
Concept explainers
Single-rate method, budgeted versus actual costs and quantities. Chocolat Inc. is a producer of premium chocolate based in Palo Alto. The company has a separate division for each of its two products: dark chocolate and milk chocolate. Chocolat purchases ingredients from Wisconsin for its dark chocolate division and from Louisiana for its milk chocolate division. Both locations are the same distance from Chocolat’s Palo Alto plant.
Chocolat Inc. operates a fleet of trucks as a cost center that charges the divisions for variable costs (drivers and fuel) and fixed costs (vehicle depreciation, insurance, and registration fees) of operating the fleet. Each division is evaluated on the basis of its operating income. For 2017, the trucking fleet had a practical capacity of 50 round-trips between the Palo Alto plant and the two suppliers. It recorded the following information:
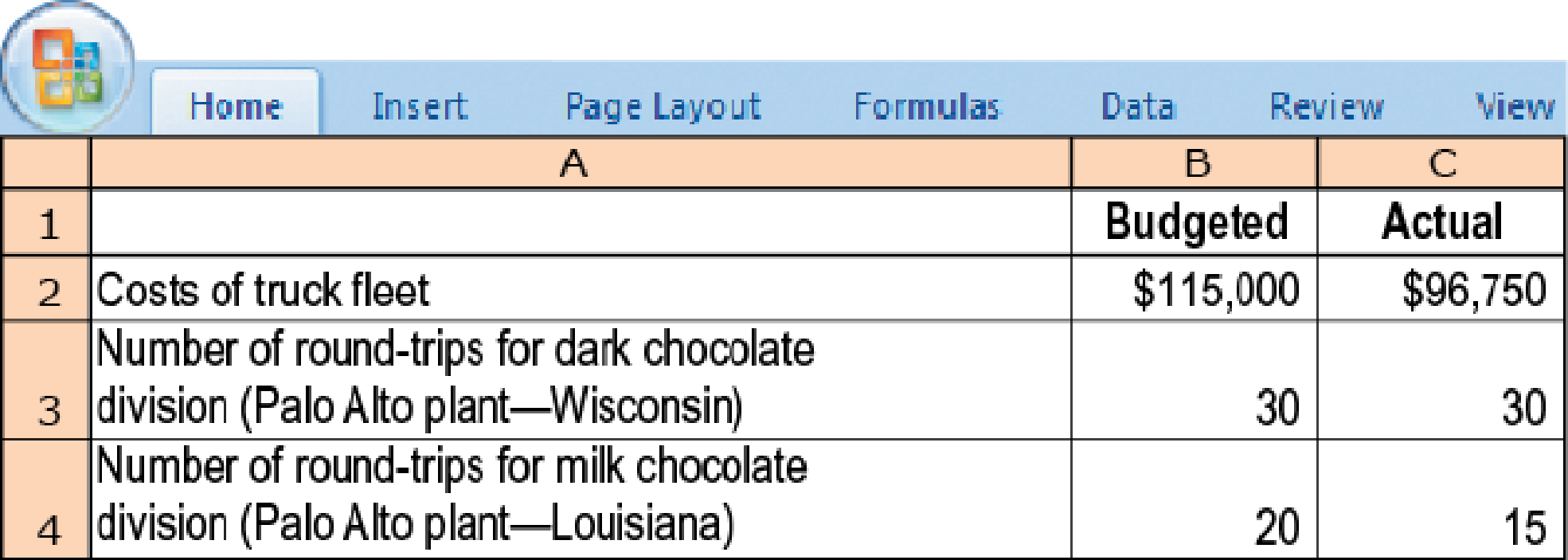
- 1. Using the single-rate method, allocate costs to the dark chocolate division and the milk chocolate division in these three ways.
- a. Calculate the budgeted rate per round-trip and allocate costs based on round-trips budgeted for each division.
- b. Calculate the budgeted rate per round-trip and allocate costs based on actual round-trips used by each division.
- c. Calculate the actual rate per round-trip and allocate costs based on actual round-trips used by each division.
- 2. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using each of the three methods in requirement 1. Would you encourage Chocolat Inc. to use one of these methods? Explain and indicate any assumptions you made.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- Cascade Containers is organized into two divisions-Manufacturing and Distribution. Manufacturing produces a product that can be sold immediately or transferred to Distribution for further processing and then sold. Distribution only buys from Manufacturing for quality control reasons. Manufacturing currently sells 2,400 units annually at a price of $600 per unit to outside customers. It sells an additional 1,200 units to Distribution. The unit variable cost in Manufacturing is $300 and annual fixed costs are $300,000. Manufacturing is located in a country with a 20 percent tax rate. Distribution can sell units that have had further processing for $1,200 each. In addition to what it pays Manufacturing, the variable costs in Distribution are $150 per unit. Annual fixed costs in Distribution are $360,000. Distribution is located in a country with a 10 percent tax rate. Required: a. Suppose Manufacturing would have excess capacity even with the demand from Distribution. Ignoring tax…arrow_forwardTeslum Inc. has a number of divisions, including the Machina Division, a producer of high-endespresso makers, and the Java Division, a chain of coffee shops.Machina Division produces the EXP-100 model espresso maker that can be used by JavaDivision to create various coffee drinks. The market price of the EXP-100 model is $950, andthe full cost of the EXP-100 model is $475.Required:1. If Teslum has a transfer pricing policy that requires transfer at full cost, what will thetransfer price be? Do you suppose that Machina and Java divisions will choose to transferat that price?2. If Teslum has a transfer pricing policy that requires transfer at market price, what wouldthe transfer price be? Do you suppose that Machina and Java divisions would choose totransfer at that price?3. Now suppose that Teslum allows negotiated transfer pricing and that Machina Divisioncan avoid $135 of selling expense by selling to Java Division. Which division sets theminimum transfer price, and what is it? Which…arrow_forwardT-Comm makes a variety of products. It is organized in two divisions, North and South. The managers for each division are paid, in part, based on the financial performance of their divisions. The South Division normally sells to outside customers but, on occasion, also sells to the North Division. When it does, corporate policy states that the price must be cost plus 15 percent to ensure a “fair” return to the selling division. South received an order from North for 600 units. South’s planned output for the year had been 2,400 units before North’s order. South’s capacity is 3,000 units per year. The costs for producing those 2,400 units follow. Total Per Unit Materials $ 480,000 $ 200 Direct labor 230,400 96 Other costs varying with output 153,600 64 Fixed costs (do not vary with output) 2,016,000 840 Total costs $ 2,880,000 $ 1,200 Required: a. If you are the manager of the South Division, what unit cost would you ask…arrow_forward
- Health Products is a cranberry cooperative that operates two divisions, a harvesting division and a processing division. Currently, all of harvesting's output is converted into cranberry juice by the processing division, and the juice is sold to large beverage companies that produce cranberry juice blends. The processing division has a produce of 500 gallons of juice per 1,000 pounds of cranberries. Cost and market price data for the two divisions are as follows: Harvesting Division Processing Division Variable cost per pound of cranberries $0.10 Variable cost per gallon of juice produced $0.18 Fixed cost per pound of cranberries $0.30 Fixed cost per gallon of juice produced $0.35 Selling price per pound of cranberries in $0.68 Selling price per gallon of juice outside market $2.45 If processing division purchases cranberries from outside supplier, the price will be $0.15 per pound. Required: 1. What is the minimum transfer price at which the harvesting division willing to accept to…arrow_forwardT-Comm makes a variety of products. It is organized in two divisions, North and South. The managers for each division are paid, in part, based on the financial performance of their divisions. The South Division normally sells to outside customers but, on occasion, also sells to the North Division. When it does, corporate policy states that the price must be cost plus 15 percent to ensure a “fair” return to the selling division. South received an order from North for 600 units. South’s planned output for the year had been 2,400 units before North’s order. South’s capacity is 3,000 units per year. The costs for producing those 2,400 units follow.arrow_forwardCran Health Products is a cranberry cooperative that operates two divisions, a harvesting division and a processing division. Currently, all of harvesting’s output is converted into cranberry juice by the processing division, and the juice is sold to large beverage companies that produce cranberry juice blends. The processing division has a yield of 500 gallons of juice per 1,000 pounds of cranberries. Cost and market price data for the two divisions are as follows: Assume that Pat Borges, CEO of Cran Health, had mandated a transfer price equal to 225% of full cost. Now he decides to decentralize some management decisions and sends around a memo that states the following: “Effective immediately, each division of Cran Health is free to make its own decisions regarding the purchase of direct materials and the sale of finished products.” Q. Borges feels that a dual transfer-pricing policy will improve goal congruence. He suggests that transfers out of the harvesting division be made at…arrow_forward
- The Mandalorian Company has two divisions, Production and Marketing. Production manufactures Beskar Head Armour for Knights of the Old Republic, which it sells to both the Marketing Division and to other retailers (the latter under a different brand name). Marketing operates several small armour stores in shopping centers throughout Corruscant. Marketing sells both Beskar Head Armour and other brands. Relevant facts for Production are as follows: Sales Price to Outsiders.............................................................$28.50 per Pcs Variable Cost to Produce...........................................................$18.00 per Pcs Fixed Costs ................................................................................$100,000 per Month The following data pertain to the sale of Mandalorian Company Beskar Head Armour by Marketing: Marketing is operating far below its capacity. Sales…arrow_forwardThe Mandalorian Company has two divisions, Production and Marketing. Production manufactures Beskar Head Armour for Knights of the Old Republic, which it sells to both the Marketing Division and to other retailers (the latter under a different brand name). Marketing operates several small armour stores in shopping centers throughout Corruscant. Marketing sells both Beskar Head Armour and other brands. Relevant facts for Production are as follows: Sales Price to Outsiders.............................................................$28.50 per Pcs Variable Cost to Produce...........................................................$18.00 per Pcs Fixed Costs ................................................................................$100,000 per Month The following data pertain to the sale of Mandalorian Company Beskar Head Armour by Marketing: Marketing is operating far below its capacity. Sales…arrow_forwardSE Spring Corp. has two divisions, Daffodil and Tulip. Daffodil produces a gadget that Tulip could use in its production. Tulip currently purchases 195,000 gadgets for $14.40 on the open market. Daffodil's variable costs are $7.90 per widget while the full cost is $12.20. Daffodil sells gadgets for $15 each. If Daffodil is operating at capacity, what would be the maximum transfer price Tulip would pay internally? Multiple Choice $7.90 $12.20 $14.40 $14.90arrow_forward
- Bostonian Inc. has a number of divisions, including the Delta Division and the Listen Now Division. The Listen Now Division owns and operates a line of MP3 players. Each year, the Listen Now Division purchases component AZ in order to manufacture the MP3 players. Currently, it purchases this component from an outside supplier for $6.50 per component. The manager of the Delta Division has approached the manager of the Listen Now Division about selling component AZ to the Listen Now Division. The full product cost of component AZ is $3.10. The Delta Division can sell all of the component AZs it makes to outside companies for $6.50. The Listen Now Division needs 18,000 component AZs per year; the Delta Division can make up to 60,000 components per year. Required: A. Which division sets the maximum transfer price? Which division sets the minimum transfer price? Maximum Minimum B. Suppose the company policy is that all transfer take place at full cost. What is the transfer…arrow_forwardSignature Scents has two divisions: the Cologne Division and the Bottle Division. The Bottle Division produces containers that can be used by the Cologne Division. The Bottle Division's variable manufacturing cost is $2, shipping cost is $0.10, and the external sales price is $3. No shipping costs are incurred on sales to the Cologne Division, and the Cologne Division can purchase similar containers in the external market for $2.60.The Bottle Division has sufficient capacity to meet all external market demands in addition to meeting the demands of the Cologne Division. Using the general rule, the transfer price from the Bottle Division to the Cologne Division would be: Select one: a. $2.00. b. $2.10. c. $2.60. d. $2.90. e. $3.00.arrow_forwardCran Health Products is a cranberry cooperative that operates two divisions, a harvesting division and a processing division. Currently, all of harvesting’s output is converted into cranberry juice by the processing division, and the juice is sold to large beverage companies that produce cranberry juice blends. The processing division has a yield of 500 gallons of juice per 1,000 pounds of cranberries. Cost and market price data for the two divisions are as follows: Q.Compute Cran Health’s operating income from harvesting 480,000 pounds of cranberries during June 2017 and processing them into juice.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





