
Use the following questions to check your understanding of some of the many types of visual information used in astronomy. For additional practice, try the Chapter 7 Visual Quiz at Mastering Astronomy.
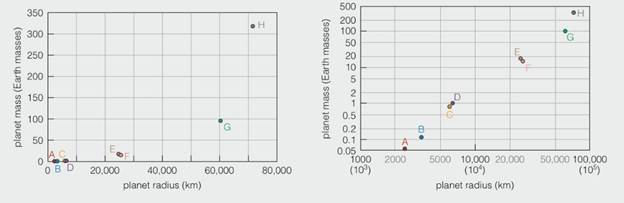
The plots above show the masses of the eight major planets on the vertical axis and their radial on the horizontal axis. The plot on the left shows the information on a linear scale, meaning that each tick mark indicates an increase by the same amount. The plot on the right shows the same information plotted on an exponential scale, meaning that each tick mark represents another actor-of-ten increase. Before proceeding, convince yourself that the points on each plot are the same.
3. Which statements most accurately describes the relationship between the largest and smallest planets?
a. The largest planet is 6000 times as wide (in diameter) and 30 times as massive as the smallest.
b. The largest planet is 6000 times as wide (in diameter) and 6000 times as massive as the smallest.
c. The largest planet is 30 times as wide (in diameter) and 30 times as massive as the smallest.
d. The largest planet is 30 times as wide (in diameter) and 6000 times as massive as the smallest.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective (9th Edition)
- The diagram below shows the orbit of a star with an exoplanet and the corresponding radial velocity curve for the star. Four locations in the planet's orbit are shown. Questions 5-8 refer to this diagram. 5. For each of the four locations of the planet, mark and label on the star's orbit where the star would be at that time. 6. For each of the four positions of the star, draw arrow to indicate which way the star is moving at that time. 7. For each of the four positions of the star, indicate whether the star's light is redshifted, blueshifted, or not shifted. 8. Mark and label the positions on the radial velocity curve that correspond to the four letters. Remember that positive radial velocities correspond to the star moving away from the Earth!! ↑ To Earth Orbit of Star Orbit of Planet D 2 Radial Velocity (m/s) 50 25 -25 -50 ←++ Timearrow_forwardDirection: Use your knowledge about solving equations to work out to complete the table below. Show your solution with proper units. R° (meters) T R° / T° { (meters) / Planet Average Times of Radius of Revolution (seconds) (seconds) } Planet's Orbit (Planet's year) R T (seconds) (meters) Mercury 5.7869 x 10:0 7.605 x 10 Venus 1.081 x 101 1.941 x 107 Earth 1.4996 x 10" 3.156 x 10 Mars 2.280 x 101 5.936 x 10 Jupiter 7.783 x 10" 3.743 x 10 Saturn 1.426 x 10 9.296 x 10arrow_forwardExplain what is meant by the distance ladder in astronomy. Describe briefly how each “rung” of the distance ladder is calibrated so that a reliable measure of distance can be obtained using each of the methods. State clearly the range of distances that can be measured by each method that makes up the distance ladder.arrow_forward
- This is Pre-Calc! Please help and Thank you! Please click the pics for the background info Directions: Answer questions 1-8 based on the information on Table 1. Round all answers to the nearest thousandth and label with the appropriate units. 1. According to Table 1, what is the closest distance between Earth and Mars? 2. According to Table 1, what is the farthest distance between Earth and Mars? 3. Based on your answers from #2 and #3, what is the average distance between the two planets? 4. Based on your answers from #2 and #3, what is the amplitude of the distances? 5. The distance has a period of 772 days. Write a sinusoidal equation relating the number of days and distance from Earth to Mars. 6. Based on the equation from #5, what is the distance between our planets on Mr. Schutt’s birthday (day 187)? 7. Write a sinusoidal equation relating the number of days and the one-waycommunication between Earth to Mars. 8. What is the one-way communication time delay between our planets on…arrow_forwardAt present there are 8 planets in the solar system. In the early models, there were only 6 planets. What is the reason behind this? Describe a model of the modern solar system in terms of the number of planets, their arrangement and the model’s center.arrow_forwardActivity 1: Drawing or Illustration Draw or illustrate Kepler's Three Laws of Motion. Label and explain each illustration. Include the equation used to describe Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion. Kepler's First Law of Planetary Kepler's Second Law of Motion: Planetary Motion: Drawing/ Illustration Drawing/Illustration Equation: Explanation: Equation: Explanation: Kepler's Third Law of Planetary Motion: Drawing/ Illustration Equation: Explanation: Activity 3: Problem Solving Activity Answer the following problems and show your process using the four guide steps for solving problems. a. The mean solar distance of Earth is 1.50 x m with a period of 1 year. What is the distance of mars from the sun if it has a period of 1.88 years? - b. Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, has a mean orbital radius of 1.22x109 m. The orbital period of Titan is 15.95 days. Hyperion, another moon of Saturn, orbits at a mean radius of 1.48x109 m. Use Kepler's third law of planetary motion to predict the orbital…arrow_forward
- You are given the following data from observations of an exoplanet: Using Kepler’s Third Law (r3 = MT2 where M is the mass of the central star) find the orbital radius in astronomical units of this planet. M = 1.5 times the mass of the sun. Remember to convert days to years using 365.25 as the length of a year in days. What is the semimajor axis of this planet in AU? - Knowing the orbital radius in both kn and AU, use the value in km to find the circumference of the orbit, then convert that to meters. (Assume the orbit is a perfect circle). - Knowing the orbital circumference and the period in days, convert the days to seconds (multiply by 86,400) and find the orbital velocity in m/s - With that orbital velocity, the radius of the orbit in meters, find the centripetal acceleration of our exoplanet - Knowing the acceleration that our planet experiences, calculate the force that the host star exerts on the planet - Knowing the force on the planet, the orbital radius, and the mass of the…arrow_forwardbetween a planet and its moon. Procedure/Analysis: Go to: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Circular-and-Satellite- Motion/Gravitational-Fields/Gravitational-Fields-Interactive Use the program to answer the following questions. 1. A planet and its moon are shown in the simulation window. Click and drag the moon to various positions about the planet and observe the gravitational force vector. In the diagram below, draw a force vector (arrow with arrowhead) to depict the direction and relative magnitude of the force acting upon the moon at the designated locations. Note: the size of the arrow should be representative of the strength of the force.arrow_forwardIn Table 2, there is a list of 15 planets, some of which are real objects discovered by the Kepler space telescope, and some are hypothetical planets. For each one, you are provided the temperature of the star that each planet orbits in degrees Kelvin (K), the distance that each planet orbits from their star in astronomical units (AUs) and the size or radius of each planet in Earth radii (RE). Since we are concerned with finding Earth-like planets, we will assume that the composition of these planets are similar to Earth's, so we will not directly look at their masses, rather their sizes (radii) along with the other characteristics. Determine which of these 15 planets meets our criteria of a planet that could possibly support Earth-like life. Use the Habitable Planet Classification Flow Chart (below) to complete Table 2. Whenever the individual value you are looking at falls within the range of values specified on the flow chart, mark the cell to the right of the value with a Y for…arrow_forward
- As discussed in class, the moon is receding from the Earth due to tides at a rate of ~4 cm/year. Let’s assume that rate has been constant throughout time (it wasn’t, but we can use it to illustrate some key points). Its current semi-major axis is 384,400 km.a) If the moon formed 4.5 billion years ago and has been receding from the Earth ever since, what was its original semi-major axis? What was its original orbital period?b) What would the apparent size of the Moon have been in the sky as viewed from Earth? That is, in Hmwk 2, you were told the diameter of the Moon spans about 0.5o when viewed from Earth today. What would it have been when the Moon first formed? Reletive Numbers Relevant Numbers1 AU = 150,000,000 km = 1.5x108 kmEccentricity of Earth’s Orbit: 0.0167Radius of Earth: 6371 kmMass of Earth: 5.96x1024 kgRadius of the Moon: 1737 kmMass of Moon: 7.34x1022 kgRadius of Mars: 3390 kmMass of Mars: 6.4x1023 kgRadius of the Sun: R⦿=696,300 kmMass of the Sun: M⦿=2x1030…arrow_forwardHow can sciences be integrated in designing a water arc? Elaborate in complete sentences. i want a lot of reasons not only 1 reason like gravity or physics i want you to provide me with more reasons please and as it said Elaborate in complete sentencesarrow_forwardSee the screenshot uploaded. Answer in a step-by-step format, add diagrams, and detailed side notes for a better understanding. For a more clear response please answer on paper Thank you!arrow_forward
