
Concept explainers
Arrange the compounds of each of the following series in order of increasing acidity:
Interpretation:
The compounds of each of the given series are to be arranged in order of increasing acidity.
Concept introduction:
Acidity depends on the
Resonance structures are the structures in which two or more possible electron structures are drawn. In the resonance structure, the position of the atoms is the same but position of the electrons is different.
Resonance causes delocalization of electron pairs, which increases the stability of the base.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
(a)
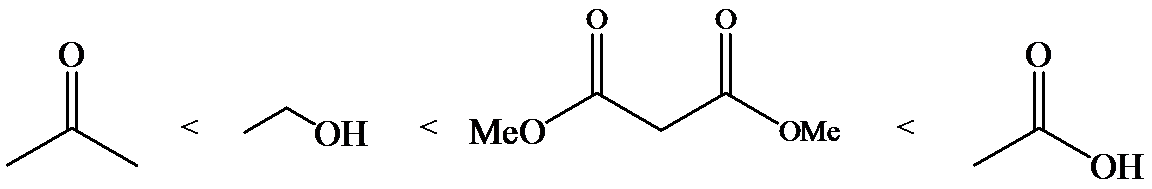
(b)
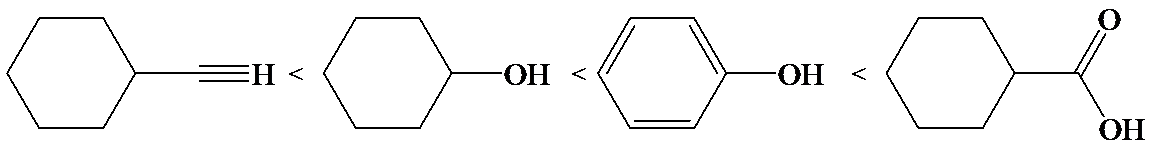
(c)

(d)
(e)
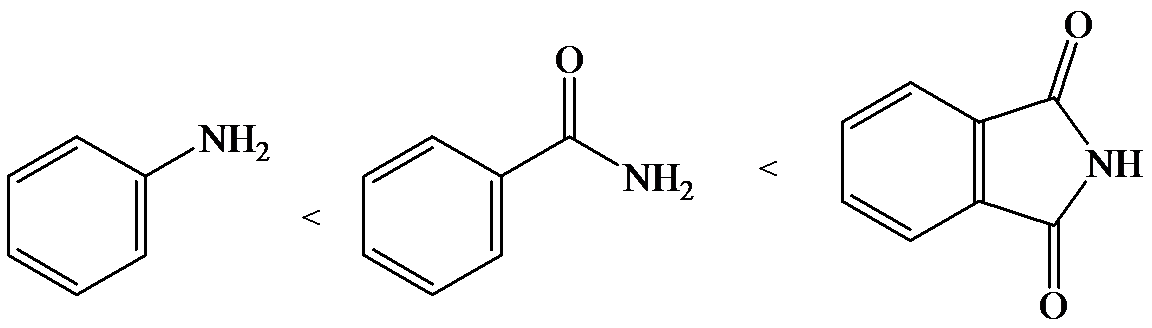
Explanation of Solution
a)
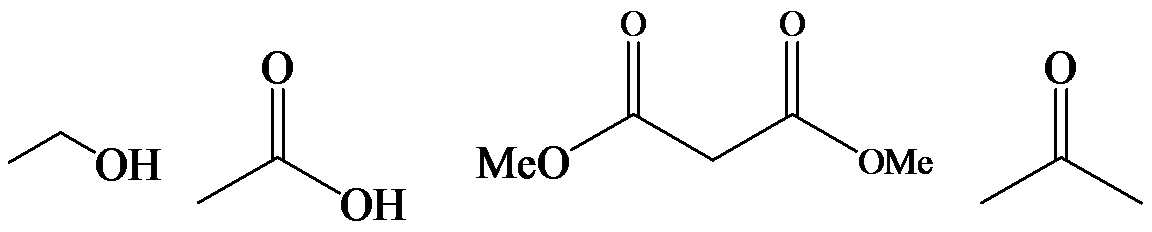
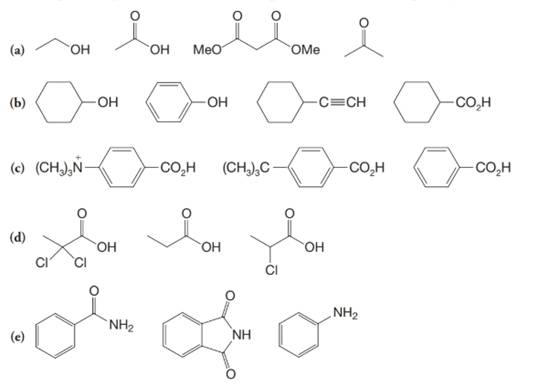
The α-hydrogen atoms of carbonyl groups are acidic. The acidity arises from the electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl and resonance stabilization of its conjugate base. The electron donating effect of  groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
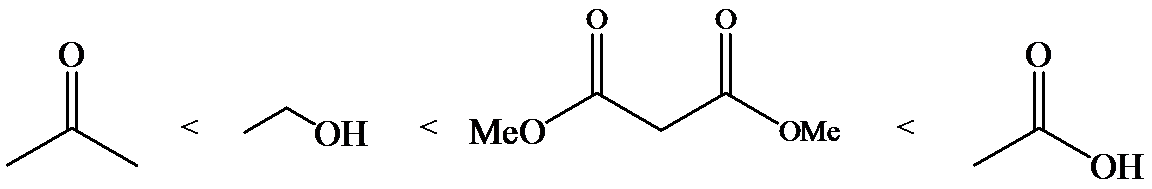
b)
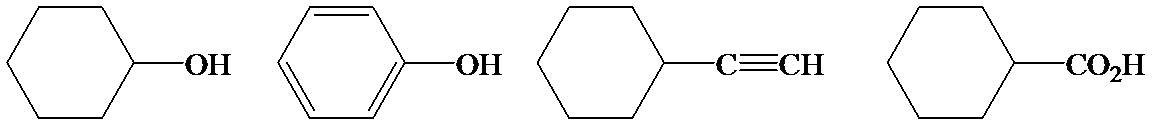
Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol because the resonance stabilization in both is different.
In the case of cyclohexane carboxylic acid, negative charge is shared between two different oxygen atoms making it more stabilized than phenoxide. Hence, the removal of proton from cyclohexane carboxylic acid is easier than phenol, making it more acidic than phenol.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
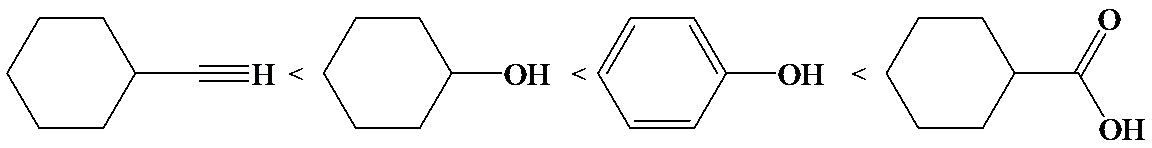
c)
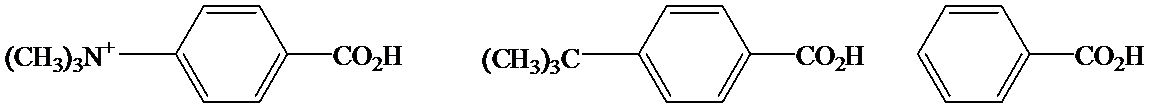
In the case of carboxylic acids, electron substituents increase acidity by inductive electron donation. The electron-donating tert-butyl group destabilizes the conjugate base of benzoic acid, making it less acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:

d)
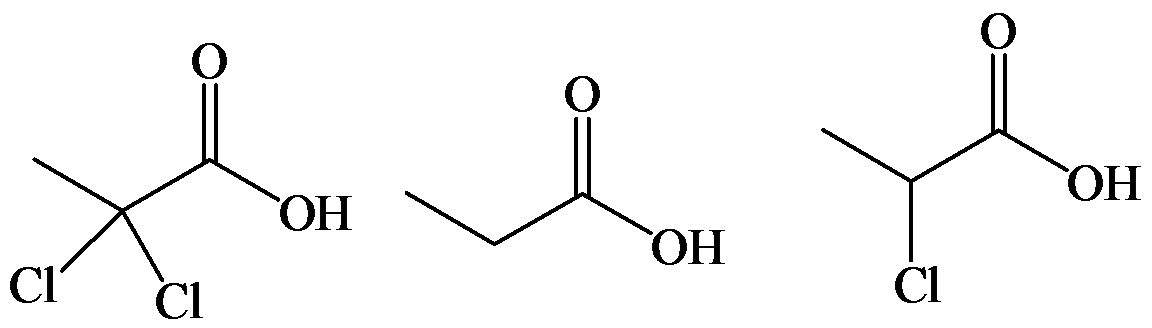
The electron-withdrawing chloro groups increase the acidity of carboxylic acid by increasing the stability of the carboxylate ion. Hence, the carboxylic acid with more chloro groups is more acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
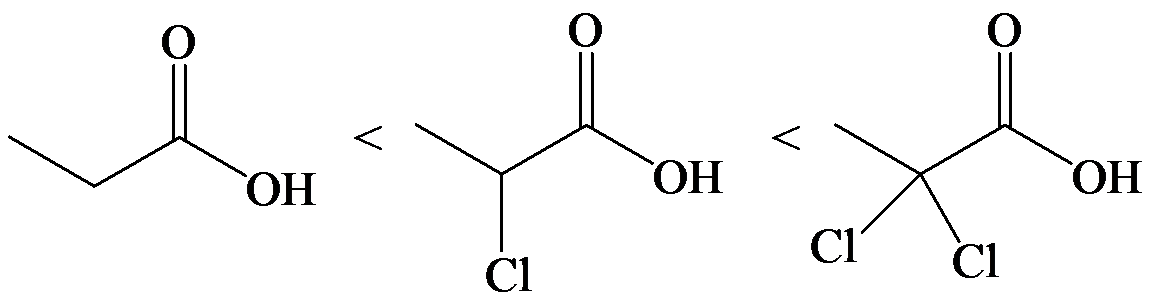
e)

The lone pair electron in aniline is localized on the nitrogen atom, whereas onbenzamide, it is delocalized between oxygen and nitrogen via resonance. Therefore, benzamide is more acidic than aniline.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
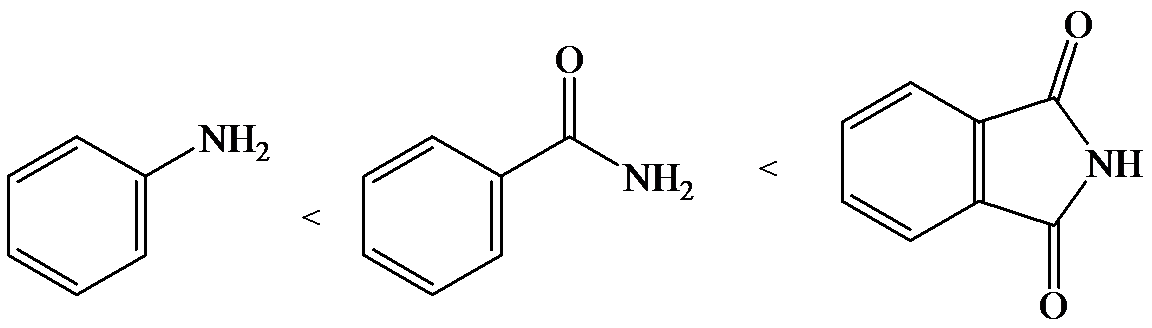
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter SRP Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- What is the lone pair or charge that surrounds the nitrogen here to give it that negative charge?arrow_forwardLast Name, Firs Statifically more chances to abstract one of these 6H 11. (10pts total) Consider the radical chlorination of 1,3-diethylcyclohexane depicted below. 4 • 6H total $ 4th total 21 total 4H total ZH 2H Statistical H < 3°C-H werkst - product bund abstraction here leads to the mo favored a) (6pts) How many unique mono-chlorinated products can be formed and what are the structures for the thermodynamically and statistically favored products? Proclict 6 Number of Unique Mono-Chlorinated Products f Thermodynamically Favored Product Statistically Favored Product b) (4pts) Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for the FIRST propagation step (p-1) for the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. Only draw the p-1 step. You do not need to include lone pairs of electrons. No enthalpy calculation necessary 'H H-Cl Waterfoxarrow_forward2. (a) Many main group oxides form acidic solutions when added to water. For example solid tetraphosphorous decaoxide reacts with water to produce phosphoric acid. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (b) Calcium phosphate reacts with silicon dioxide and carbon graphite at elevated temperatures to produce white phosphorous (P4) as a gas along with calcium silicate (Silcate ion is SiO3²-) and carbon monoxide. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.arrow_forward
- this is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution in your hand writing not an AI generated answer please draw the figures and structures if needed to support your explanation hand drawn only!!!! answer the question in a very simple and straight forward manner thanks!!!!! im reposting this please solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forward2B: The retrosynthetic cut below provides two options for a Suzuki coupling, provide the identities of A, B, C and D then identify which pairing is better and justify your choice. O₂N. Retro-Suzuki NO2 MeO OMe A + B OR C + Darrow_forwardthis is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution in your hand writing not an AI generated answer please draw the figures and structures if needed to support your explanation hand drawn only!!!! answer the question in a very simple and straight forward manner thanks!!!!! im reposting this please solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

