
The correctly labeled graph which shows the quantity of antivirus software purchased, the socially optimal quantity of antivirus software,
Explanation of Solution
The graph for the quantity of antivirus software:
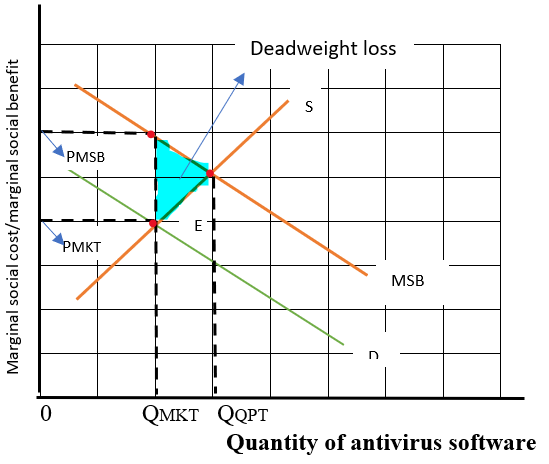
The vertical axis of the graph represents the marginal social benefit and price of antivirus software and the horizontal axis shows the quantity of antivirus software. The supply curve which is equal to the marginal cost curve indicates an upward slope because when there is no external cost, then the marginal private cost is equal to the marginal
And, the socially optimal quantity of antivirus software in the market is at the point of QQPT where the supply curve and marginal social benefit curve intersect and this quantity is shown on the horizontal axis.
In this case, two different government policies that could bring about an optimal quantity of antivirus software would consider:
Pigouvian subsidy: At the socially optimal quantity of antivirus software, the Pigouvian subsidy would be equal to the marginal external benefit at the optimal quantity.
Policy of optimal quantity: The government regulation would require the optimal quantity of antivirus software where marginal social benefits and costs are equal.
Introduction: Externality problems such as pollution refer to the fundamental economic policy problems while firms do not internalize the indirect costs or indirect benefits from any of their economic transactions in the market. The quantity where all the costs and benefits are accounted for is called socially optimal quantity. When demand and supply go out of equilibrium due to market inefficiencies, then it is a situation of deadweight loss.
Chapter 75 Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course
- General Accounting Question solution and give me Blank ? Carrow_forwardIt is possible to use transformational leadership strategies to reach unethical objectives. Traditional leadership theories and morals standards are not adequate to help employees solve complex organizational issues. For the statement above, argue in position for both in favor or opposed to the statements.arrow_forwardDiscuss the preferred deterrent method employed by the Zambian government to combat tax evasion, monetary fines. As noted in the reading the potential penalty for corporate tax evasion is a fine of 52.5% of the amount evaded plus interest assessed at 5% annually along with a possibility of jail time. In general, monetary fines as a deterrent are preferred to blacklisting of company directors, revoking business operation licenses, or calling for prison sentences. Do you agree with this preference? Should companies that are guilty of tax evasion face something more severe than a monetary fine? Something less severe? Should the fine and interest amount be set at a different rate? If so at why? Provide support and rationale for your responses.arrow_forward
- answerarrow_forwardDiscuss the preferred deterrent method employed by the Zambian government to combat tax evasion, monetary fines. As noted in the reading the potential penalty for corporate tax evasion is a fine of 52.5% of the amount evaded plus interest assessed at 5% annually along with a possibility of jail time. In general, monetary fines as a deterrent are preferred to blacklisting of company directors, revoking business operation licenses, or calling for prison sentences. Do you agree with this preference? Should companies that are guilty of tax evasion face something more severe than a monetary fine? Something less severe? Should the fine and interest amount be set at a different rate? If so at why? Provide support and rationale for your responses.arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- For the statement below, argue in position for both in favor or opposed to the statement. Incompetent leaders can't be ethical leaders. Traditional leadership theories and moral standards are not adequate to help employees solve complex organizational issues.arrow_forwardpresentation on "Dandelion Insomnia." Poemarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- "Whether the regulator sells or gives away tradeable emission permits free of charge, the quantities of emissions produced by firms are the same." Assume that there are n identical profit-maximising firms where profit for each firm is given by π(e) with л'(e) > 0; π"(e) < 0 and e denotes emissions. Individual emissions summed over all firms gives E which generates environmental damages D(E). Show that the regulator achieves the optimal level of total pollution through a tradeable emission permit scheme, where the permits are distributed according to the following cases: Case (i) the firm purchases all permits; Case (ii) the firm receives all permits free; and Page 3 of 5 ES30031 Case (iii) the firm purchases a portion of its permits and receives the remainder free of charge.arrow_forwardcompare and/or contrast the two plays we've been reading, Antigone and A Doll's House.arrow_forwardPlease answer step by steparrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





