
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
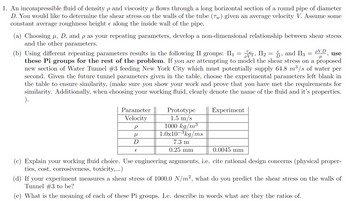
Transcribed Image Text:1. An incompressible fluid of density p and viscosity µ flows through a long horizontal section of a round pipe of diameter
D. You would like to determine the shear stress on the walls of the tube (7) given an average velocity V. Assume some
constant average roughness height & along the inside wall of the pipe.
(a) Choosing μ, D, and p as your repeating parameters, develop a non-dimensional relationship between shear stress
and the other parameters.
Tw
Π2
PV2,
use
PVD
(b) Using different repeating parameters results in the following II groups: II₁ = 2, II₂ = 5, and II3 =
μ
these Pi groups for the rest of the problem. If you are attempting to model the shear stress on a proposed
new section of Water Tunnel #3 feeding New York City which must potentially supply 64.8 m³/s of water per
second. Given the future tunnel parameters given in the table, choose the experimental parameters left blank in
the table to ensure similarity, (make sure you show your work and prove that you have met the requirements for
similarity. Additionally, when choosing your working fluid, clearly denote the name of the fluid and it's properties.
).
Parameter
Velocity
ρ
μ
D
€
Prototype
1.5 m/s
1000 kg/m³
1.0x10-3kg/ms
7.3 m
0.25 mm
Experiment
0.0045 mm
(c) Explain your working fluid choice. Use engineering arguments, i.e. cite rational design concerns (physical proper-
ties, cost, corrosiveness, toxicity,...)
(d) If your experiment measures a shear stress of 1000.0 N/m², what do you predict the shear stress on the walls of
Tunnel #3 to be?
(e) What is the meaning of each of these Pi groups. I.e. describe in words what are they the ratios of.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The true optionarrow_forwardA- Womersley number (a) of a human aorta is 20 and for the rabbit aorta is 17, the blood density is approximately the same across the species. The values of viscosity were 0.0035 Ns/m² for the human and 0.0040 Ns/m² for the rabbit. The diameter of the aorta is 2.0 cm for the man, and 0.7 cm for the rabbit, estimate the heart rate beats per minute (bpm) for both speciesarrow_forwardPlease the optionarrow_forward
- fluid mechanicsarrow_forwardA liquid of density ? and viscosity ? flows by gravity through a hole of diameter d in the bottom of a tank of diameter DFig. . At the start of the experiment, the liquid surface is at height h above the bottom of the tank, as sketched. The liquid exits the tank as a jet with average velocity V straight down as also sketched. Using dimensional analysis, generate a dimensionless relationship for V as a function of the other parameters in the problem. Identify any established nondimensional parameters that appear in your result. (Hint: There are three length scales in this problem. For consistency, choose h as your length scale.) except for a different dependent parameter, namely, the time required to empty the tank tempty. Generate a dimensionless relationship for tempty as a function of the following independent parameters: hole diameter d, tank diameter D, density ? , viscosity ? , initial liquid surface height h, and gravitational acceleration g.arrow_forwardPlease help me to answer these questions by today. Please try to explain it in details sothat I can understand.arrow_forward
- HW1.1: Equation 2.7 in the text provides the velocity profile, u(y) for a narrow, infinitely long, slit-like microchannel. Use the no-slip boundary conditions (channel walls not moving) to obtain 1 dp - hy} 2n dx the standard solution, u(y)= For an incompressible, Newtonian fluid, with fluid properties as described in the text, shear stress du is typically given by t =n· dy Write-out an expression for the shear stress as a function of y. Calculate shear stress at: (a) y = 0; (b) y = h; and (c) y = h/2.arrow_forward1. The thrust of a marine propeller Fr depends on water density p, propeller diameter D, speed of advance through the water V, acceleration due to gravity g, the angular speed of the propeller w, the water pressure p, and the water viscosity μ. You want to find a set of dimensionless variables on which the thrust coefficient depends. In other words CT = FT · = ƒen(#1, #2, ...) pV2D2 (a) What is k? Explain. (b) Find the 's on the right-hand-side of equation 1 if one of them HAS to be a Froude number gD/V², (1)arrow_forwardDerive an expression for the shear stress at the pipe wall when an incompressible fluid flows through a pipe under pressure. Use dimensional analysis with the following significant parameters: pipe diameter D, flow velocity V, and viscosity u and density p of the fluid.arrow_forward
- can someone explain this question pleasearrow_forwardPLEASE BOX YOUR ANSWERS Problem 2 In an experiment conducted in a laboratory, the surface tension (Y) acting on a rotating square plate in a viscous fluid is a function of the external torque (t), plate length (a), area moment of inertia of plate (I), specific weight of the fluid (Y) and angular displacement of the plate (0). Using Buckingham-Pi theorem, find a suitable set of pi terms (in M, L and T primary dimensions). Your final answer should be written in proper functional form. Refer Table 5.1/ page-296 for secondary dimension of the variables.arrow_forwardBooks on porous media and atomization claim that the viscosityμ and surface tension Y of a fl uid can be combinedwith a characteristic velocity U to form an important dimensionlessparameter. ( a ) Verify that this is so. ( b ) Evaluatethis parameter for water at 20°C and a velocity of3.5 cm/s. Note: You get extra credit if you know the nameof this parameter.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY