
Wireless Power Transmission
Your laptop has wireless communications connectivity, and you might even have a wireless keyboard or mouse. But there’s one wire you haven’t been able to get rid of yet—the power cord.
Researchers are working on ways to circumvent the need for a direct electrical connection for power, and they are experiencing some success. Recently, investigators were able to use current lowing through a primary coil to power a 60 W lightbulb connected to a secondary coil 2.0 m away, with approximately 15% efficiency. The coils were large and the efficiency low, but it's a start.
Figure VI.2
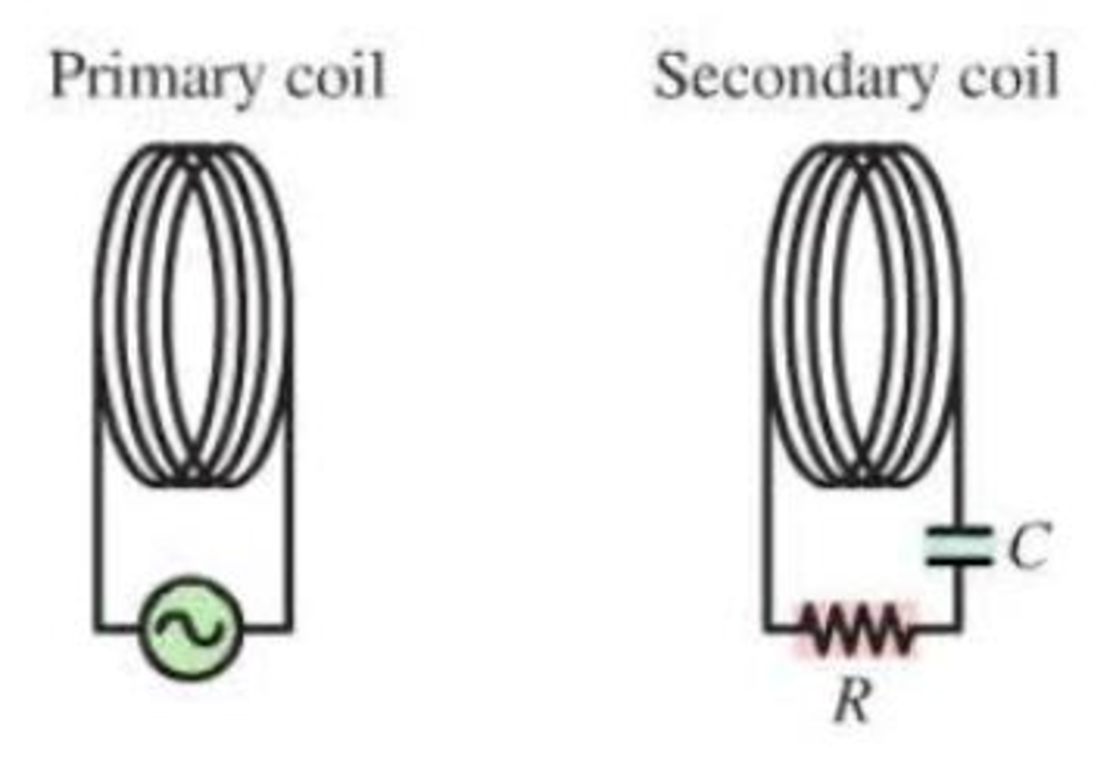
The wireless power transfer system is outlined in Figure VI.2. An AC supply generates a current through the primary coil, creating a varying magnetic Held. This field induces a current in the secondary coil, which is connected to a resistance (the lightbulb) and a capacitor that sets the resonance frequency of the secondary circuit to match the frequency of the primary circuit.
At a particular moment, the magnetic field from the primary coil points to the right and is increasing in strength. The field due to the induced current in the secondary coil is
- A. To the right.
- B. To the left.
- C. Zero.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- a cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forwardFrom number 2 and 3 I just want to show all problems step by step please do not short cut look for formulaarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





