
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A small ball is attached to one end of light rope that has a length of 4.0 m. The other end of the rope is attached to the ceiling. The ball is held with the rope horizontal and released from rest. The ball moves in the motion of an arc of the circle. When the ball is at its lowest point, with the rope vertical, the tesion of the rope is 15.5 N. What is the mass of the ball?
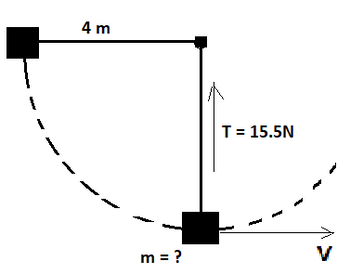
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a physics problem involving a pendulum. A mass \( m \) is suspended by a rigid horizontal bar, and a vertical string forms an angle as it swings. The components of the system are as follows:
- The horizontal bar is 4 meters long.
- The string exerts a tension (\( T \)) of 15.5 Newtons.
- The mass at the end of the pendulum is unknown, denoted as \( m = ? \).
- The pendulum is shown to swing in an arc, indicated by a dashed line.
- The direction of velocity (\( V \)) is shown as a horizontal arrow to the right.
This setup can be used to analyze circular motion and the forces acting on a pendulum. The key elements to explore include the calculation of the mass \( m \), dynamics of tension, gravitational forces, and motion characteristics at various points in the pendulum's path.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 980-gg rock is whirled in a horizontal circle at the end of a 1.7-mm-long string. If the breaking strength of the string is 110 NN , what’s the minimum angle the string can make with the horizontal? At this minimum angle, what’s the rock’s speed?arrow_forward54. A puck of mass m, is tied to a string and allowed to revolve in a circle of R radius R on a friction- less, horizontal table. The other end of the string passes through a small hole in the cen- m2 ter of the table, and an object of mass m, is tied to it (Fig. P6.54). The suspended object remains in equilibrium while the puck on the tabletop revolves. Find symbolic expressions for (a) the tension in the string, (b) the radial force acting on the puck, and (c) the speed of the puck. Figure P6.54arrow_forwardThe Gravitron ride has people step in, lean against a wall and “stick” when it spins and the floor drops out after a certain velocity. A rider has a mass of 50kg. The coefficient of static friction of the body against a wall is 0.8. The diameter of the ride is 10m. What is the maximum period of the ride’s rotation that will keep the student pinned to the wall once the floor drops?arrow_forward
- A 0.1-kg ball is attached to a string and whirled around in a horizontal circle overhead. The string breaks if the force on it exceeds 60 N. What is the maximum speed the ball can achieve if the radius is 1 m?arrow_forwardA student of mass M = 98 kg takes a ride in a frictionless loop-the-loop at an amusement park. The radius of the loop-the-loop is R = 24 m. The normal force by the track on the student at the top of the loop-the-loop is N₁ = 944 N. Find the speed of M at the top of the loop-the-loop. m/s Determine the normal force on M by the track at the bottom of the loop-the-loop, assuming the speed at the bottom is the same as at the top. Narrow_forwardA 0.20 kg object attached to the end of a string swings in a vertical circle (radius = 8 cm). At the top of the circle the speed of the object is 4.5 m/s. What is the magnitude of the tension in the string at this position?arrow_forward
- A tennis ball connected to a string is spun counterclockwise around in a vertical, circular path at a uniform speed. The ball has a mass m = 0.14 kg and moves at speed v = 2.7 m/s. The circular path has a radius of R = 0.35 m. The ball is at the bottom of the circle as shown. What is the magnitude of the tension force on the ball at this instant, in Newtons? Use g = 10 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardAn 0.55 kg puck slides in a r =20 cm circle on a frictionless table while attached to a hanging cyliner of mass M = 2.50 kg. What frequency of rotation keeps the cylinder at rest? Express your answer in Hz (cycles per second). Hint: Solve for speed then convert to frequency. Use g=10N/kg.arrow_forwardA 30 kg child slides down a slide with h = 4.0 m and arrives at the ground with a speed of 6.0 m/s. The slide forms the arc of a circle with a radius of 21 m with the ground tangent to the bottom of the slide. Determine the average friction force acting on the child. Hint: Use h = R(1 - cos(θ)) and s = Rθ where θ is in radians and s = arc length.arrow_forward
- A small object with a mass of m = 860 g is whirled at the end of a rope in a vertical circle with a radius of r = 146 cm. When the object is at the location shown - mid-height -, its speed is v = 4.11 m/s. Determine the tension in the rope. Submit Answer Tries 0/10 Calculate the magnitude of the total force acting on the mass at that location. Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forwardA tennis ball connected to a string is spun counterclockwise around in a vertical, circular path at a uniform speed. The ball has a mass m = 0.16 kg and moves at speed v = 2.4 m/s. The circular path has a radius of R = 0.26 m. The ball is at the bottom of the circle as shown. What is the magnitude of the tension force on the ball at this instant, in Newtons? Use g = 10 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardA small 0.250-kg object is attached to a string (see figure), where it swings in a section of a vertical circle of radius 2.50 m. Find the magnitude of the tension in the string when θ = 28.0°, the speed of the object is 4.50 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON