this disease, the researcher measures the diameter of 25 bacteria. What is the probability that a sample of 25 bacteria will have a mean average diameter under 11 nm?arrow_forwardIn a human genome there are 6.4X109 basepairs and the mutation rate per generation per basepair is 1.8X10-8 basepairs. What is the expected number of new mutations (not carried by either of your parents) present in you? What is the probability that you contain 20 new mutations? Use Poisson distribution to solve.arrow_forward
- Suppose you are a quality control manager at a manufacturing company that produces light bulbs. The company has recently made changes to the manufacturing process, and you want to investigate whether these changes have had a significant impact on the average lifespan of the bulbs. You collect a random sample of 30 light bulbs produced under the new process and find that the sample mean lifespan is 1200 hours with a sample standard deviation of 100 hours. Additionally, you collect a random sample of 35 light bulbs produced under the old process and find that the sample mean lifespan is 1180 hours with a sample standard deviation of 90 hours. Assuming that the population standard deviations are unknown but equal, test at a 5% significance level that the average lifespan of the light bulb has changed with the new manufacturing process. NOT FOR MARKS, just a book sample questionarrow_forwardThis question has several parts that must be completed sequentially. If you skip a part of the question, you will not receive any points for the skipped part, and you will not be able to come back to the skipped part. Tutorial Exercise You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. A sample of 21 items from population 1 has a sample variance s₁² = 5.5 and a sample of 26 items from population 2 has a sample variance s₂² = 2.25. Test the following hypotheses at the 0.05 level of significance. Ho: H₂:₁² (a) What is your conclusion using the p-value approach? (b) Repeat the test using the critical value approach. Step 1 (a) What is your conclusion using the p-value approach? A hypothesis test comparing two population variances uses the F distribution. The F distribution is not symmetric and its shape will depend on two values of degrees of freedom, a numerator and denominator degrees of freedom. It is important to note that the values will never be negative. The F…arrow_forwardYou have been asked to determine if two different production processes have different mean numbers of units produced per hour. Process 1 has a mean defined as μ₁ and process 2 has a mean defined as µ₂. The null and alternative hypotheses are H₂: μ₁ −μ₂ ≤0 and H₁ : µ₁ − µ₂ > 0. The process variances are unknown but assumed to be equal. Using random samples of 36 observations from process 1 and 49 observations from process 2, the sample means are 60 and 50 for populations 1 and 2 respectively. Complete parts a through d below. Click the icon to view a table of critical values for the Student's t-distribution. THIV IVVI VIMUVUV IVA Since the test statistic is IV The test statistic is t = MITM IV ܝ The critical value(s) is(are) 1.663. (Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) greater than t + ny – 2,0 ² reject Ho. c. Can you reject the null hypothesis, using a probability of Type I error x = 0.05, if the sample standard deviation from process 1…arrow_forward
- In a production line that makes resistors, 5 resistors are discarded per hour on averagedue to defects. What is the probability of discarding at least 25 resistors in any 4-hour time period? need the solution without the aid of statistical software, with full working. It is OK to use statistical tables in your solutions, as long as you indicate which table you have used and how you have used it.arrow_forwardThe owner of a fast-food restaurant knows that, on average, 2.4 cars (customers) use the drive-through window between 3 pm and 3.15 pm. Find the variance and standard deviation Find the probability that exactly two cars will use the drive-through window Find the probability that at least three cars will use the drive-through windowarrow_forwardComputer hard drives must rotate in a balanced way and away from level is called pitch.Samples are taken regularly from production and each disk in the sample is placed in test equipment that results in a pitch measurement. From various samples it is concluded that the population is normal. The variance = image 1 when the process is in control. A sample of 10 is collected each week. The process will be declared out of control if the sample variance exceeds 0.122 What is the probability that it is declared out of control even when variance = image 1?arrow_forward
- A diagnostic test for disease X correctly identifies the disease 90% of the time. Flase positives occur 12%. It is estimated that 5.36% of the population suffers from disease X. Suppose the test is applied to a random individual from the population. What is the percentage chance that given a negative result, the person does not have disease X? What is the percentage chance that, the person will be misclassified?arrow_forwardThe exit gate has an outflow rate of 20 cars per minute which can be modeled as a Poisson Random Process. Suppose the west gate is also opened and given that cars choose it 30% of the time. What will be the new average time it takes for a car to exit the exit gate? (in seconds)arrow_forwardQ3 A mixed-model assembly line has eight stations. Average cycle time is 15 mimutes, but times vary due to model type and natural randomness. The estimated standard deviation of processing time in a station is 4.5 minutes. Estimate the production rate for the asynchronous line if no buffer is allowed.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman