
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780321909107
Author: Paul G. Hewitt
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 89RCQ
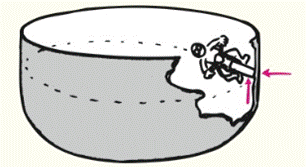
A motorcyclist is able to ride on the vertical wall of a bowl-shaped track as shown. Friction of the wall on the tires is shown by the vertical red vector,
(a) How does the magnitude of this vertical vector compare with the weight of the motorcycle and rider?
(b) Does the horizontal red vector represent the normal force acting on the bike and rider, the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A 1,200-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 260 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below.
F
F
20.0°
a
b
20.0°
i
(a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.)
(b) If the 260-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of
friction is the same as that found in part (a).
m/s²
A block of mass m1 on a rough, horizontal surface is connected to a second mass m; by a light cord over a light frictionless pulley as shown in the figure. ('Light' means that we can neglect the mass of the cord and the mass of the pulley.) A force of magnitude Fis applied to the mass m4 as shown, such that m1 moves to the right. The coefficient of kinetic friction between m1 and the surface is p. Derive a formula for the acceleration of the masses. [Serway 5th ed., pg.135, Fig 5.14]
A 1.33 kg crate is moved rightward across a horizontal surface by a horizontal force such that it has constant velocity. If the coefficient of the kinetic force is 1.33, calculate the magnitude of the kinetic friction force. Round off your final answer to two decimal places.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Ch. 8 - What are the units of measurement for tangential...Ch. 8 - On a rotating turntable, does tangential speed or...Ch. 8 - A tapered cup rolled on a flat surface makes a...Ch. 8 - How does the tapered rim of a wheel on a railroad...Ch. 8 - 5. What is rotational inertia, and how is it...Ch. 8 - 6. Inertia depends on mass; rotational inertia...Ch. 8 - 7. As distance increases between most of the mass...Ch. 8 - 8. Consider three axes of rotation for a pencil:...Ch. 8 - 9. Which is easier to get swinging: a baseball bat...Ch. 8 - Why does bending your legs when running enable you...
Ch. 8 - 11. Which will have the greater acceleration...Ch. 8 - 12. What does a torque tend to do to an object?
Ch. 8 - 13. What is meant by the “lever arm” of a...Ch. 8 - 14. How do clockwise and counterclockwise torques...Ch. 8 - 15. If you toss a stick into the air, it appears...Ch. 8 - Prob. 16RCQCh. 8 - 17. If you hang at rest by your hands from a...Ch. 8 - Where is the center of mass of a hollow soccer...Ch. 8 - 19. What is the relationship between the center of...Ch. 8 - 20. Why doesn’t the Leaning Tower of Pisa topple...Ch. 8 - 21. In terms of center of gravity, support base,...Ch. 8 - 22.When you whirl a can at the end of a string in...Ch. 8 - 23. Is it an inward force or an outward force that...Ch. 8 - 24. If the string that holds a whirling can in its...Ch. 8 - 25. If you are not wearing a seat belt in a car...Ch. 8 - 26. Why is centrifugal force in a rotating frame...Ch. 8 - 27. How can gravity be simulated in an orbiting...Ch. 8 - 28. Distinguish between linear momentum and...Ch. 8 - 29. What is the law of inertia for rotating...Ch. 8 - If a skater who is spinning pulls her arms in so...Ch. 8 - Contact Grandpa and tell him how you’re learning...Ch. 8 - Prob. 32RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 33RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 34RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 35RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 36RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 37RCQCh. 8 - Torque = lever arm ×...Ch. 8 - 39. Calculate the torque produced by the same 50-N...Ch. 8 - Prob. 40RCQCh. 8 - 41. Calculate the force of friction that keeps an...Ch. 8 - Angular momentum =...Ch. 8 - 43. If a persons speed doubles and all else...Ch. 8 - 44. The diameter of the base of a tapered...Ch. 8 - To tighten a bolt, you push with a force of 80 N...Ch. 8 - 46. The rock and meterstick balance at the 25-cm...Ch. 8 - In one of the photos at the beginning of this...Ch. 8 - 48. An ice puck of mass m revolves on an icy...Ch. 8 - 49. If a trapeze artist rotates once each second...Ch. 8 - A small space telescope at the end of a tether...Ch. 8 - 51. The three cups are rolled on a level surface....Ch. 8 - 52. Three types of rollers are placed on slightly...Ch. 8 - 53. Beginning from a rest position, a solid disk...Ch. 8 - 54. You hold a meterstick at one end with the same...Ch. 8 - 55. Three physics majors in good physical shape...Ch. 8 - Prob. 56RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 57RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 58RCQCh. 8 - 59. The wheels of railroad trains are tapered, a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60RCQCh. 8 - 61. The front wheels of a racing vehicle are...Ch. 8 - 62. Which will have the greater acceleration...Ch. 8 - Prob. 63RCQCh. 8 - 64. Is the net torque changed when a partner on a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 65RCQCh. 8 - 66. When you pedal a bicycle, maximum torque is...Ch. 8 - Prob. 67RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 68RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 69RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 70RCQCh. 8 - 71. Explain why a long pole is more beneficial to...Ch. 8 - Prob. 72RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 73RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 74RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 75RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 76RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 77RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 78RCQCh. 8 - 79. The centers of gravity of the three trucks...Ch. 8 - Prob. 80RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 81RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 82RCQCh. 8 - 83. When you are in the front passenger seat of a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 84RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 85RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 86RCQCh. 8 - 87. The occupant inside a rotating space habitat...Ch. 8 - Prob. 88RCQCh. 8 - A motorcyclist is able to ride on the vertical...Ch. 8 - 90. The sketch shows a conical pendulum. The bob...Ch. 8 - Prob. 91RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 92RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 93RCQCh. 8 - 94. If all of Earth’s inhabitants moved to the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 95RCQCh. 8 - If the world’s populations moved to the North Pole...Ch. 8 - Prob. 97RCQCh. 8 - 98. Why does a typical small helicopter with a...Ch. 8 - 99. We believe that our galaxy was formed from a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 100RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 101RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 102RCQCh. 8 - Prob. 103RCQCh. 8 - 104.When a car drives off a cliff it rotates...Ch. 8 - 105. Discuss why a car noses up when accelerating...Ch. 8 - 106. Discuss how a ramp would help you to...Ch. 8 - 107. Which will roll down an incline faster: a can...Ch. 8 - 108. Why are lightweight tires preferred in...Ch. 8 - 109. A youngster who has entered a soapbox derby...Ch. 8 - 110. The spool is pulled in three ways, as shown....Ch. 8 - 111. Nobody at the playground wants to play with...Ch. 8 - 112. How can the three bricks be stacked so that...Ch. 8 - 113. A long track balanced like a seesaw supports...Ch. 8 - With respect to Diana’s finger, where is the...Ch. 8 - When a long-range cannonball is fired toward the...Ch. 8 - Most often we say that force causes acceleration....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 1,380-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 240 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. F 20.0° F 20.0° a. (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) (b) If the 240-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a).arrow_forwardA 1,400-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 200 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. F F 20.0° a b 20.0° (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) 0.127 (b) If the 200-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a). Read It X Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four-digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error. m/s² Need Help?arrow_forwardA 1,420-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 350 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. F F 20.0° b (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) 20.0⁰ (b) If the 350-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a). m/s² Need Help? Read Itarrow_forward
- At a construction site, a pallet of bricks is to be suspended by attaching a rope to it and connecting the other end to a couple of heavy crates on the roof of a building, as shown in (Figure 1). The rope pulls horizontally on the lower crate, and the coefficient of static friction between the lower crate and the roof is 0.509. What is the weight of the heaviest pallet of bricks that can be supported this way? (Hint: Start by drawing appropriate free-body diagrams.) (Express your answer in pounds.) What is the friction force on the upper crate under the conditions given in Part 1? (Express your answer in pounds.)arrow_forwardA 1,480-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 320 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. F 20.0° 20.0° (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) (b) If the 320-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what willI be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a). |m/s²arrow_forwardA 1,360-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force Fof 350 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. 20.0° 120.0° (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) (b) If the 350-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a). |m/s?arrow_forward
- At a construction site, a pallet of bricks is to be suspended by attaching a rope to it and connecting the other end to a couple of heavy crates on the roof of a building, as shown in (Figure 1). The rope pulls horizontally on the lower crate, and the coefficient of static friction between the lower crate and the roof is 0.707. What is the weight of the heaviest pallet of bricks that can be supported this way? (Hint: Start by drawing appropriate free-body diagrams.)arrow_forwardI already posted this question and both answers I receieved were wrong so posted again!arrow_forwardA 1,040-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 400 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal. (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) (b) If the 400-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a).arrow_forward
- Karev is lowering two boxes, one on top of the other, down the ramp, as shown in the figure, by pulling on a rope parallel to the surface of the ramp. Both boxes move together at a constant speed of 15 cm/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ramp and the lower box is 0.444, and the coefficient of static friction between the two boxes is 0.800. (a) What force do you need to exert to accomplish this?arrow_forwardKarev is lowering two boxes, one on top of the other, down the ramp, as shown in the figure, by pulling on a rope parallel to the surface of the ramp. Both boxes move together at a constant speed of 15 cm/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ramp and the lower box is 0.444, and the coefficient of static friction between the two boxes is 0.800. (b) What are the magnitude of the friction force on the upper box?arrow_forwardA box of bananas weighing 40.0 NN rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the surface is 0.40 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. If no horizontal force is applied to the box and the box is at rest, how large is the friction force exerted on the box? My question, what is the equation to solve for the force of friction? what affect do the kinetic and static friction have on this?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY