
A model rocket is fired horn the roof of a 50 ft tall building as shown in Fig. P8.1.
The height of the rocket is given by
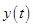
where
(a) Write the
(b) The velocity
(c) The acceleration
(d) The time required to reach the maximum height as well as the corresponding height
(a)
The quadratic equation for the height 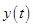 of the rocket.
of the rocket.
Answer to Problem 1P
The quadratic equation for the height 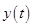 is
is 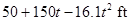
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The height of the rocket is
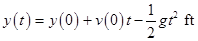 .......(1)
.......(1)
The initial height of the rocket 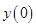 is
is 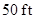
The initial velocity of the rocket 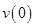 is
is 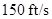
The value of acceleration due to gravity is 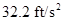
Calculation:
Substitute 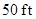 for
for 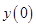
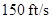 for
for 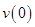 and
and 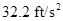 for
for 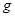 in equation (1).
in equation (1).
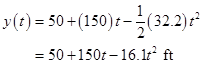
Conclusion:
Thus, the quadratic equation for the height 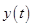 is
is 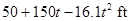
(b)
The velocity 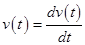
Answer to Problem 1P
The velocity 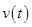 is
is 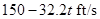
Explanation of Solution
Concept used:
Write the expression for the velocity
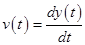 .......(2)
.......(2)
Here, 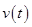 is the velocity and
is the velocity and 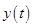 is the height of the rocket at time
is the height of the rocket at time 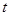
Calculation:
Substitute 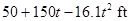 for
for 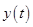 in equation (2).
in equation (2).
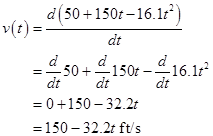
Conclusion:
Thus, the velocity 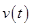 is
is 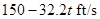
(c)
The acceleration 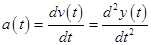
Answer to Problem 1P
The acceleration 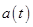 is
is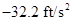
Explanation of Solution
Concept used:
Write the expression for the acceleration.
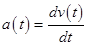 .......(3)
.......(3)
Here, the 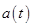 is the acceleration and
is the acceleration and 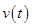 is the velocity of the rocket at time
is the velocity of the rocket at time 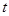
Calculation:
Substitute 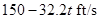 for
for 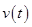 in equation (3).
in equation (3).
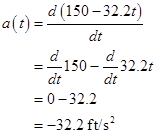
Conclusion:
Thus, the acceleration 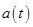 is
is
(d)
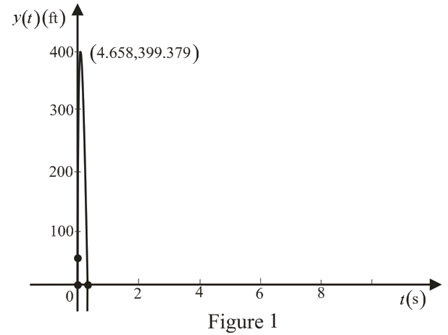
The time required to reach the maximum height, as well as, corresponding maximum height and sketch the result 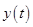 and use the result to sketch
and use the result to sketch 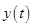
Answer to Problem 1P
The maximum height of the rocket is 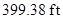 at
at 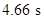 and sketch for the height
and sketch for the height
 is drawn as shown in Figure 1.
is drawn as shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
Concept used:
Write the expression for the maximum height.
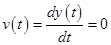 .......(4)
.......(4)
Calculation:
Equate the derivative of 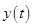 to zero
to zero
Substitute 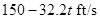 for
for 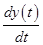 in equation (4).
in equation (4).
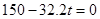
Rearrange for 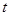
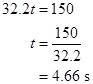
Therefore, the time at maximum height is 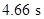
Write the expression for maximum height of the rocket.
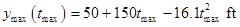 .......(5)
.......(5)
Substitute 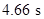 for
for 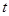 in equation (5).
in equation (5).
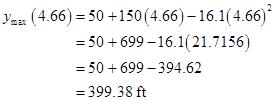
Therefore, the maximum height of the rocket reached is 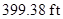
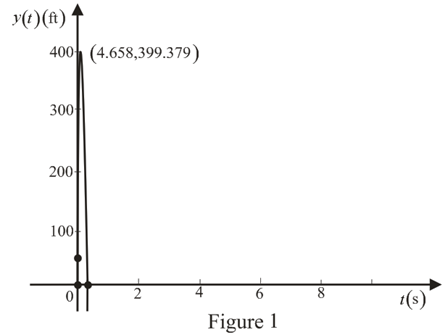
The sketch for the height  is drawn as shown in Figure 1.
is drawn as shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion:
Thus, the maximum height of the rocket is 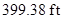 at
at 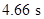 and sketch for the height
and sketch for the height
 is drawn as shown in Figure 1.
is drawn as shown in Figure 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applications
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- 6. [10 marks] Let T be a tree with n ≥ 2 vertices and leaves. Let BL(T) denote the block graph of T. (a) How many vertices does BL(T) have? (b) How many edges does BL(T) have? Prove that your answers are correct.arrow_forward4. [10 marks] Find both a matching of maximum size and a vertex cover of minimum size in the following bipartite graph. Prove that your answer is correct. ย ພarrow_forward5. [10 marks] Let G = (V,E) be a graph, and let X C V be a set of vertices. Prove that if |S||N(S)\X for every SCX, then G contains a matching M that matches every vertex of X (i.e., such that every x X is an end of an edge in M).arrow_forward
- Q/show that 2" +4 has a removable discontinuity at Z=2i Z(≥2-21)arrow_forwardRefer to page 100 for problems on graph theory and linear algebra. Instructions: • Analyze the adjacency matrix of a given graph to find its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. • Interpret the eigenvalues in the context of graph properties like connectivity or clustering. Discuss applications of spectral graph theory in network analysis. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS3IZ9qoHazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forwardRefer to page 110 for problems on optimization. Instructions: Given a loss function, analyze its critical points to identify minima and maxima. • Discuss the role of gradient descent in finding the optimal solution. . Compare convex and non-convex functions and their implications for optimization. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qo Hazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forward
- Refer to page 140 for problems on infinite sets. Instructions: • Compare the cardinalities of given sets and classify them as finite, countable, or uncountable. • Prove or disprove the equivalence of two sets using bijections. • Discuss the implications of Cantor's theorem on real-world computation. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qoHazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forwardRefer to page 120 for problems on numerical computation. Instructions: • Analyze the sources of error in a given numerical method (e.g., round-off, truncation). • Compute the error bounds for approximating the solution of an equation. • Discuss strategies to minimize error in iterative methods like Newton-Raphson. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qo Hazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forwardRefer to page 145 for problems on constrained optimization. Instructions: • Solve an optimization problem with constraints using the method of Lagrange multipliers. • • Interpret the significance of the Lagrange multipliers in the given context. Discuss the applications of this method in machine learning or operations research. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qo Hazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forward
- Give an example of a graph with at least 3 vertices that has exactly 2 automorphisms(one of which is necessarily the identity automorphism). Prove that your example iscorrect.arrow_forward3. [10 marks] Let Go (Vo, Eo) and G₁ = (V1, E1) be two graphs that ⚫ have at least 2 vertices each, ⚫are disjoint (i.e., Von V₁ = 0), ⚫ and are both Eulerian. Consider connecting Go and G₁ by adding a set of new edges F, where each new edge has one end in Vo and the other end in V₁. (a) Is it possible to add a set of edges F of the form (x, y) with x € Vo and y = V₁ so that the resulting graph (VUV₁, Eo UE₁ UF) is Eulerian? (b) If so, what is the size of the smallest possible F? Prove that your answers are correct.arrow_forwardLet T be a tree. Prove that if T has a vertex of degree k, then T has at least k leaves.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw HillAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw HillAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





