
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation: Determine the order policy for the item based on silver-meal method.
Concept Introduction: Silver-Meal method is mainly used to determine the production quantities of the firm to be produced at the minimum cost.it is also provides the appropriate solutions to the time varying demand in production patterns.
a)
Answer to Problem 14P
The order policy according to silver meal method is 18 units in period-1,23 units in Period-4,50 units in Period-6,35 units in period-9 and 12 units in period-12.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The anticipated demand for an inventory is as follows:
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Demand | 6 | 12 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 25 | 20 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 12 |
Current inventory is 4 and ending inventory is 8.
Holding cost (h) is $1 per period, set up cost (K) is $40
The objective of this method is to minimize the per-period-cost of ordering policy.
Net Requirements:
The order policy (lot-size) of the item under silver meal method can be calculated as follows:
According to silver meal method the average cost per period C (T) is a function of the average holding and set up cost per period for T number of Periods. The production in period 1 is equal to the demand in that period 1 to incur the order cost K.
Hence
And
And general equation is
Once
Now, calculate the order policy using the above formula as follows:
Starting in period 1:
Stop the process since
Starting in period 4:
Stop the process since
Starting in period 6:
Stop the process since
Starting in period 9:
Stop the process since
The same is explained with the help of a table shown below:
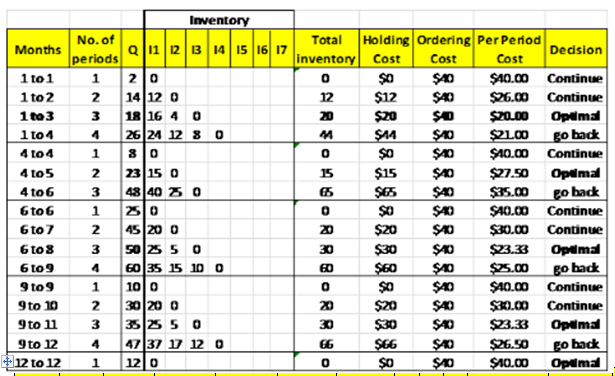
Table 1: Order Quantity using Silver-Meal Method:
| Months | No.of periods | Q | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | Total inventory | Holding Cost | Ordering Cost | Per Period Cost | Decision |
| 1 to 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | =SUM(D3:J3) | =K3*1 | 40 | =SUM((L3:M3)/B3) | Continue | ||||||
| 1 to 2 | 2 | =2+12 | 12 | 0 | =SUM(D4:J4) | =K4*1 | 40 | =SUM((L4:M4)/B4) | Continue | |||||
| 1 to 3 | 3 | =14+4 | =C5-C3 | =C5-C4 | 0 | =SUM(D5:J5) | =K5*1 | 40 | =SUM((L5:M5)/B5) | Optimal | ||||
| 1 to 4 | 4 | =C5+8 | =C6-C3 | =C6-C4 | =C6-C5 | 0 | =SUM(D6:J6) | =K6*1 | 40 | =SUM((L6:M6)/B6) | Go Back | |||
| 4 to 4 | 1 | 8 | 0 | =SUM(D7:J7) | =K7*1 | 40 | =SUM((L7:M7)/B7) | Continue | ||||||
| 4 to 5 | 2 | =C7+15 | =C8-C7 | 0 | =SUM(D8:J8) | =K8*1 | 40 | =SUM((L8:M8)/B8) | Optimal | |||||
| 4 to 6 | 3 | =C8+25 | =C9-C7 | =C9-C8 | 0 | =SUM(D9:J9) | =K9*1 | 40 | =SUM((L9:M9)/B9) | Go Back | ||||
| 6 to 6 | 1 | 25 | 0 | =SUM(D10:J10) | =K10*1 | 40 | =SUM((L10:M10)/B10) | Continue | ||||||
| 6to 7 | 2 | =C10+20 | =C11-C10 | 0 | =SUM(D11:J11) | =K11*1 | 40 | =SUM((L11:M11)/B11) | Continue | |||||
| 6 to 8 | 3 | =C11+5 | =C12-C10 | =C12-C11 | 0 | =SUM(D12:J12) | =K12*1 | 40 | =SUM((L12:M12)/B12) | Optimal | ||||
| 6 to 9 | 4 | =C12+10 | =C13--C10 | =C13-C11 | =C13-C12 | =C13-C13 | =SUM(D13:J13) | =K13*1 | 40 | =SUM((L13:M13)/B13) | Go Back | |||
| 9 to 9 | 1 | 10 | 0 | =SUM(D14:J14) | =K14*1 | 40 | =SUM((L14:M14)/B14) | Continue | ||||||
| 9 to 10 | 2 | =C14+20 | =C15-C14 | 0 | =SUM(D15:J15) | =K15*1 | 40 | =SUM((L15:M15)/B15) | Continue | |||||
| 9 to 11 | 3 | =C15+5 | =C16-C14 | =C16-C15 | 0 | =SUM(D16:J16) | =K16*1 | 40 | =SUM((L16:M16)/B16) | Optimal | ||||
| 9 to 12 | 4 | =C16+12 | =C17--C14 | =C17-C15 | =C17-C16 | =C17-C17 | =SUM(D17:J17) | =K17*1 | 40 | =SUM((L17:M17)/B17) | Go Back | |||
| 12 to 12 | 1 | 12 | 0 | =SUM(D18:J18) | =K18*1 | 40 | =SUM((L18:M18)/B18) | Optimal |
b)
Interpretation: Determine the order policy for the item based on Least Unit Cost method.
Concept Introduction: Least unit cost produced the demand of the present periods based on the trial basis, yield the future periods. The method is calculated by adding the setup cost and carrying inventory cost and finally find the smallest cost per unit.
b)
Answer to Problem 14P
The order policy according to LUC method is 26 units in period-1, 40 units in Period-5, 25 units in Period-7, 35 units in period-9 and 12 units in period-12.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The anticipated demand for a component VC is as follows:
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Demand | 42 | 42 | 32 | 12 | 26 | 112 | 45 | 14 | 76 | 38 |
Holding cost (h) is $0.60 per period, set up cost (K) is $132
The order policy (lot-size) of the item under Least Unit Cost(LUC)method can be calculated as follows:
LUC divides the average cost per period C (T) by the total number of units demanded. Hence
And
And general equation is
Once
Starting from period 1
Stop the process since
Starting in period 5:
Stop the process since
Starting in period 7:
Stop the process since
Starting in period 9:
Stop the process since
The same is explained with the help of a table shown below:
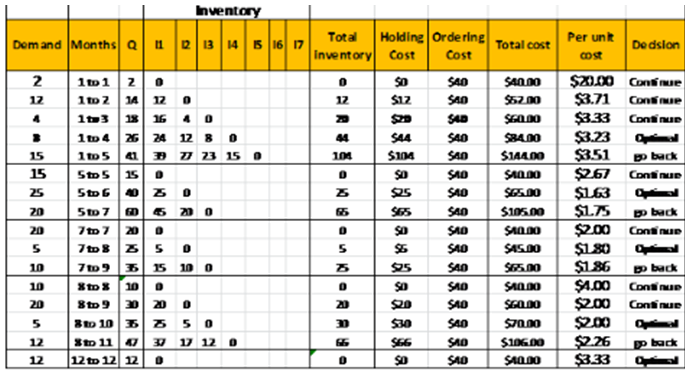
Table 2: Order Quantity using Least-Unit-Cost Method:
| Demand | Months | Q | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | Total inventory | Holding Cost | Ordering Cost | Total Cost | Per Period Cost | Decision |
| 2 | 1 to 1 | =A3 | 0 | =SUM(D3:H3) | =L3*1 | 40 | =K3+J3 | =L3/C3 | Continue | ||||
| 12 | 1 to 2 | =C3+A4 | =C4-C3 | 0 | =SUM(D4:H4) | =L4*1 | 40 | =K4+J4 | =L4/C4 | Continue | |||
| 4 | 1 to 3 | =C4+A5 | =C5-C3 | =C5-C4 | 0 | =SUM(D5:H5) | =L5*1 | 40 | =K5+J5 | =L5/C5 | Continue | ||
| 8 | 1 to 4 | =C5+A6 | =C6-C3 | =C6-C4 | =C6-C5 | =C6-C6 | =SUM(D6:H6) | =L6*1 | 40 | =K6+J6 | =L6/C6 | Optimal | |
| 15 | 1 to 5 | =C6+A7 | =C7-C3 | =C7-C4 | =C7-C5 | =C7-C6 | =C7-C7 | =SUM(D7:H7) | =L7*1 | =K7+J7 | =L7/C7 | Go Back | |
| 15 | 5 to 5 | =A8 | 0 | =SUM(D8:H8) | =L8*1 | 40 | =K8+J8 | =L8/C8 | Continue | ||||
| 25 | 5 to 6 | =C8+A9 | =C9-C8 | 0 | =SUM(D9:H9) | =L9*1 | 40 | =K9+J8 | =L9/C9 | Optimal | |||
| 20 | 5 to 7 | =C9+A11 | =C10-C8 | =C10-C9 | =C10-C10 | =SUM(D10:H10) | =L10*1 | 40 | =K10+J10 | =L10/C10 | Go Back | ||
| 20 | 7 to 7 | =A11 | 0 | =SUM(D11:H11) | =L11*1 | 40 | =K11+J11 | =L11/C11 | Continue | ||||
| 5 | 7 to 8 | =C11+A12 | =C12-C11 | 0 | =SUM(D12:H12) | =L12*1 | 40 | =K12+J12 | =L12/C12 | Optimal | |||
| 10 | 7 to 9 | =C12+A13 | =C13-C11 | =C13-C12 | =C13-C13 | =SUM(D13:H13) | =L13*1 | 40 | =K13+J13 | =L13/C13 | Go Back | ||
| 10 | 8 to 8 | =A14 | 0 | =SUM(D14:H14) | =L14*1 | 40 | =K14+J14 | =L14/C14 | Continue | ||||
| 20 | 8 to 9 | =C14+A15 | =C15-C14 | 0 | =SUM(D15:H15) | =L15*1 | 40 | =K15+J15 | =L15/C15 | Continue | |||
| 5 | 8 to 10 | =C15+A16 | =C16-C14 | =C16-C15 | 0 | =SUM(D16:H16) | =L16*1 | 40 | =K16+J16 | =L16/C16 | Optimal | ||
| 12 | 8 to 11 | =C16+A17 | =C17-C14 | =C17-C15 | -C17-C16 | =C17-C17 | =SUM(D17:H17) | =L17*1 | 40 | =K17+J17 | =L17/C17 | Go Back | |
| 12 | 12 to 12 | 12 | 0 | =SUM(D18:H18) | =L18*1 | 40 | =K18+J18 | ==L18/C18 | Optimal |
c)
Interpretation: Determine the order policy for the item based on Part Period Balancing method.
Concept Introduction: Part Period Balancing method is the lot-size method which use the starting and ending of the process function to consider the multiple periods to modifying the calculation based on the least total cost.
c)
Answer to Problem 14P
The order policy according to part period balancing method is 26 units in period-1, 60 units in Period-5, 35 units in Period-8, 17 units in period-11.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The anticipated demand for a component VC is as follows:
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Demand | 42 | 42 | 32 | 12 | 26 | 112 | 45 | 14 | 76 | 38 |
Holding cost (h) is $0.60 per period, set up cost (K) is $132
The order policy (lot size) according to part period balancing method can be calculated as follows:
In this method the order horizon that equates holding and setup cost over that period has to be calculated as follows:
Starting from Period 1
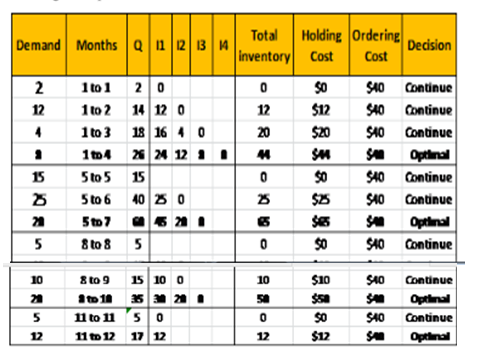
d)
Interpretation: Determine the three lot-sizing method resulted in the lowest cost for the 12 periods.
Concept Introduction: Lot size is determined the quantity order during the production time. The size of the lot may be dynamic or fixed.ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is the inbuilt multiple heuristic methods to determine the size of the lot to the production unit.
d)
Answer to Problem 14P
The Silver-meal method is giving lowest cost.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The anticipated demand for a component VC is as follows:
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Demand | 42 | 42 | 32 | 12 | 26 | 112 | 45 | 14 | 76 | 38 |
Holding cost (h) is $0.60 per period, set up cost (K) is $132
Calculate the total cost of the ordering for the three methods as shown below:
| Silver-meal | Least Unit Cost | Part Period Balancing | |
| Holding Cost | =20+15+30+30 | =44+25+5+30 | =44+65+50+12 |
| Setup Cost | =40*5 | =40*5 | =4*40 |
| Total Cost | =B3+B2 | =C3+C2 | =D3+D2 |
| Silver-meal | Least Unit Cost | Part Period Balancing | |
| Holding Cost | 95 | 104 | 171 |
| Setup Cost | 200 | 200 | 160 |
| Total Cost | 295 | 304 | 331 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS ANALYSIS
- 22. The order cost per order of an inventory is P400 with an annual carrying cost of P10 per unit. What is the Economic order quantity for an annual demand of 2,000 units?arrow_forwardThe materials manager for a billiard ball maker must periodically place orders for resin, one of the raw materials used in producing billiard balls. She knows that manufacturing uses resin at a rate of 50 kilograms each day, and that it costs $.04 per day to carry a kilogram of resin in inventory. She also knows that the order costs for resin are $100 per order, and that the lead time for delivery is four days. If the order size was 1,000 kilograms of resin, what would be the average inventory level?arrow_forward3) The TCC Art Gallery prints a brochure for visitors to the senior art showcase it sponsors at thecollege. There are about 16000 visitors per year to this event (held year round). Holding costs for thebrochures are 25% and it costs $40 to place an order with the printer. The printer has offered thefollowing discount schedule:Category Order Size Unit Cost1 0 - 1499 $2.602 1500 - 2999 $2.303 3000 and over $1.90Answer the following questions in a text box in the worksheet.A) How many orders should be made?B) How many brochures should be printed at a time?C) Please copy these two numbers and include them on the executive summary (the first worksheet).arrow_forward
- Using the same information, how do I: Determine the total inventory-related costs associated with the optimal ordering policy (do not include the cost of the coal). and If 5 days of lead time are required to receive an order of coal, how much coal should be on hand when an order is placed?arrow_forwardReorder PointConsider an economic order quantity case where annual demand D = 1,000 units, economic order quantity Q = 200 units, the desired probability of not stocking out P = .95, the standard deviation of demand during lead time σL = 25 units, and lead time L = 15 days. Determine the reorder point. Assume that demand is over a 250-workday year.arrow_forwardWhat changes can you envisage in economic order quantity based planning when the demand for the item increases by 5%? A) The economic order quantity will come down by √(5%) B) The carrying cost will increase by 1/ √(5%) C) The total cost of the plan will go up by √(5%) D) The total cost of the plan will go up by 5%arrow_forward
- Problem 1: Jill's Job Shop buys the following Part (X-123) for use in its production system. The parts are needed throughout the entire 52-week year. Data for the part are as follows: ITEM X-123 Annual demand 10,000 Holding cost per unit per year $4 Order cost $35 Lead time 2 weeks Safety stock 150 units Item cost $10.00 Use the Fixed-Order Quantity Model to find the following: a) Compute the optimum order quantity (Q). b) What is the reorder point (R) for the item? c) Find the Total Annual Cost (TC) for the item.arrow_forward1. Calculate Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), number of orders, annual ordering costs, annual carrying costs and total inventory costs from the following: Annual consumption: 6000 units ; Cost of placing one Order: RO 60 Carrying cost per unit: RO 22. Find out the EOQ, Annual ordering cost and annual holding cost from the following information. The demand is 19500 units per year, holding cost is RO 4 per unit for a year and ordering cost is RO 25 order. 3. Find out the ordering cost from the following information, Annual demand is 240 units, holding cost RO 4 per unit for a year and EOQ is 60 units.arrow_forwardCurrent decision to buy: Ross White's machine shop uses 200 brackets each month during the course of a year. This usage is relatively constant throughout the year. Currently, these brackets are purchased from a supplier 100 miles away for $16 each and the lead time is 2 days. The holding cost per bracket per year is $1.60 (10% of the unit cost) and the annual ordering cost per order is $18.50. There are 240 working days per year. Possible future decision to make in-house: Ross White is reconsidering his decision of buying the brackets and is considering making the brackets in-house. He has determined the set up costs would be $24.50 in machinist time and lost production time. Forty eight brackets could be produced in a day once the machine has been set up. Ross estimates that the cost (including labor and materials) of producing one bracket would be $14.85. The holding cost would be 10% of the cost. a. What is the EOQ given Ross' current decision to buy the brackets? What is the total…arrow_forward
- ARP Engines is a producer of outboard motors and ships worldwide. The company has recently set up a new distribution centre and wants to decide on an inventory policy for one of its products. It has determined the following pertinent information: expected average weekly demand weekly demand standard deviation holding cost production setup cost delivery lead time 400 motors 50 motors $25/motor $5,000/order 3 weeks The company plans to operate 5 days per week, 50 weeks per year. a. Compute the Economic Order Quantity (ignore the variation in demand) given the informa- tion gathered by the company. What is the time between orders and the total cost of operating the EOQ inventory policy? b. The company is considering using the EOQ as the order quantity in a continuous review system. Compute the reorder point and safety stock to meet a service level of 99%. What is the cost of this Q system inventory policy? c. If the company thinks to use the TBO (computed in part a) as the period for a…arrow_forwardUNCERTAIN DEMAND Lead time demand for an item averages 100 units, with a standard deviation of 30. The order quantity is 200 units. Management desires that 99 percent of all demand be met from stock. a) What is the optimal order point? b) Suppose management wanted a 98 percent service level; what would be optimal order point be c)Suppose management wanted 90 service level. Compute the optimal order pointarrow_forwardCurrent decision to buy: Ross White's machine shop uses 300 brackets each month during the course of a year. This usage is relatively constant throughout the year. Currently, these brackets are purchased from a supplier 100 miles away for $25 each and the lead time is 2 days. The holding cost per bracket per year is $3.75 (15% of the unit cost) and the annual ordering cost per order is $18.50. There are 240 working days per year. Possible future decision to make in-house: Ross White is reconsidering his decision of buying the brackets and is considering making the brackets in-house. He has determined the set up costs would be $22.50 in machinist time and lost production time. Forty eight brackets could be produced in a day once the machine has been set up. Ross estimates that the cost (including labor and materials) of producing one bracket would be $22.85. The holding cost would be 12% of the cost. What is the EOQ given Ross' current decision to buy the brackets? What is the…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





