
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is a bond that results from the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms. Lewis structures are representations of the covalent bond. In this, Lewis symbols show how the valence electrons are present in the molecule.
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound that has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Estimate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
The formula to calculate formal charge of the atom is as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.57QE
The Lewis structure of
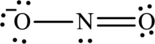
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is made up of oxygen, and nitrogen atoms.
The rules applied to obtain the Lewis structure of
1. Write the skeleton structure.
In the skeleton structure, two bonds are formed.
2. Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
The valence electron of oxygen is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of nitrogen is calculated as follows:
Also, the structure has charge of
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as follows:
3. Calculate the remaining electrons that are not used in skeleton structure.
The skeleton structure has two bonds. Therefore four electrons are used in bonds.
The remaining electrons are calculated as follows:
4 To obey the octet rule, the oxygen atom needs six electrons and nitrogen atom needs 6 electrons.
5. Satisfy the octet rule.
There are ten remaining electrons. Multiple bonds can be formed. In this compound, an additional bond is needed to complete the structure. Also, remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on nitrogen and oxygen atom to satisfy octet.
The Lewis structure of
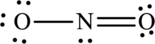
6. The Lewis structure is finished except for formal charges.
7. The formal charge on an atom in this Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
The formal charge on nitrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 5 for number of valence electrons, 2 for number of lone pairs and 6 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on first oxygen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on second oxygen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
In this Lewis structure, nitrogen has formal charge 0. First oxygen atom has formal charge
The Lewis structure made from
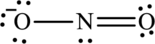
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.57QE
The Lewis structure made of
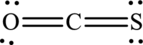
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is made up of oxygen, sulfur, and carbon atoms.
The rules applied to obtain the Lewis structure of
1. Write the skeleton structure.
There is one sulfur atom, one oxygen atom and carbon is place as central atom. Therefore, two bonds are formed between carbon, sulfur and oxygen atom.
2. Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
The valence electron of oxygen is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of sulfur is calculated as follows:
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as follows:
3. Calculate the remaining electrons that are not used in skeleton structure.
The skeleton structure has two bonds. Therefore four electrons are used in bonds. The remaining electrons are calculated as follows:
4 To obey the octet rule, the oxygen atom needs six electrons, carbon atom needs 4electrons and sulfur atom needs 6 electrons.
5. Satisfy the octet rule.
There are 12 remaining electrons. Multiple bonds can be formed. In this compound, an additional bond is needed to complete the structure. Also, remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on sulfur and oxygen atom to satisfy octet.
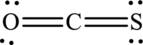
The Lewis structure of
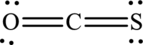
6. The Lewis structure is finished except for formal charges.
7. The formal charge on an atom in this Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
The formal charge on carbon atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 4 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 8 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on oxygen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs and 4 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on sulfur atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs and 4 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
In this Lewis structure, nitrogen has formal charge 0. Oxygen atom has formal charge0 and sulfur atom has formal charge 0.
The Lewis structure of
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(c)
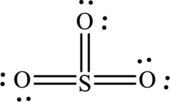
Answer to Problem 9.57QE
The Lewis structure made from
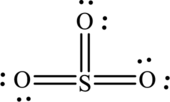
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is made up of oxygen, and sulfur atoms.
The rules applied to obtain the Lewis structure of
1. Write the skeleton structure.
There are one sulfur atom and three oxygen atoms. Therefore, three bonds are formed between sulfur and each oxygen atoms.
2. Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
The valence electron of oxygen is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of sulfur is calculated as follows:
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as follows:
3. Calculate the remaining electrons that are not used in skeleton structure.
The skeleton structure has three bonds. Therefore, six electrons are used in bonds.
The remaining electrons are calculated as follows:
4 To obey the octet rule, the oxygen atom needs six electrons, carbon atom needs 4el and sulfur atom needs 6 electrons.
5. Satisfy the octet rule.
There are 18 remaining electrons. Multiple bonds can be formed. In this compound, an additional bond is needed to complete the structure. Also, remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on oxygen atom to satisfy octet.
The Lewis structure of
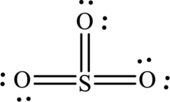
6. The Lewis structure is finished except for formal charges.
7. The formal charge on an atom in this Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
The formal charge on sulfur atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 12 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on first oxygen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs and 4 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on second oxygen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs and 4 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on the third oxygen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 6 for number of valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs and 4 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
In this Lewis structure, sulfur has formal charge 0. All oxygen atoms have formal charge 0.
The Lewis structure made from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- Draw Lewis structures for these ions and show which atom in each bears the formal charge. Q.) HCO3-arrow_forwardThe cyanate ion, NCO-, has three possible Lewis structures.(a) Draw these three structures and assign formal charges ineach. (b) Which Lewis structure is dominant?arrow_forwardWhat is the formal charge on the anionic molecule (BrO3)-?arrow_forward
- What is the formal charge on carbon in COCl2?arrow_forwardThe thiocyanate ion , NCS- , has three possible Lewis structures.a. Draw these three structures and assign formal charges in each.b. Which Lewis structure is dominant?arrow_forwardDraw three resonance structures for carbonate ion, CO32-, and assign formal charges on all the atoms.arrow_forward
- Draw Lewis structures for these ions and show which atom (or atoms) in each bears the formal charge. Q.) OH-arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure with lowest formal charges, anddetermine the charge of each atom in (a) BF₄⁻; (b) ClNO.arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the nitrate ion, NO3-, with formal charges on each atom and resonance structures.arrow_forward
- Write a Lewis structure for HC2─ and assign any formal charges to the correct atom.arrow_forwardDraw a Lewis structure for H3C—NH2. Based on this Lewis structure, what is the value for the formal charge on the nitrogen atom?arrow_forwardThe formal charge on the nitrogen atom in the resonance structure of nitrate (NO3-) isarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





