Given Information:
Finding the roots of the equation given in Problem 7.5.
Calculation:
Code for Problem 7.5(a):
OptionExplicit
SubPolynomialRoot()
Dim num AsInteger
DimmaxItrAsInteger,ierAsInteger,iAsInteger
Dimarr(10)AsDouble, real(10)AsDouble
Dimimaginary(10)AsDouble' Variable to provide negative or positive sign
Dim r AsDouble, s AsDouble, es AsDouble
'In example, the function is having 3 as highest power, so num is initialized to 3.
num =3
'Values of coefficients of the variables in function is given
arr(0) = -2: arr(1) = 6.2: arr(2) = -4: arr(3) = 0.7
'Maximum number of iterations are defined.
maxItr=20
es =0.0001
r =-1
s =-1
CallBairstow_method(arr(), num, es, r, s,maxItr, real(), imaginary(),ier)
'Loop will run to all the powers of function to assign sign between real and imaginary numbers.
Fori=1To num
' If the value at iteration is greater than or equal to 0, assign '+' sign.
If imaginary(i)>=0Then
MsgBox real(i)&" + "& imaginary(i)&"i"
' If the value at iteration is lesser than 0, assign '-' sign.
Else
MsgBox real(i)&" - "& Abs(imaginary(i))&"i"
EndIf
Nexti
EndSub
'method with arguments to apply bairstow method in function.
SubBairstow_method(arr,nn, es,rr, ss,maxItr, real, imaginary,ier)
DimiterAsInteger, num AsInteger,iAsInteger
Dim r AsDouble, s AsDouble, ea1 AsDouble, ea2 AsDouble
Dim determine AsDouble,drAsDouble, ds AsDouble
Dim r_1 AsDouble, i1 AsDouble, r_2 AsDouble, i2 AsDouble
Dimbrr(10)AsDouble,crr(10)AsDouble
' Assigning values.
r =rr
s = ss
num =nn
ier=0
ea1 =1
ea2 =1
Do
'Loop will get terminated if power is less than 3 or if iteration is equal to or greater than maximum iteration.
If num <3Oriter>=maxItrThenExitDo
iter=0
Do
'Incrementing iter variable by 1.
iter=iter+1
'assigning values of array into another array.
brr(num)=arr(num)
'Disc brr(num-1) is calculated.
brr(num -1)=arr(num -1)+ r *brr(num)
crr(num)=brr(num)
'Disc crr(num-1) is calculated.
crr(num -1)=brr(num -1)+ r *crr(num)
'Loop will run for powers less than 3 till power 0.
Fori= num -2To0Step-1
'Values of brr(i) and crr(i) are updated.
brr(i)=arr(i)+ r *brr(i+1)+ s *brr(i+2)
crr(i)=brr(i)+ r *crr(i+1)+ s *crr(i+2)
Nexti
determine =crr(2)*crr(2)-crr(3)*crr(1)
If determine <>0Then
dr=(-brr(1)*crr(2)+brr(0)*crr(3))/ determine
ds =(-brr(0)*crr(2)+brr(1)*crr(1))/ determine
r = r +dr
s = s + ds
'Values of ea1 and ea2 are determined for different values in loop .
If r <>0Then ea1 =Abs(dr/ r)*100
If s <>0Then ea2 =Abs(ds / s)*100
Else
' Incrementing r and s by 1.
r = r +1
s = s +1
iter=0
EndIf
' If the values of ea1 and ea2 are less than value of es or iterations are completed then loop will be terminated
If ea1 <= es And ea2 <= es Oriter>=maxItrThenExitDo
Loop
'method call to find quadratic roots.
CallQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
'Formulae to calculate real and imaginary values at the every term of function.
real(num)= r_1
imaginary(num)= i1
real(num -1)= r_2
imaginary(num -1)= i2
num = num -2
'Updating the coeffinents of function at every iteration.
Fori=0To num
arr(i)=brr(i+2)
Nexti
Loop
Ifiter<maxItrThen
If num =2Then
r =-arr(1)/arr(2)
s =-arr(0)/arr(2)
CallQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
'Use the values of i1, i2, r_1 and r_2 to determine real(num), imaginary(num), real(num-1) and imaginary(num-1).
real(num)= r_1
imaginary(num)= i1
real(num -1)= r_2
imaginary(num -1)= i2
Else
real(num)=-arr(0)/arr(1)
imaginary(num)=0
EndIf
Else
ier=1
EndIf
EndSub
SubQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
Dim Disc
'Value of Disc is calculated.
Disc = r ^2+4* s
'Condition for Disc>0.
If Disc >0Then
r_1 =(r +Sqr(Disc))/2
r_2 =(r -Sqr(Disc))/2
i1 =0
i2 =0
'Condition if Disc less than or equal to 0.
Else
r_1 = r /2
r_2 = r_1
i1 =Sqr(Abs(Disc))/2
i2 =-i1
EndIf
EndSub
Code for Problem 7.5(b):
OptionExplicit
SubPolynomialRoot()
Dim num AsInteger
DimmaxItrAsInteger,ierAsInteger,iAsInteger
Dimarr(10)AsDouble, real(10)AsDouble
Dimimaginary(10)AsDouble' Variable to provide negative or positive sign
Dim r AsDouble, s AsDouble, es AsDouble
'In example, the function is having 3 as highest power, so num is initialized to 3.
num =3
'Values of coefficients of the variables in function is given
arr(0) = 9.34: arr(1) = -21.97: arr(2) = 16.3: arr(3) = 3.704
'Maximum number of iterations are defined.
maxItr=20
es =0.0001
r =-1
s =-1
CallBairstow_method(arr(), num, es, r, s,maxItr, real(), imaginary(),ier)
'Loop will run to all the powers of function to assign sign between real and imaginary numbers.
Fori=1To num
' If the value at iteration is greater than or equal to 0, assign '+' sign.
If imaginary(i)>=0Then
MsgBox real(i)&" + "& imaginary(i)&"i"
' If the value at iteration is lesser than 0, assign '-' sign.
Else
MsgBox real(i)&" - "& Abs(imaginary(i))&"i"
EndIf
Nexti
EndSub
'method with arguments to apply bairstow method in function.
SubBairstow_method(arr,nn, es,rr, ss,maxItr, real, imaginary,ier)
DimiterAsInteger, num AsInteger,iAsInteger
Dim r AsDouble, s AsDouble, ea1 AsDouble, ea2 AsDouble
Dim determine AsDouble,drAsDouble, ds AsDouble
Dim r_1 AsDouble, i1 AsDouble, r_2 AsDouble, i2 AsDouble
Dimbrr(10)AsDouble,crr(10)AsDouble
' Assigning values.
r =rr
s = ss
num =nn
ier=0
ea1 =1
ea2 =1
Do
'Loop will get terminated if power is less than 3 or if iteration is equal to or greater than maximum iteration.
If num <3Oriter>=maxItrThenExitDo
iter=0
Do
'Incrementing iter variable by 1.
iter=iter+1
'assigning values of array into another array.
brr(num)=arr(num)
'Disc brr(num-1) is calculated.
brr(num -1)=arr(num -1)+ r *brr(num)
crr(num)=brr(num)
'Disc crr(num-1) is calculated.
crr(num -1)=brr(num -1)+ r *crr(num)
'Loop will run for powers less than 3 till power 0.
Fori= num -2To0Step-1
'Values of brr(i) and crr(i) are updated.
brr(i)=arr(i)+ r *brr(i+1)+ s *brr(i+2)
crr(i)=brr(i)+ r *crr(i+1)+ s *crr(i+2)
Nexti
determine =crr(2)*crr(2)-crr(3)*crr(1)
If determine <>0Then
dr=(-brr(1)*crr(2)+brr(0)*crr(3))/ determine
ds =(-brr(0)*crr(2)+brr(1)*crr(1))/ determine
r = r +dr
s = s + ds
'Values of ea1 and ea2 are determined for different values in loop .
If r <>0Then ea1 =Abs(dr/ r)*100
If s <>0Then ea2 =Abs(ds / s)*100
Else
' Incrementing r and s by 1.
r = r +1
s = s +1
iter=0
EndIf
' If the values of ea1 and ea2 are less than value of es or iterations are completed then loop will be terminated
If ea1 <= es And ea2 <= es Oriter>=maxItrThenExitDo
Loop
'method call to find quadratic roots.
CallQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
'Formulae to calculate real and imaginary values at the every term of function.
real(num)= r_1
imaginary(num)= i1
real(num -1)= r_2
imaginary(num -1)= i2
num = num -2
'Updating the coeffinents of function at every iteration.
Fori=0To num
arr(i)=brr(i+2)
Nexti
Loop
Ifiter<maxItrThen
If num =2Then
r =-arr(1)/arr(2)
s =-arr(0)/arr(2)
CallQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
'Use the values of i1, i2, r_1 and r_2 to determine real(num), imaginary(num), real(num-1) and imaginary(num-1).
real(num)= r_1
imaginary(num)= i1
real(num -1)= r_2
imaginary(num -1)= i2
Else
real(num)=-arr(0)/arr(1)
imaginary(num)=0
EndIf
Else
ier=1
EndIf
EndSub
SubQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
Dim Disc
'Value of Disc is calculated.
Disc = r ^2+4* s
'Condition for Disc>0.
If Disc >0Then
r_1 =(r +Sqr(Disc))/2
r_2 =(r -Sqr(Disc))/2
i1 =0
i2 =0
'Condition if Disc less than or equal to 0.
Else
r_1 = r /2
r_2 = r_1
i1 =Sqr(Abs(Disc))/2
i2 =-i1
EndIf
EndSub
Code for Problem 7.5(c):
OptionExplicit
SubPolynomialRoot()
Dim num AsInteger
DimmaxItrAsInteger,ierAsInteger,iAsInteger
Dimarr(10)AsDouble, real(10)AsDouble
Dimimaginary(10)AsDouble' Variable to provide negative or positive sign
Dim r AsDouble, s AsDouble, es AsDouble
'In example, the function is having 4 as highest power, so num is initialized to 4.
num =4
'Values of coefficients of the variables in function is given
arr(0) = 5: arr(1) = -2: arr(2) = 6: arr(3) = -2: arr(4) = 1
'Maximum number of iterations are defined.
maxItr=20
es =0.0001
r =-1
s =-1
CallBairstow_method(arr(), num, es, r, s,maxItr, real(), imaginary(),ier)
'Loop will run to all the powers of function to assign sign between real and imaginary numbers.
Fori=1To num
' If the value at iteration is greater than or equal to 0, assign '+' sign.
If imaginary(i)>=0Then
MsgBox real(i)&" + "& imaginary(i)&"i"
' If the value at iteration is lesser than 0, assign '-' sign.
Else
MsgBox real(i)&" - "& Abs(imaginary(i))&"i"
EndIf
Nexti
EndSub
'method with arguments to apply bairstow method in function.
SubBairstow_method(arr,nn, es,rr, ss,maxItr, real, imaginary,ier)
DimiterAsInteger, num AsInteger,iAsInteger
Dim r AsDouble, s AsDouble, ea1 AsDouble, ea2 AsDouble
Dim determine AsDouble,drAsDouble, ds AsDouble
Dim r_1 AsDouble, i1 AsDouble, r_2 AsDouble, i2 AsDouble
Dimbrr(10)AsDouble,crr(10)AsDouble
' Assigning values.
r =rr
s = ss
num =nn
ier=0
ea1 =1
ea2 =1
Do
'Loop will get terminated if power is less than 3 or if iteration is equal to or greater than maximum iteration.
If num <3Oriter>=maxItrThenExitDo
iter=0
Do
'Incrementing iter variable by 1.
iter=iter+1
'assigning values of array into another array.
brr(num)=arr(num)
'Disc brr(num-1) is calculated.
brr(num -1)=arr(num -1)+ r *brr(num)
crr(num)=brr(num)
'Disc crr(num-1) is calculated.
crr(num -1)=brr(num -1)+ r *crr(num)
'Loop will run for powers less than 3 till power 0.
Fori= num -2To0Step-1
'Values of brr(i) and crr(i) are updated.
brr(i)=arr(i)+ r *brr(i+1)+ s *brr(i+2)
crr(i)=brr(i)+ r *crr(i+1)+ s *crr(i+2)
Nexti
determine =crr(2)*crr(2)-crr(3)*crr(1)
If determine <>0Then
dr=(-brr(1)*crr(2)+brr(0)*crr(3))/ determine
ds =(-brr(0)*crr(2)+brr(1)*crr(1))/ determine
r = r +dr
s = s + ds
'Values of ea1 and ea2 are determined for different values in loop .
If r <>0Then ea1 =Abs(dr/ r)*100
If s <>0Then ea2 =Abs(ds / s)*100
Else
' Incrementing r and s by 1.
r = r +1
s = s +1
iter=0
EndIf
' If the values of ea1 and ea2 are less than value of es or iterations are completed then loop will be terminated
If ea1 <= es And ea2 <= es Oriter>=maxItrThenExitDo
Loop
'method call to find quadratic roots.
CallQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
'Formulae to calculate real and imaginary values at the every term of function.
real(num)= r_1
imaginary(num)= i1
real(num -1)= r_2
imaginary(num -1)= i2
num = num -2
'Updating the coeffinents of function at every iteration.
Fori=0To num
arr(i)=brr(i+2)
Nexti
Loop
Ifiter<maxItrThen
If num =2Then
r =-arr(1)/arr(2)
s =-arr(0)/arr(2)
CallQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
'Use the values of i1, i2, r_1 and r_2 to determine real(num), imaginary(num), real(num-1) and imaginary(num-1).
real(num)= r_1
imaginary(num)= i1
real(num -1)= r_2
imaginary(num -1)= i2
Else
real(num)=-arr(0)/arr(1)
imaginary(num)=0
EndIf
Else
ier=1
EndIf
EndSub
SubQuadroot(r, s, r_1, i1, r_2, i2)
Dim Disc
'Value of Disc is calculated.
Disc = r ^2+4* s
'Condition for Disc>0.
If Disc >0Then
r_1 =(r +Sqr(Disc))/2
r_2 =(r -Sqr(Disc))/2
i1 =0
i2 =0
'Condition if Disc less than or equal to 0.
Else
r_1 = r /2
r_2 = r_1
i1 =Sqr(Abs(Disc))/2
i2 =-i1
EndIf
EndSub
Output for Problem 7.5(a):
Now, run the code by pressing ‘F5’ key. Hence the output will be,
1st Root:
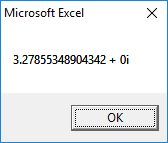
2nd Root:
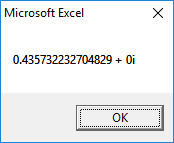
3rd Root:
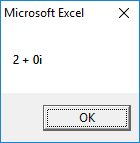
Output for Problem 7.5(b):
Now, run the code by pressing ‘F5’ key. Hence the output will be,
1st Root:
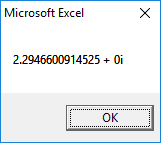
2nd Root:
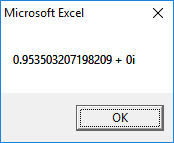
3rd Root:
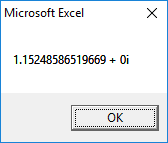
Output for Problem 7.5(c):
Now, run the code by pressing ‘F5’ key. Hence the output will be,
1st Root:
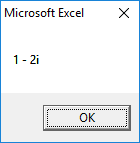
2nd Root:
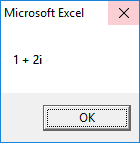
3rd Root:
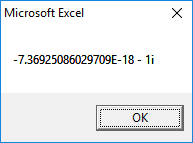
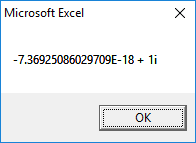
4th Root:











 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY




