
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781259969478
Author: WILLIAM LANEN, Shannon Anderson, Michael Maher
Publisher: McGraw Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 54P
Finding Missing Data
A new computer virus (AcctBGone) destroyed most of the company records at BackupsRntUs. The computer experts at the company could recover only a few fragments of the company’s factory ledger for March as follows:
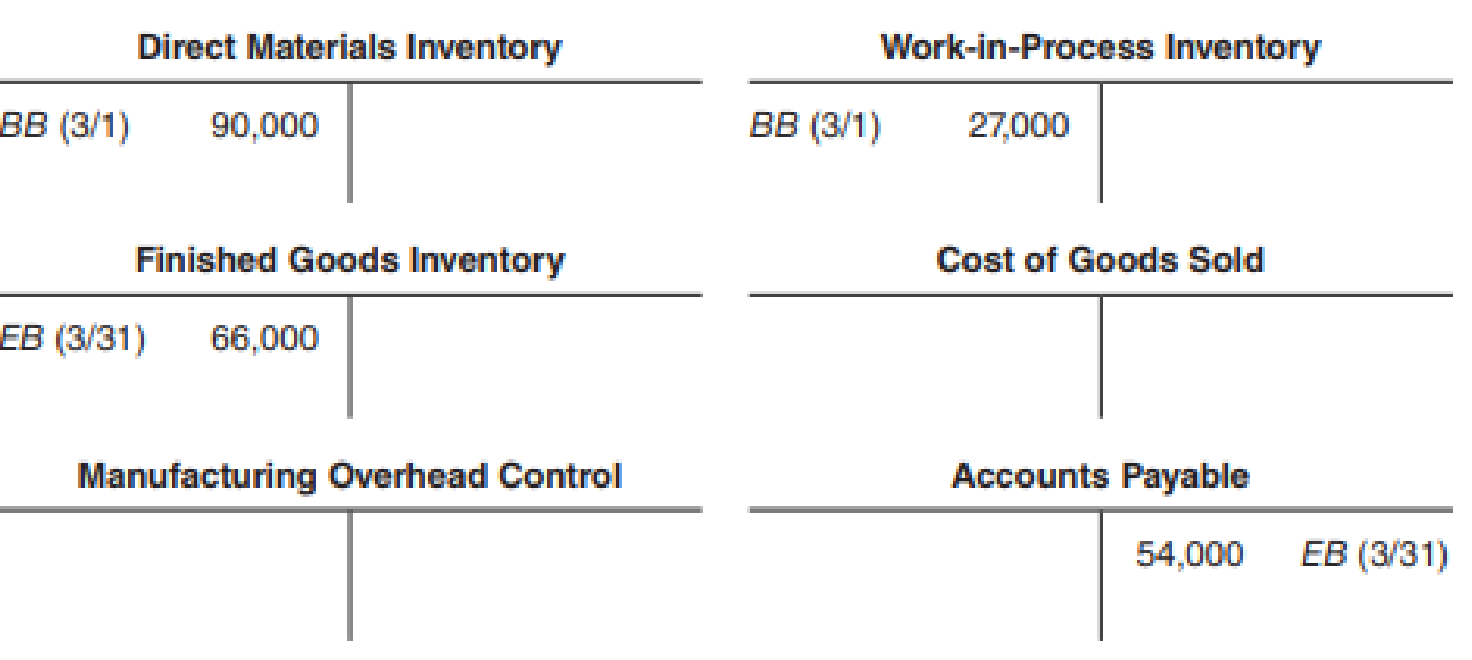
Further investigation and reconstruction from other sources yielded the following additional information:
- The controller remembers clearly that actual
manufacturing overhead costs are recorded at $18 per direct labor-hour. (The company assigns actual overhead to Work-in-Process Inventory.) - The production superintendent’s cost sheets showed only one job in Work-in-Process Inventory on March 31. Materials of $15,600 had been added to the job, and 300 direct labor-hours had been expended at $36 per hour.
- The Accounts Payable are for direct materials purchases only, according to the accounts payable clerk. He clearly remembers that the balance in the account was $36,000 on March 1. An analysis of canceled checks (kept in the treasurer’s office) shows that payments of $252,000 were made to suppliers during the month.
- The payroll ledger shows that 5,200 direct labor-hours were recorded for the month. The employment department has verified that there are no variations in pay rates among employees (this infuriated Steve Fung, who believed that his services were underpaid).
- Records maintained in the finished goods warehouse indicate that the finished goods inventory totaled $108,000 on March 1.
- The cost of goods manufactured in March was $564,000.
Required
Determine the following amounts:
- a. Work-in-process inventory, March 31.
- b. Direct materials purchased during March.
- c. Actual manufacturing overhead incurred during March.
- d. Cost of goods sold for March.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Action to increase net income
Please given answer general accounting question
Subject. General accounting
Chapter 7 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
Ch. 7 - What are characteristics of companies that are...Ch. 7 - Direct labor-hours and direct labor dollars are...Ch. 7 - What is the purpose of having two manufacturing...Ch. 7 - How does the accountant know what to record for...Ch. 7 - How is job costing in service organizations (for...Ch. 7 - What are the costs of a product using normal...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7RQCh. 7 - What are three common sources of improprieties in...Ch. 7 - In the context of job costing, what are projects?...Ch. 7 - Why do most companies use normal or standard...
