
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A 4.0-kg object is attached to a vertical rod by two strings as shown in Figure P7.69. The object rotates in a horizontal circle at constant speed 6.00 m/s. Find the tension in (a) the upper string and (b) the lower string.
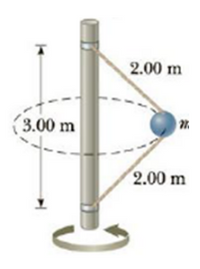
Transcribed Image Text:2.00 m
3.00 m
2.00 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Ferris wheel has radius of 4.8 m and makes one revolution in 7.4 seconds. A person weighing 686 N is sitting on one of the benches attached at the rim of the wheel. What is the apparent weight (that is, the normal force exerted on her by the bench) of the person as she passes through the highest point of her motion?arrow_forwardA goat stands on a merry-go-round that is rotating at 6.1 rad/s. If the coefficient of static friction between the goat's hooves and the merry-go-round is 0.45, how far from the axis of rotation can the goat stand without sliding? Express your answer in m, to at least one digit after the decimal point. plz help use g = 9.8arrow_forwardThe tension is growing!Context At your summer job, your supervisor wants to test your physics skills. A new winch (a cable driven by a motor) is to be used to hoist loads up an inclined ramp. Your supervisor is worried about the packages arriving too quickly at the top of the ramp. Constraints The inclined ramp is made up of small cylinders that are free to rotate: there is no friction between the ramp and the load.The angle theta of the ramp from the horizontal is known.The winch cable exerts a known force.The cable is oriented at an angle a from the horizontal.The charge, initially immobile, has a known mass.The length of the ramp is known. Schematization Draw a diagram of the object that interests us. Draw your x and y axes. Draw and name each force experienced by the object that interests us. Modelization Build a model to calculate the final speed of the load as it arrives at the top of the ramp, given the known parameters. Then test your model with the following values: Ramp…arrow_forward
- Red blood cells can be separated from blood plasma using a centrifuge. This device spins the whole blood samples rapidly in a circular path and can generate forces many times that of gravity. The more dense material (red blood cells) accumulates at the outer end of the container while the less dense material (plasma) is closer to the centre of rotation. One “g” is the equivalent of 9.80 ms-2. How many “g”s is experienced by the material spinning in the centrifuge at a distance of 18.4 cm from the centre of rotation at 2,457 revolutions per minute?arrow_forwardA highway curve has a radius of 0.14 km and is unbanked. A car weighing 12 kN goes around the curve at a speed of 24 m/s without slipping. What is the magnitude of the horizontal force of the road on the car? 17 kN 12 kN O 5.0 kN 13 kN 49 KN p q# 19 p. 242 chap 7arrow_forwardA 1.5 kg block is connected by a rope across a 50-cm-diameter, 2.0 kg pulley, as shown. There is no friction in the axle, but there is friction between the rope and the pulley; the rope doesn’t slip. The weight is accelerating upward at 1.2 m/s2. What is the tension in the rope on the right side of the pulley?arrow_forward
- A rubber ball is attached to a 1.44-meter string and spun in a horizontal circle. The tension in the string is 2.91 N. It takes 0.644 s for the ball to complete one revolution. Determine the mass (in kg) of the ball.arrow_forwardWhen a person stands on tiptoe (a strenuous position), the position of the foot is as shown in Figure a. The total gravitational force on the body, F, is supported by the force n exerted by the floor on the toes of one foot. A mechanical model of the situation is shown in Figure b, where T is the force exerted by the Achilles tendon on the foot and R is the force exerted by the tibia on the foot. Find the values of T, R, and e when F, = n = 675 N. (For e, enter the smaller of the two possible values between 0° and 90°.) Achilles tendon Tibia 15.0° 18.0 cm 25.0 cm T = N R = N Need Help? Read Itarrow_forwardYou are swinging a 0.25 kg water balloon vertically. The distance from your shoulder (acting as the center of rotation) and the water balloon is about 0.65 m. You estimate the water balloon is traveling at 7.0 m/s. At the very top of the circular path, how much force is your hand holding the water balloon? Enter absolute value. Hint: the water balloon is experiencing uniform circular motion.arrow_forward
- A small ball is attached to one end of light rope that has a length of 4.0 m. The other end of the rope is attached to the ceiling. The ball is held with the rope horizontal and released from rest. The ball moves in the motion of an arc of the circle. When the ball is at its lowest point, with the rope vertical, the tesion of the rope is 15.5 N. What is the mass of the ball?arrow_forwarda. What is the magnitude of acceleration of the block? b. What is the magnitude of the tension force from the block on the cylinder?arrow_forwardA space station is constructed in the shape of a wheel 20 m in diameter, with essentially all of its 5.2×105 kg mass at the rim. Once the station is completed, it is set rotating at a rate that requires an object at the rim to have radial acceleration g , thereby simulating Earth's surface gravity. This is accomplished using two small rockets, each with 130 N thrust, that are mounted on the rim of the station. How long will it take to reach the desired spin rate, and how many revolutions will the station make in this time?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON