
Concept explainers
a.
Stored procedures:
- A procedure is a collection of procedural and SQL statements.
- A procedure may have input parameter, output parameter and both parameters.
- It has a declared with a unique named with a unit of procedural code using the proprietary RDBMS and it is invoked by a host language library routine.
Syntax for stored procedure:
CREATE FUNCTION fun_name(argument IN data-type)RETRUN data-type[IS]
BEGIN
PL/SQL statements;
Return (value or expression);
END;
Explanation of Solution
Query to create stored procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DISP_CUST_CRED (I_CUSTOMER_NUM IN CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM%TYPE) AS
I_CUSTOMER_NAME CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NAME%TYPE;
I_CREDIT_LIMIT CUSTOMER.CREDIT_LIMIT%TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT CUSTOMER_NAME, CREDIT_LIMIT
INTO I_CUSTOMER_NAME, I_CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM CUSTOMER
WHERE CUSTOMER_NUM = I_CUSTOMER_NUM;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (I_CUSTOMER_NAME);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (I_CREDIT_LIMIT);
END;
/
Explanation:
- The above query is used to create a procedure named “DISP_CUST_CRED” to select the records in the “CUSTOMER” table.
- Change the “CUSTOMER_NUM” into “I_CUSTOMER_NUM” and place the “CUSTOMER_NAME” and “CREDIT_LIMIT” values into “I_CUSTOMER_NAME” and “I_CREDIT_LIMIT”.
- After placing these values, display the “I_CUSTOMER_NAME” and “I_CREDIT_LIMIT” from the “CUSTOMER” table.
- Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Query to view the customer name and credit limit:
BEGIN
DISP_CUST_CRED (126);
END;
The above query is used to view the customer name and credit limit for the number 126.
Output:
Toys Galore
7500
Explanation of Solution
b.
Query to create stored procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DISP_ORDERS (I_ORDER_NUM ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE) AS
I_ORDER_DATE ORDERS.ORDER_DATE%TYPE;
I_CUSTOMER_NUM CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM%TYPE;
I_CUSTOMER_NAME CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NAME%TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT ORDER_DATE, CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM, CUSTOMER_NAME
INTO I_ORDER_DATE, I_CUSTOMER_NUM, I_CUSTOMER_NAME
FROM ORDERS, CUSTOMER
WHERE ORDERS.CUSTOMER_NUM = CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM
AND ORDER_NUM = I_ORDER_NUM;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(I_ORDER_DATE);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(I_CUSTOMER_NUM);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(I_CUSTOMER_NAME);
END;
/
Explanation:
- The above query is used to create a procedure named “DISP_ORDERS” to select the records in the “CUSTOMER” and “ORDERS” tables.
- Change the “ORDER_NUM” into “I_ORDER_NUM” and place the “ORDER_DATE”, “CUSTOMER_NUM”, and “CUSTOMER_NAME” values into “I_ORDER_DATE”, “I_CUSTOMER_NUM”, and “I_CUSTOMER_NAME”.
- After placing these values, display the “I_ORDER_DATE”, “I_CUSTOMER_NUM”, and “I_CUSTOMER_NAME” from the “CUSTOMER” and “ORDERS” tables.
- Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Query to view the order date, customer name and customer number:
BEGIN
DISP_ORDERS (51608);
END;
The above query is used to view the order date, customer name and customer number for the number 51608.
Output:
10/12/2015
126
Toys Galore
Explanation of Solution
c.
Query to insert the value:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE ADD_ORDER
(I_ORDER_NUM IN ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE,
I_ORDER_DATE IN ORDERS.ORDER_DATE%TYPE,
I_CUSTOMER_NUM IN ORDERS.CUSTOMER_NUM%TYPE) AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO ORDERS (ORDER_NUM, ORDER_DATE, CUSTOMER_NUM)
VALUES
(I_ORDER_NUM, I_ORDER_DATE, I_CUSTOMER_NUM);
END;
/
Explanation:
The above query is used to create a stored procedure named “ADD_ORDER” to insert the new record in the “ORDERS” table. Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Query to execute the stored procedure:
BEGIN
ADD_ORDER (51627,'10/16/2015', 334);
END;
After executing the above query, the new record is inserted into the table “ORDERS”.
Output:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output
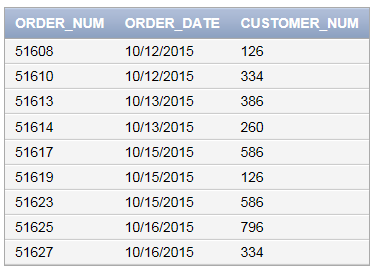
Explanation of Solution
d.
Query to update stored procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE UPDATE_ORDER_DATE
(I_ORDER_NUM IN ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE,
I_ORDER_DATE IN ORDERS.ORDER_DATE%TYPE) AS
BEGIN
UPDATE ORDERS
SET ORDER_DATE = I_ORDER_DATE
WHERE ORDER_NUM = I_ORDER_NUM;
END;
/
Explanation:
The above query is used to create a stored procedure named “UPDATE_ORDER_DATE” to update the date of the order whose number is stored in “I_ORDER_DATE” to the date presently found in “I_ORDER_DATE”, it needs to be executed.
Executing the stored procedure:
The Content of “ORDERS” table before creating the procedure is given below:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT*FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output

Query to execute the stored procedure:
BEGIN
UPDATE_ORDER_DATE (51614, '02/12/2019');
END;
/
After executing the above query, the date is changed in the table “ORDERS”.
Output:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output
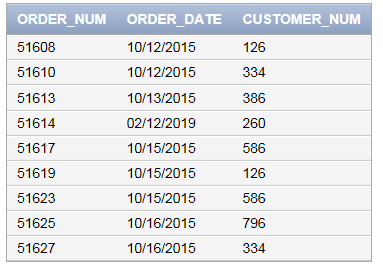
Explanation of Solution
e.
Query to delete the value:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DELETE_ORDERS
(I_ORDER_NUM ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE) AS
BEGIN
DELETE
FROM ORDERS
WHERE ORDER_NUM = I_ORDER_NUM;
END;
/
Explanation:
- The above query is used to create a procedure named “DELETE_ORDERS” to delete a record in the “ORDERS” table.
- Once the record is deleted, a procedure should create order number as a parameter.
- Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Executing the stored procedure:
The Content of “ORDERS” table before creating the procedure is given below:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output

Query to execute the stored procedure:
BEGIN
DELETE_ORDERS (51613);
END;
The above query is used to delete the order number 51613.
Output:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table after deleting the order number 51613 as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output
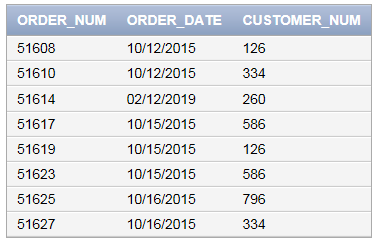
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
A Guide to SQL
 A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
 Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning



