
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
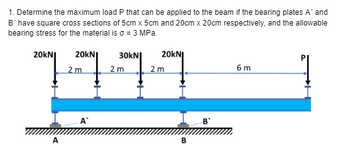
Transcribed Image Text:1. Determine the maximum load P that can be applied to the beam if the bearing plates A' and
B' have square cross sections of 5cm x 5cm and 20cm x 20cm respectively, and the allowable
bearing stress for the material is σ = 3 MPa.
20KNI 20KNI 30kN 20KNI
7777
2 m
A
2 m
2 m
B
6 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve using Fbd and equation. Have 30min onlyarrow_forwardUpvote will be given. Please write the solutions legibly. Solve in 2 decimal places. A 10 KN 10 KN 25 KN.m 20 KN/m Im B Tm C Tm Dm E m 1 F FIGURE 1 A. What is the maximum shear stress of the beam in FIGURE 1 if the beam is a 200mm x 400mm beam? B. What is the maximum flexural stress of the beam in FIGURE 1 if the beam is a 200mm x 400mm beam?arrow_forwardThe beam shown below with a length L = 16 m and a rectangular cross section that has a width of b = 50 mm and a depth d = 150 mm, has a load applied a x = 3 m away from the left hand support. What is the maximum load P that can be applied on the beam if the maximum bending stress can't exceed 14.0 MPa. Ignore any load factors or strength reduction factors.arrow_forward
- A wooden beam is fabricated by bolting together three members. The cross-sectional dimensions are shown. The 7-mm-diameter bolts are spaced at intervals of s 100 mm along the x axis of the beam. If the internal shear force in the beam is V-11 kN, determine the shear stress r in each bolt. Assume by - 46 mm, b₂-39 mm, dj-62 mm, d₂ - 290 mm. M Answer: r = i MPa. di Tarrow_forwardtelutip wollen A Situation 4 - An angle bracket having thickness t 20 mm is attached to the flange of a column by two 16-mm- diameter bolts as shown in Figure S01-7152. A uniformly distributed load from a floor joist acts on the top face of the bracket with a pressure p = 1900 kPa. The top face of the bracket has length L = 200 mm and width b = 75 mm. 25. Determine the average bearing pressure between the angle bracket and the bolts, in MPa. A. 48.7 C. 40.1 B. 50.2 D. 44.5 Fri 26. Determine the average shear stress in the bolts in MPa. (Disregard friction between the bracket and the column.) A. 76.32 C. 65.47 B. 60.89 eard antea mulos fest D. 70.87 Distributed pressure on angle bracket Floor slab WITH Floor joist Angle tracker 002 Figure S01-7152 Angle bracketarrow_forwardA stepped shaft made of steel is fixed at one end and 1.5 kN-m torque is applied at other end. What additional torque that can be applied at point B if the maximum shear stress is not to be exceeded 105 MPa and the total angle of twist should not exceeds 3°. The modulus of elasticity of steel may be taken as 200 GPa and Poisson's ratio as 0.3. 750 B 600 3-11- 70 90arrow_forward
- The steel beam has the cross section shown. The beam length is L = 4.2 m, and the cross-sectional dimensions are d = 360 mm, bf = 180 mm, tf = 16 mm, and tw = 6 mm. Calculate the largest intensity of distributed load w0 that can be supported by this beam if the allowable bending stress is 210 MPa.arrow_forwardThe allowable shear stress is τallow=895 psi�allow=895 psi. The supports at A� and B� are smootharrow_forwardRead the question carefully and give me right solution with clear calculationsarrow_forward
- Axial loads are applied with rigid bearing plates to the solid cylindrical rods shown. The normal stress in aluminum rod (1) must be limited to 18 ksi, the normal stress in brass rod (2) must be limited to 23 ksi, and the normal stress in steel rod (3) must be limited to 14 ksi. Determine the minimum diameter required for each of the three rods. Assume P = 8 kips, Q = 6 kips, R = 16 kips and S = 23 kips. SI (1) VQ (2) (3) A Answer: F₁ = B R C D First: Calculate the internal force (positive if tensile, negative if compresive) in rod (1). Use a FBD cutting through the rod in the section that includes the free end A. i kips.arrow_forwardThe shown L-shape cantilver is loaded as shown and fixed at A. It has a constant section of 40 mm X 20 mm. For point I located at 50 mm from support A, at the midheight of the section, determine the principal stresses, the principal planes and the maximum shear stress. y 50 mm 150 mm 40 mm 0.5 kN H- I 20 mm 3 kN 160 mm 2.5 kNarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning