
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular orbital diagram of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration is,
The molecular orbital diagram of
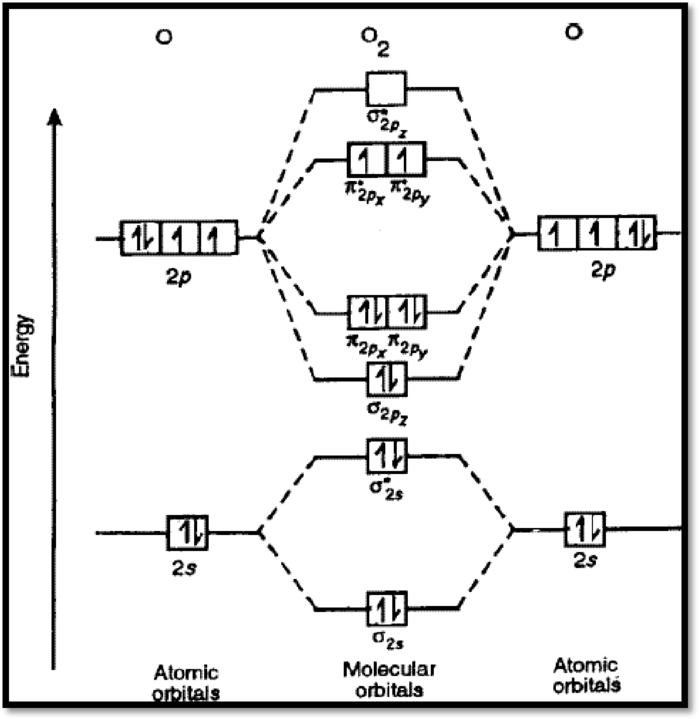
Figure 1
The bond order of
The bond order of
The magnetic nature of
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular property of oxygen that is explained by its molecular orbital diagram but not by Lewis structure has to be given.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The molecular property of oxygen that is explained by its molecular orbital diagram is magnetic property.
The Lewis structure of oxygen is,

From the Lewis structure, it can be seen that all electrons are paired, and it is diamagnetic in nature. However, the molecular orbital diagram of oxygen (figure 1) shows the presence of two unpaired electrons and therefore, oxygen is paramagnetic.
(c)
Interpretation:
The nature of highest occupied molecular orbital in oxygen has to be given.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of oxygen in the ground state is
(d)
Interpretation:
The bond order and magnetic property in peroxide ion and superoxide ion has to be given.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The formula of peroxide ion is
The formula of superoxide ion is
Superoxide ion
The molecular orbital diagram of
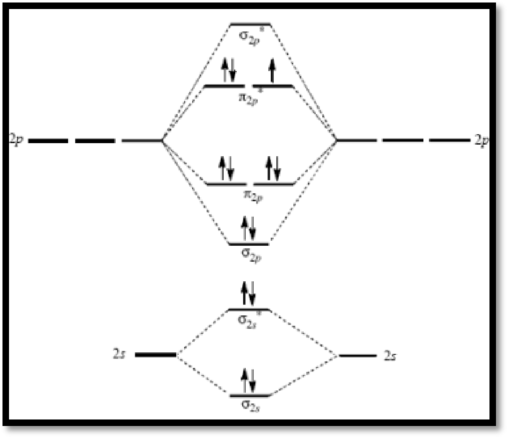
Figure 2
The bond order of
Superoxide ion
Peroxide ion
The molecular orbital diagram of
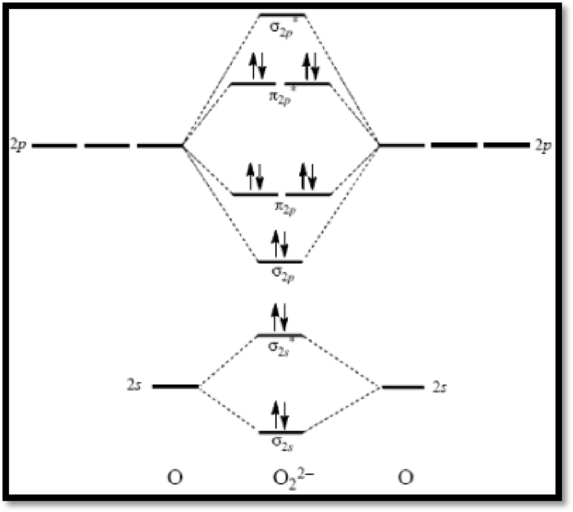
Figure 3
The bond order of
Peroxide ion
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 2TERM
- (a) Which poisonous gas is evolved when white phosphorus is heated with Cone. NaOH solution? Write the chemical equation. (b) Write the formula of first noble gas compound prepared by N. Bartlett. What inspired N. Bartlett to prepare this compound? (c) Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine. Why? (d)Write one use of chlorine gas.arrow_forwardChlorine dioxide gas (ClO2) is used as a commercial bleachingagent. It bleaches materials by oxidizing them. In thecourse of these reactions, the ClO2 is itself reduced. (a)What is the Lewis structure for ClO2? (b) Why do you thinkthat ClO2 is reduced so readily? (c) When a ClO2 moleculegains an electron, the chlorite ion, ClO2-, forms. Draw theLewis structure for ClO2-. (d) Predict the O—Cl—O bondangle in the ClO2- ion. (e) One method of preparing ClO2is by the reaction of chlorine and sodium chlorite:Cl2(g) + 2 NaClO2(s)------>2 ClO2(g) + 2 NaCl(s)If you allow 15.0 g of NaClO2 to react with 2.00 L of chlorinegas at a pressure of 1.50 atm at 21 °C, how many gramsof ClO2 can be prepared?arrow_forward(i) How is HNO3 prepared commercially?(ii) Write chemical equations of the reactions involved.(iii) What concentration by mass of HNO3 is obtained?arrow_forward
- A molecular property of the Group 6A(16) hydrides changes abruptly down the group. This change has been ex-plained in terms of a change in orbital hybridization.(a) Between what periods does the change occur?(b) What is the change in the molecular property?(c) What is the change in hybridization?(d) What other group displays a similar change?arrow_forwardWrite the Lewis structure for each of the following. You may wish to review the chapter on chemical bonding and molecular geometry.(a) PH3(b) PH4+(c) P2H4(d) PO43−(e) PF5arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following acid-base equations:(a) A solution of HClO4 is added to a solution of LiOH.(b) Aqueous H2SO4 reacts with NaOH.(c) Ba(OH)2 reacts with HF gas.arrow_forward
- Describe the hybridization of silicon and the molecular structure of the following molecules and ions:(a) (CH3)3SiH(b) SiO44−(c) Si2H6(d) Si(OH)4(e) SiF62−arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true?(a) Both nitrogen and phosphorus can form a pentafluoridecompound.(b) Although CO is a well-known compound, SiO does notexist under ordinary conditions.(c) Cl2 is easier to oxidize than I2.(d) At room temperature, the stable form of oxygen is O2,whereas that of sulfur is S8.arrow_forwardTake about 5 ml of dil. HCl in a test tube and add a few pieces of fine granules to it.Which gas is evolved?(a) Chlorine(b) Hydrogen(c) HCl(d) Nitrogenarrow_forward
- Borane (BH3) is unstable under normal conditions, but it has been detected at lowpressure.(a) Draw the Lewis structure for borane.(b) Draw a diagram of the bonding in BH3, and label the hybridization of each orbital.(c) Predict the H¬B¬H bond anglearrow_forward(c) Suggest how the following boron species could be prepared, showing any intermediates. -B(OH)2 B(OH)2arrow_forwardAccount for the following: (i) NH3 is a stronger base than PH3. (ii) Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen. (iii) Bond dissociation energy of F2 is less than that of Cl?arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

