The relation between the
Explanation of Solution
The inverse relation between the bond price and its interest rate is shown in the figure below:
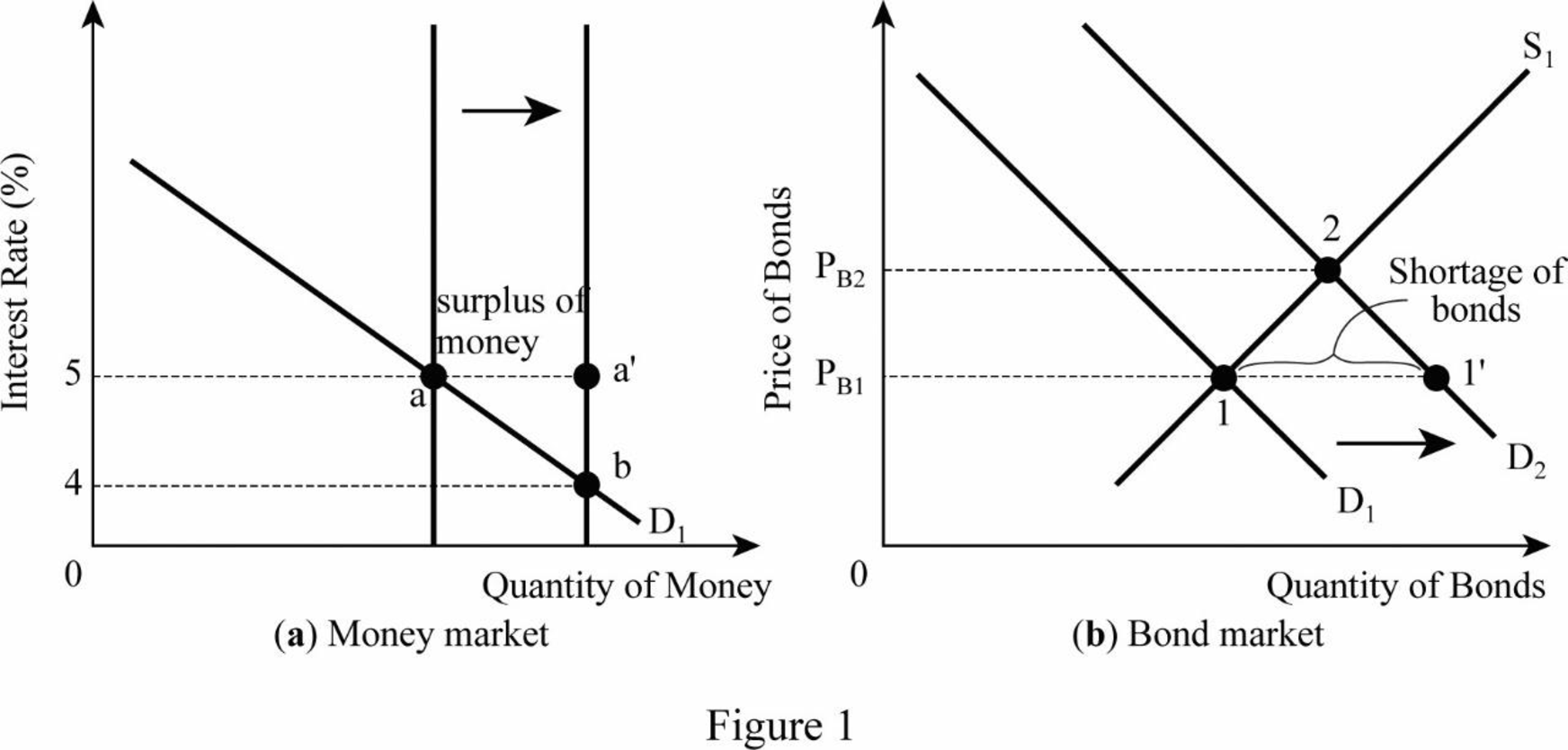
According to the diagram, initially, the
Bond price: Bond price is the present value of a bond compared to its future promises of pay. It is inversely related to its interest rate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter D Solutions
Macroeconomics
- 1. Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer. State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically.arrow_forward2. Consider the following table of long-run total costs for three different firms: Quantity Total Cost ($) Firm A Firm B Firm C 1 60 11 21 2 70 24 34 3 80 39 49 4 90 56 66 5 100 75 85 6 110 96 106 7 120 119 129 Does each of these firms experience economies of scale or diseconomies of scale? Explain your answer with necessary calculations.arrow_forward1. Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer. State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically.arrow_forward
- Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added5 units to Sadid’s utility, while the last bread added 7 units.arrow_forward1. Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer. State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically.arrow_forwardTopic Discussion - If you are a dís X ses/1545/discussion_topics/15678?module_item_id=111458 er > Discussions > Discussion - If you are a distrib... You must post before seeing replies. Edit history will be available to instructors. Due Dec 21 11:59pm 10 points possible 32 Replies, 32 Unread Discussion - If you are a distributer of Gerber, how do you promote selling our product? equirement: Include Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Your initial Discussion posting should be at least 150 words in length. Be sure to include a related Title, at least two different citations and references to support your statement Read and post brief responses to at least two of your classmates' postings (minimum 75 words).arrow_forward
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardQ Search entries or author... All ↓ Sort View Split Screen Expand Threads i You must post before seeing replies. Edit history will be available to instructors. Due Dec 21 11:59pm 10 points poss 18 Replies, 18 Unread Discussion 15: Organizational Structures Select one of the questions below and write a 150 - 200 word discussion post. Respond to at least one other student in 50 - 100 words. 1. Describe the characteristics of a bureaucracy. 2. Describe a matrix organization. Q Search hparrow_forwardQ Search entries or author... All i ↓ Sort View Split Screen Expand Threads You must post before seeing replies. Edit history will be available to instructors. Due Dec 21 11:59pm 10 points pos 19 Replies, 19 Unread Discussion 14: Conflict Write a 150-200 word discussion post based on the 3 prompts below. Respond to at least one other student in 50 - 100 words 1. Define conflict. 2. Contrast task, relationship, and process conflict. 3. Explain contemporary perspectives of conflict. Reply Q Searcharrow_forward
- X Topic: Discussion 12: Leadership X /courses/1548/discussion_topics/15744?module_item_id=111746 Winter > Discussions > Discussion 12: Leadership You must post before seeing replies. Edit history will be available to instructors. Due Dec 14 11:59pm 时☆ 10 points possible 18 Replies, 18 Unread Discussion 12: Leadership Select one of the questions below and write a 150 - 200 word discussion post. Respond to at least one other student in 50 - 100 words. 1. Define the characteristics of a charismatic leader. 2. Contrast transformational with transactional leaders. Reply Search X 4 b 12/arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning






