
Concept explainers
Label the
a.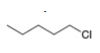 b.
b.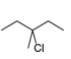 c.
c.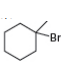
(a)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction: Carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached is known as
Answer to Problem 8.1P
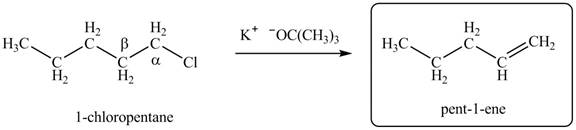
Explanation of Solution
There are different types of carbon atoms present in an alkyl halide depending on their relative position to the halogen atom.
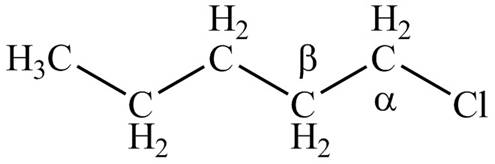
Figure 1
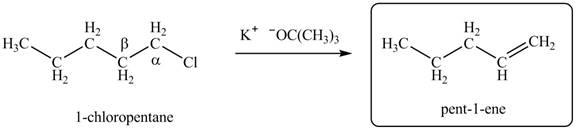
Figure 2
(b)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction: Carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached is known as
Answer to Problem 8.1P
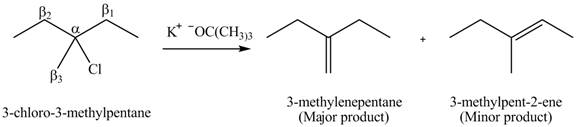
Explanation of Solution
There are different types of carbon atoms present in an alkyl halide depending on their relative position to the halogen atom.
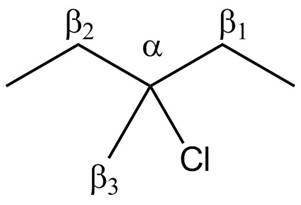
Figure 3
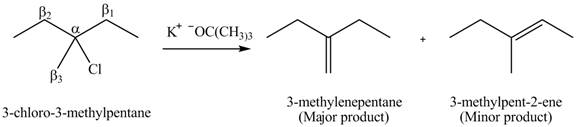
Figure 4
(c)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction: Carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached is known as
Answer to Problem 8.1P
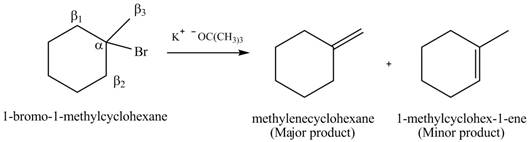
Explanation of Solution
There are different types of carbon atoms present in an alkyl halide depending on their relative position to the halogen atom.
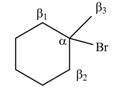
Figure 5
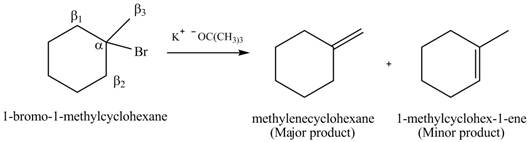
Figure 6
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- Unshared, or lone, electron pairs play an important role in determining the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Thus, it is important to know which atoms carry unshared pairs. Use the structural formulas below to determine the number of unshared pairs at each designated atom. Be sure your answers are consistent with the formal charges on the formulas. CH. H₂ fo H2 H The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is The number of unshared pairs at atom c is HC HC HC CH The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is The number of unshared pairs at atom c isarrow_forwardDraw curved arrows for the following reaction step. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 H H-O-H +/ H3C-C+ H3C-C-0: CH3 CH3 Harrow_forward1:14 PM Fri 20 Dec 67% Grade 7 CBE 03/12/2024 (OOW_7D 2024-25 Ms Sunita Harikesh) Activity Hi, Nimish. When you submit this form, the owner will see your name and email address. Teams Assignments * Required Camera Calendar Files ... More Skill: Advanced or complex data representation or interpretation. Vidya lit a candle and covered it with a glass. The candle burned for some time and then went off. She wanted to check whether the length of the candle would affect the time for which it burns. She performed the experiment again after changing something. Which of these would be the correct experimental setup for her to use? * (1 Point) She wanted to check whether the length of the candle would affect the time for which it burns. She performed the experiment again after changing something. Which of these would be the correct experimental setup for her to use? A Longer candle; No glass C B Longer candle; Longer glass D D B Longer candle; Same glass Same candle; Longer glassarrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardJON Determine the bund energy for UCI (in kJ/mol Hcl) using me balanced chemical equation and bund energies listed? का (My (9) +36/2(g)-(((3(g) + 3(g) A Hryn = -330. KJ bond energy и-н 432 bond bond C-1413 C=C 839 N-H 391 C=O 1010 S-H 363 б-н 467 02 498 N-N 160 N=N 243 418 C-C 341 C-0 358 C=C C-C 339 N-Br 243 Br-Br C-Br 274 193 614 (-1 214||(=olin (02) 799 C=N 615 AALarrow_forwardDetermine the bond energy for HCI ( in kJ/mol HCI) using he balanced cremiculequecticnand bund energles listed? also c double bond to N is 615, read numbets carefully please!!!! Determine the bund energy for UCI (in kJ/mol cl) using me balanced chemical equation and bund energies listed? 51 (My (9) +312(g)-73(g) + 3(g) =-330. KJ спод bond energy Hryn H-H bond band 432 C-1 413 C=C 839 NH 391 C=O 1010 S-1 343 6-H 02 498 N-N 160 467 N=N C-C 341 CL- 243 418 339 N-Br 243 C-O 358 Br-Br C=C C-Br 274 193 614 (-1 216 (=olin (02) 799 C=N 618arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