Ch. 7 - Why is control of materials important from a...Ch. 7 - Worrying about the choice of an overhead...Ch. 7 - Prob. 13CADQCh. 7 - Interview the manager of a campus print shop or a...Ch. 7 - Would a dentist, an architect, a landscaper, and a...Ch. 7 - Consider two firms in the same industry. Is it...Ch. 7 - Prob. 17CADQCh. 7 - Assume that you have been asked to paint the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 19CADQCh. 7 - ABC Consultants works for only two clients: a...Ch. 7 - Prob. 21CADQCh. 7 - Assigning Costs to Jobs The following transactions...Ch. 7 - Assigning Costs to Jobs Sunset Products...Ch. 7 - Assigning Costs to Jobs Forest Components makes...Ch. 7 - Assigning Costs to Jobs Partially completed...Ch. 7 - Assigning Costs to Jobs Selected information from...Ch. 7 - Assigning Costs to Jobs Partially completed...Ch. 7 - Predetermined Overhead Rates Dixboro Company...Ch. 7 - Predetermined Overhead Rates Southern Rim Parts...Ch. 7 - Refer to the information in Exercise 7-29. Prepare...Ch. 7 - How much overhead was applied to each of the four...Ch. 7 - Refer to the information in Exercise 7-31. Prepare...Ch. 7 - Predetermined Overhead Rates Aspen Company...Ch. 7 - Prob. 34ECh. 7 - Applying Overhead Using a Predetermined Rate Marys...Ch. 7 - Applying Overhead Using a Predetermined Rate Turco...Ch. 7 - Calculating Over- or Underapplied Overhead Toms...Ch. 7 - Predetermined Overhead Rates: Ethical Issues...Ch. 7 - Compute the predetermined rate assuming that...Ch. 7 - Job Costing in a Service Organization At the...Ch. 7 - Job Costing in a Service Organization For August,...Ch. 7 - Job Costing in a Service Organization Allocation...Ch. 7 - Job Costing in a Service Organization TechMaster...Ch. 7 - Prob. 44ECh. 7 - Prob. 45ECh. 7 - Prob. 46PCh. 7 - Estimate Machine-Hours Worked from Overhead Data...Ch. 7 - Estimate Hours Worked from Overhead Data Capitol,...Ch. 7 - What will Wabash report as Cost of Goods Sold for...Ch. 7 - Assigning CostsMissing Data The following...Ch. 7 - Assigning Costs: Missing Data The following...Ch. 7 - Analysis of Overhead Using a Predetermined Rate...Ch. 7 - Analysis of Overhead Using a Predetermined Rate...Ch. 7 - Finding Missing Data A new computer virus...Ch. 7 - Cost Accumulation: Service Youth Athletic Services...Ch. 7 - Job Costs: Service Company For the month of July,...Ch. 7 - Job Costs in a Service Company On September 1, two...Ch. 7 - Tracing Costs in a Job Company The following...Ch. 7 - Cost Flows through Accounts Brighton Services...Ch. 7 - Show Flow of Costs to Jobs Kims Asphalt does...Ch. 7 - Reconstruct Missing Data A tornado struck the only...Ch. 7 - Find Missing Data IYF Corporation manufactures...Ch. 7 - Find Missing Data Accounting records for NIC...Ch. 7 - Incomplete Data: Job Costing Chelsea Household...Ch. 7 - Job Costing and Ethics Old Port Shipyards does...Ch. 7 - Job Costing and Ethics Chuck Moore supervises two...Ch. 7 - Job Costing and Ethics Global Partners is a...Ch. 7 - Prob. 68ICCh. 7 - What is the predetermined overhead rate for...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Compute the assets turnover ratioarrow_forwardExercise 5-18 (Algo) Calculate receivables ratios (LO5-8) Below are amounts (in millions) from three companies' annual reports. WalCo TarMart Costbet Beginning Accounts Receivable $1,795 6,066 609 Ending Accounts Receivable $2,742 6,594 645 Net Sales $320,427 65,878 66,963 Required: 1. Calculate the receivables turnover ratio and the average collection period for WalCo, TarMart and CostGet 2. Which company appears most efficient in collecting cash from sales? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required C Calculate the receivables turnover ratio and the average collection period for WalCo, TarMart and CostGet. (Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place.) Receivables Turnover Ratio: WalCo S TarMart. S CostGet S Choose Numerator Choose Numerator "ValCo FarMart CostGet 320,427 $ 65.878 66,963 Choose Denominator Receivables turnover ratio 2,742.0 116.9 times 0 times 0 times Average Collection Period Choose Denominator Average…arrow_forwardWhat is the Whistleblower Protection Act of 1989 (amended in 2011)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pkg Acc Infor Systems MS VISIO CDFinanceISBN:9781133935940Author:Ulric J. GelinasPublisher:CENGAGE L
Pkg Acc Infor Systems MS VISIO CDFinanceISBN:9781133935940Author:Ulric J. GelinasPublisher:CENGAGE L

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172685
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619455
Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Pkg Acc Infor Systems MS VISIO CD
Finance
ISBN:9781133935940
Author:Ulric J. Gelinas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Job Costing and Spoilage | Topic 2 | Spoilage, Re-work, and Scrap; Author: Samantha Taylor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VP55_W2oXic;License: CC-BY