
Concept explainers
Solve Prob. 8.93 assuming that the normal force per unit area between the disk and the floor varies linearly from a maximum at the center to zero at the circumference of the disk.
8.93 A 50-lb electric floor polisher is operated on a surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Assuming that the normal force per unit area between the disk and the floor is uniformly distributed, determine the magnitude Q of the horizontal forces required to prevent motion of the machine.
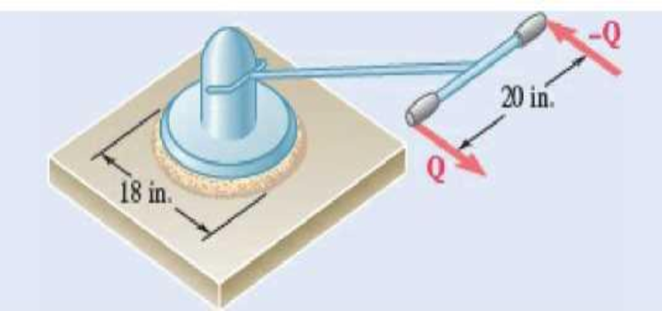
Fig. P8.93
Find the magnitude Q of the horizontal force required to prevent motion of the machine.
Answer to Problem 8.97P
The magnitude Q of the horizontal force is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diameter of the electric floor polisher is
The weight of the electric floor polisher is
The coefficient of kinetic friction is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the thrust bearing as in Figure 1.
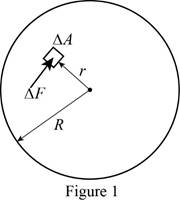
It has been assumed that the normal force per unit area is inversely proportional to r.
Here, the distance between the point to the axis of the shaft is r, the change is angle is
Find the normal force exerted
Substitute
Find the value of k using the relation.
Substitute
Substitute
Find the change in friction force
Substitute
Find the change in moment
Substitute
Integrate the equation to find the couple M.
Substitute
Substitute 0.25 for
Refer to the given figure;
Resolve the moment component in y-axis as follows;
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude Q of the horizontal force is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- : +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardFor the beam show below, draw A.F.D, S.F.D, B.M.D 6 kN/m 1 M B. 3 M Marrow_forward1. Two long rods of the same diameter-one made of brass (k=85w/m.k) and the other made of copper (k=375 w/m.k) have one of their ends inserted into a furnace (as shown in the following figure). Both rods are exposed to the same environment. At a distance of 105 mm from the furnace, the temperature of the brass rod is 120°C. At what distance from the furnace will the same temperature be reached in the copper rod? Furnace 105 mm T₁ Brass rod ⑪ h Too- x2- Ti Copper rodarrow_forward
- : +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardمشر on ۲/۱ Two rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass(k=85 m K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. 22.05 ofthearrow_forwardThe composite wall of oven with A= 1m² as in Fig.1 consists of three materials, two of with kA = 20 W/m K and kc = 50 W/m K with thickness, LA=0.3 m, L= 0.15 m and Lc 0.15 m. The inner surface temperature T1=900 K and the outer surface temperature T4 300 K, and an oven air temperature of To=1100 K, h=25 W/m². K. Determine kɛ and the temperatures T2 and T3 also draw the thermal resistance networkarrow_forward
- Two rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass (k = 85 Wm K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. Ans 22.05arrow_forwardA long wire (k-8 W/m °C.) with ro 5 mm and surface temperature Ts=180°C as shown in Fig.2. Heat is generated in the wire uniformly at a rate of 5 x107 W/m³. If the energy equation is given by: d 11(77) + - =0 k r dr dr Derive an expression for T(r) and determine the temperature at the center of the wire and at r=2 mm. Air Th T KA LA T2 T3 T Fig.1 KB kc 180°C Го Fig.2arrow_forwardB: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) T₂ 0 T3 0 I need a real solution, not artificial intelligence locarrow_forward
- Can I solve this problem by calculating the initial kinetic energy with respect to G instead of A.arrow_forwardB: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) T₂ 0 T3 0 locarrow_forwardShow all work. Indicate the origin that is used for each plane. Identify the Miller indices for the following planes. N 23 1 A) X B) yarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





