Question
Transcribed Image Text:1) A HYPOSTATIC structure:
a)
Is a structure fixed with more than the strictly necessary number of constraints;
b) Is a statically determinate structure;
c) Can be hyperstatic if the constraints are ill-disposed.
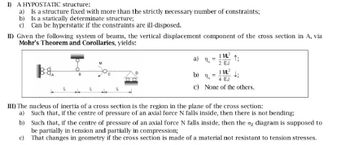
II) Given the following system of beams, the vertical displacement component of the cross section in A, via
Mohr's Theorem and Corollaries, yields:
38
a)
1 ML
2 EJ
1:
b) 11
1 ML2
c) None of the others.
III) The nucleus of inertia of a cross section is the region in the plane of the cross section:
a) Such that, if the centre of pressure of an axial force N falls inside, then there is not bending;
b) Such that, if the centre of pressure of an axial force N falls inside, then the σ, diagram is supposed to
be partially in tension and partially in compression;
c) That changes in geometry if the cross section is made of a material not resistant to tension stresses.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Compute the line energy of dislocation in fcc, diamond. The shear modulus of carbon is 462 GNm 2. The diameter of carbon atom in diamond is 1.54Å. Answer: 1.46 x 10-³J/marrow_forwardA 11 N horizontal force F→ pushes a block weighing 4.1 N against a vertical wall (see the figure). The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the block is 0.56, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.49. Assume that the block is not moving initially. (a) Will the block move? ("yes" or "no") (b) In unit-vector notation Fxî+Fyĵ, what is the force on the block from the wall?arrow_forwardIn the methane molecule, CH4, each hydrogen atom is at the corner of a regular tetrahedron with the carbon atom at the center. If one of the C-H is in the direction of and an adjacent C-H bond is at the direction . results to an angular bond of approximately 109o for a static frozen molecule. However, the molecule we can encounter everyday continuously vibrates and interact with the surrounding causing its bond vector to vary slightly. According to a new spectroscopy analysis, the adjacent bond vectors was found to be A = 0.93i + 0.91j + 1.09k B = 1.02i + -0.99j + -1.08karrow_forward
- During a dunk, a basketball player will elevate theircenter of mass 70 cm (or more) while jumping off of one leg. What is the strain energy contribution to the energy required to elevate the center of mass given the following parameters? How much energy has to be contributed by active muscle contraction? mass = 82 kg, K leg = 35000N/m, dispacement = 0.11 m.arrow_forwardModern commercial airliners are largely made of aluminum, a light and strong metal. But the fact that aluminum is cheap enough that airplanes can be made out of it is a bit of historical luck. Before the discovery of the Hall-Héroult process in 1886, aluminum was as rare and expensive as gold. What would happen if airplanes had to be made of steel? The fuselage of the Boeing 747, which can carry 400 passengers, is approximately a hollow aluminum cylinder without ends, 70.7 m long, 6.5 m wide, and 2.5 mm thick (see sketch at right). The fuselage of an airplane Suppose this fuselage was made of steel (density 7.87 g/cm³) instead of aluminum (density 2.70 g/cm³), and let's say the average passenger has a mass of 79 kg. We'll also assume the engines can't lift any greater mass than they already do. Calculate the number of passengers that the Boeing 747 could carry if its fuselage was made of steel. 0 Xarrow_forwardA high-carbon steel with a fully pearlitic microstructure was used to form a high-strength bolt (H.-C. Lee et al., J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 211, 1044 (2011)). It was found that the bolt head had an average interlamellar spacing of 257 nm whereas the average spacing in the body of the bolt was 134 nm. Assuming that dislocation pileup is the primary mechanism responsible for the strength of this alloy, what ratio of strength (or hardness) might be expected in the head and body of the bolt?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios