
Concept explainers
Label the
a.![]() b.
b.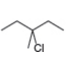 c.
c.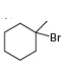
(a)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction: Carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached is known as
Answer to Problem 8.1P
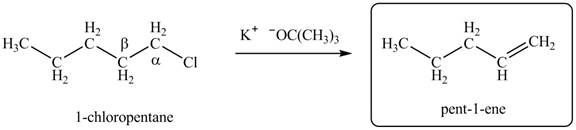
Explanation of Solution
There are different types of carbon atoms present in an alkyl halide depending on their relative position to the halogen atom.
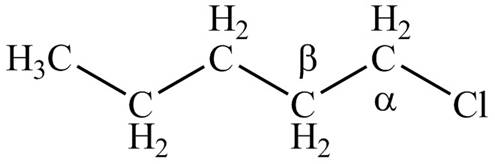
Figure 1
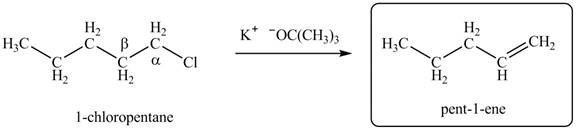
Figure 2
(b)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction: Carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached is known as
Answer to Problem 8.1P
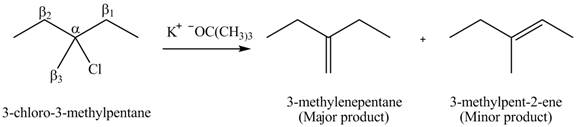
Explanation of Solution
There are different types of carbon atoms present in an alkyl halide depending on their relative position to the halogen atom.
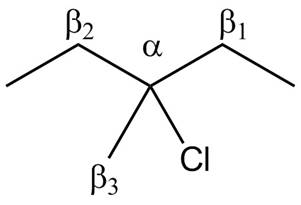
Figure 3
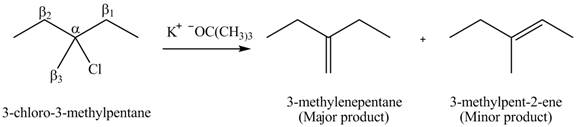
Figure 4
(c)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction: Carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached is known as
Answer to Problem 8.1P
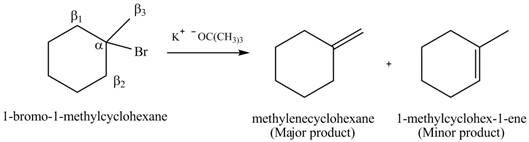
Explanation of Solution
There are different types of carbon atoms present in an alkyl halide depending on their relative position to the halogen atom.
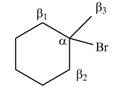
Figure 5
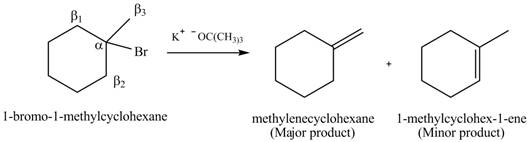
Figure 6
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the products formed when phenol(C6H5OH) is treated with each reagent. Give an explanation. d. (CH3CH2)2CHCOCl, AlCl3 j. product in (d), then NH2NH2, – OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each compound is treated with CH;CH,COCI, AICI3. CH(CH3)2 N(CH)2 Br CH3 CH(CH)2 a. b. C. d. е.arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when pentanal (CH3 CH₂ CH₂ CH₂ CHO) is treated with each reagent. With some reagents, no reaction occurs. a. NaBH4, CH3OH b. [1] LiAiH4: [2] H₂O c. H₂, Pd-C d. PCC e. Na₂Cr₂O7, H₂SO4, H₂O f. Ag₂O, NH4OH g. [1] CH3 MgBr; [2] H₂O h. [1] C6H5 Li: [2] H₂O i. [1] (CH3)2 CuLi; [2] H₂O J. [1] HC=CNa; [2] H₂O k. [1] CH 3 C=CLI; [2] H₂O 1. The product in (a), then TBDMS-CI, imidazolearrow_forward
- Does the equilibrium favor the reactants or products in each substitution reaction? a. CH;CH2-NH2 Br CH;CH2-Br + "NH2 b. "CN CN + I-arrow_forwardMaltose is a carbohydrate present in malt, the liquid obtained from barley and other grains. Although maltose has numerous functional groups, its reactions are explained by the same principles we have already encountered.a. Label the acetal and hemiacetal carbons.b. What products are formed when maltose is treated with each of these reagents: [1] H3O+; [2] CH3OH and HCl; [3] excess NaH, then excess CH3I?c. Draw the products formed when the compound formed in Reaction [3] of part (b) is treated with aqueous acid.The reactions in parts (b) and (c) are used to determine structural features of carbohydrates like maltose.arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when (CH3)2CHOH is treated with each reagent. a.SOCl2, pyridine b. TsCl, pyridine c.H2SO4 d.HBr e.PBr3, then NaCN f.POCl3, pyridinearrow_forward
- Which is a thiol? CH3 HS SH b. HO. CH3 H.CS CHa CH C. H. d. భిగింగడి 工 a.arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when phenol (C6H5OH) is treated with each set of reagents.a. [1] HNO3, H2SO4; [2] Sn, HCIb. [1] (CH3CH2)2CHCOCI, AlCl3; [2] Zn(Hg), HCIc. [1] CH3CH2CI, AlCl3; [2] Br2, hvd. [1] (CH3)2CHCI, AlCl3; [2] KMnO4arrow_forward1. Draw the product formed when phenylacetaldehyde (C6H5CH2CHO) is treated with each reagent:arrow_forward
- Draw the product formed when pentanal (CH;CH,CH2CH;CHO) is treated with each reagent. With some reagents, no reaction occurs. a. NaBH4, CH,OH b. [1] LIAIH4; (2] H20 c. H2, Pd-C d. PCC e. NazCr,07, H2SO4, H2O f. Ag,0, NH,OH g. [1) CH,MgBr; (2] H2O h. [1] CęH,Li; [2] H20 i. [1] (CH3),CuLi; (2] H2O j. [1] HC=CNa; [2] H2O k. [1] CH;C=CLi; [2] H2O I. The product in (a), then TBDMS-CI, imidazolearrow_forwardDraw the products formed when phenol(C6H5OH) is treated with each reagent. Give an explanation. e. Br2, FeBr3 f. Br2arrow_forwardtaken in order to gor the product Please explain the mechanisms/stepsarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
