
Concept explainers
The nuchal ligament is a cord-like structure that runs along the back of the neck and supports much of the head’s weight in animals like horses and cows. The ligament is extremely stiff for small stretches, but loosens as it stretches further, thus functioning as a biological shock absorber. Figure 7.17 shows the force-distance curve for a particular nuchal ligament; the curve can be modeled approximately by the expression F(x) = 0.43x − 0.033x2 + 0.00086x3, with F in kN and x in cm. Find the energy stored in the ligament when it’s been stretched (a) 7.5 cm and (b) 15 cm.
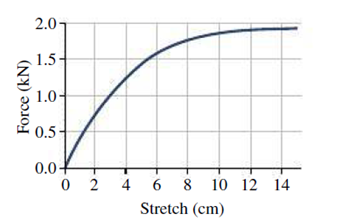
FIGURE 7.17 Problem 42
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Modern Physics
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
College Physics
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
- I'm not sure how to work this problem. The problem gives an answer of Itot=Icm+Md^2=18.1 kg*m^2 for part A. The problem also gives an answer of a=6.41 rad/s^2 for part B but does not show how to work the problems to get to these answers.arrow_forwardThe spring connects two objects. In this case, it's the object that moves and accelerates, and the wall. I will take x to be the distance from the particle to the wall -- the length of the spring. The problem is one-dimensional. (There are two- and three-dimensional forms of the problem.) The ideal spring exerts a force (F) on the object, with the following properties: The spring has a length (ℓ) where it exerts no force. (I usually call it the relaxed length. I might call it the "zero-force length" or the "equilibrium length".) The compressed spring pushes. The stretched string pulls. The force on the block is F = -k(x - ℓ). (Figure out what the negative sign on k does.) Often, people use x for the difference from equilibrium, and write F = -kx instead. Sometimes, both sides of the spring are at different positions. The force on the object on the right side is -k(x2 - x1 - ℓ). In the pictured situation, x1 = 0 and x2 = x. Understand what is physically happening with…arrow_forwardA slingshot, consisting of a leather pouch attached to two rubber bands which are tied to the prongs of a wooden Y- shaped frame, is used to shoot a pebble horizontally. When the slingshot is stretched by a distance d, it gives the pebble speed v. What speed does it give the same pebble when it is stretched to distance 3d?arrow_forward
- To test the speed of a bullet, you create a pendulum by attaching a 5.00 kg wooden block to the bottom of a 2.40 m long, 1.40 kg rod. The top of the rod is attached to a frictionless axle and is free to rotate about that point. You fire a 10 g bullet into the block, where it sticks, and the pendulum swings out to an angle of 34.0°. What was the speed of the bullet?arrow_forwardTwo springs, with force constants k1=140N/m and k2=275N/m, are connected in series, as shown in the figure. When a mass m=0.50kg is attached to the springs, what is the amount of stretch, x?arrow_forwardA swift blow with the hand can break a pine board. As the hand hits the board, the kinetic energy of the hand is transformed into elastic potential energy of the bending board; if the board bends far enough, it breaks. Applying a force to the center of a particular pine board deflects the center of the board by a distance that increases in proportion to the force.Ultimately the board breaks at an applied force of 800 N and a deflection of 1.2 cm.a. To break the board with a blow from the hand, how fast must the hand be moving? Use 0.50 kg for the mass of the hand.b. If the hand is moving this fast and comes to rest in a distance of 1.2 cm, what is the average force on the hand?arrow_forward
- A gymnast of mass 52.0 kg is jumping on a trampoline. She jumps so that her feet reach maximum height of 2.49 m above the trampoline and, when she lands, her feet stretch the trampoline 68.0 cm down. How far does the trampoline stretch when she stands on it at rest? Assume that the trampoline is described by Hooke's law when it is stretched. Give your answer in cm.arrow_forwardYou have a new internship, where you are helping to design a new freight yard for the train station in your city. There will be a number of dead-end sidings where single cars can be stored until they are needed. To keep the cars from running off the tracks at the end of the siding, you have designed a combination of two coiled springs as illustrated in Figure P7.41. When a car moves to the right in the figure and strikes the springs, they exert a force to the left on the car to slow it down. Both springs are described by Hooke's law and have spring constants k1= 1600 N/m and k2 = 3400 N/m. After the first spring compresses by a distance of d = 30.0 cm, the second spring acts with the first to increase the force to the left on the car in Figure P7.41.When the spring with spring constant k2 compresses by 50.0 cm, the coils of both springs are pressed together, so that the springs can no longer compress. A typical car on the siding has a mass of 6000 kg. When you present your design to…arrow_forwardAn 8.0-cm-long spring is attached to the ceiling. When a 2.3 kg mass is hung from it, the spring stretches to a length of 16 cm. How long is the spring when a 3.0 kg mass is suspended from it? y=arrow_forward
- I find a spring that is labeled "80 N/m", but it is actually 3.5 inches long. I fasten a beam (horizontal rod) 789 mm above the table-top, and hang the spring from it. Where is the spring's bottom end? (presume the spring does not stretch due to its own weight; 1 inch is 25.4 mm) 786 mm above the table 307 mm above the table 89 mm above the table 709 mm above the table 878 mm above the table 780 mm above the table 789 mm above the table 70 mm above the table O 777 mm above the table 700 mm above the table O touching the table-toparrow_forwardA spring is hanging from the ceiling. A physicist with mass of 80 kg jumps up and grabs ahold of the spring. He then bounces up and down without touching the floor. How far down does the spring stretch from its rest length? The spring constant is k = 3768 N/m.arrow_forwardA muscle cell in the biceps is 23 cm long and contains 1500 myofibrils arranged in parallel to each other. each myofibril is made up of many sarcomeres, organized in series, that behave as springs. A relaxed sarcomere is 5 μm long. When contracted, the cell shortens to half its length and develops a force of 33 mN. Each of those structures, the cell, myofibril, and sarcomere, can be modeled as a spring.When we shiver in the cold, our muscles oscillate at a frequency of 13 Hz and with an amplitude of 5 cm. Assume a muscle is a simple harmonic oscillatory and calculate the mass of the load on that oscillator. Calculate the mass of the load on a single myofibril.Calculate the mass of the load on a single sarcomere.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





