
Concept explainers
INSTRUCTIONS
- 1. Open the general ledger accounts and
accounts receivable ledger accounts indicated below. - 2.
Post the entries from the general journal in Problem 7.2B to the appropriate accounts in the general ledger and in the accounts receivable ledger. - 3. Prepare a schedule of accounts receivable. Compare the balance of the Accounts Receivable control account with the total of the schedule.
GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE LEDGER ACCOUNTS

Analyze: Damaged or defective goods decreased sales by what dollar amount? By what percentage?
Problem 7.2B
Appliances for Less began operations November 1, 2019. The firm sells its merchandise for cash and on open account. Sales are subject to a 6 percent sales tax. During November, Appliances for Less engaged in the following transactions:
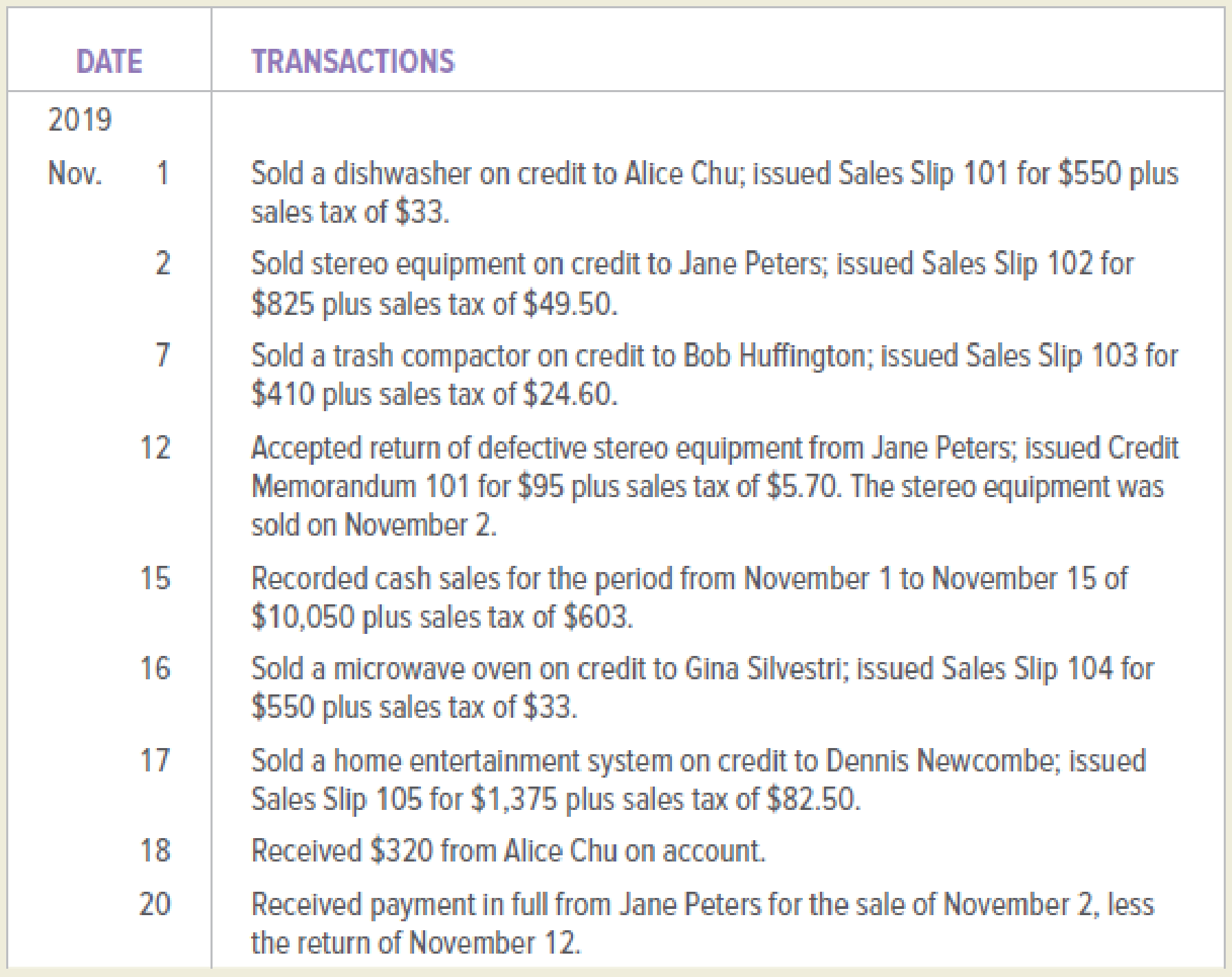

INSTRUCTIONS
Record the transactions in a general journal. Use 1 as the journal page number.
Analyze: What is the total amount due from Bob Huffington for the November 29 sale?
1 and 2
Prepare the general ledger for Company AL.
Explanation of Solution
General ledger: General ledger is a record of all accounts of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity, necessary to prepare financial statements. In the ledger all the entries are recorded in the account order, for which the transactions actually take place.
Post the journal entries in the General Ledger:
| GENERAL LEDGER | ||||||
| ACCOUNT: Cash | Account No.: 101 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | |||||
| 2019 | ||||||
| November 15 | J2 | $ 10,653.00 | $ 10,653.00 | |||
| November 18 | J2 | $ 320.00 | $ 10,973.00 | |||
| November 20 | J3 | $ 773.80 | $ 11,746.80 | |||
| November 28 | J3 | $ 434.60 | $ 12,181.40 | |||
| November 30 | J3 | $ 10,971.00 | $ 23,152.40 | |||
| ACCOUNT: Accounts receivable | Account No.: 111 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | |||||
| 2019 | ||||||
| November 1 | J1 | $ 583.00 | $ 583.00 | |||
| November 2 | J1 | $ 874.50 | $ 1,457.50 | |||
| November 7 | J2 | $ 434.60 | $ 1,892.10 | |||
| November 12 | J2 | $ 100.70 | $ 1,791.40 | |||
| November 16 | J2 | $ 583.00 | $ 2,374.40 | |||
| November 17 | J2 | $ 1,457.50 | $ 3,831.90 | |||
| November 18 | J2 | $ 320.00 | $ 3,511.90 | |||
| November 20 | J3 | $ 773.80 | $ 2,738.10 | |||
| November 24 | J3 | $ 127.20 | $ 2,610.90 | |||
| November 28 | J3 | $ 434.60 | $ 2,176.30 | |||
| November 29 | J3 | $ 715.50 | $ 2,891.80 | |||
Table (1)
| GENERAL LEDGER | ||||||
| ACCOUNT: Sales Tax Payable | Account No.: 221 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | |||||
| 2019 | ||||||
| November 1 | J1 | $ 33.00 | $ 33.00 | |||
| November 2 | J1 | $ 49.50 | $ 82.50 | |||
| November 7 | J2 | $ 24.60 | $ 107.10 | |||
| November 12 | J2 | $ 5.70 | $ 101.40 | |||
| November 15 | J2 | $ 603.00 | $ 704.40 | |||
| November 16 | J2 | $ 33.00 | $ 737.40 | |||
| November 17 | J2 | $ 82.50 | $ 819.90 | |||
| November 24 | J3 | $ 7.20 | $ 812.70 | |||
| November 29 | J3 | $ 40.50 | $ 853.20 | |||
| November 30 | J3 | $ 621.00 | $ 1,474.20 | |||
| ACCOUNT: Sales | Account No.: 401 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | |||||
| 2019 | ||||||
| November 1 | J1 | $ 550.00 | $ 550.00 | |||
| November 2 | J1 | $ 825.00 | $ 1,375.00 | |||
| November 7 | J2 | $ 410.00 | $ 1,785.00 | |||
| November 15 | J2 | $ 10,020.00 | $ 11,805.00 | |||
| November 16 | J2 | $ 550.00 | $ 12,355.00 | |||
| November 17 | J2 | $ 1,375.00 | $ 13,730.00 | |||
| November 29 | J3 | $ 675.00 | $ 14,405.00 | |||
| November 30 | J3 | $ 10,350.00 | $ 24,755.00 | |||
| ACCOUNT: Sales Returns and Allowances | Account No.: 421 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | |||||
| 2019 | ||||||
| November 12 | J2 | $ 95.00 | $ 95.00 | |||
| November 24 | J3 | $ 120.00 | $ 215.00 | |||
Table (2)
Reference Notes:
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit: A debit is an accounting term that refers to the left side of an account. The term debit is be denoted by (Dr). The recording amount on the left side of the account is known as debiting.
Credit: A credit is an accounting term that refers to the right side of an account. The term credit is denoted as (Cr). The recording amount on the right side of the account is known as crediting.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all the increase in the assets, the expenses and the dividends, all the decrease in liabilities, revenues and the stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all the increase in the liabilities, the revenues, and the stockholders’ equities, and all decreases in the assets, and the expenses.
Pass the journal entries for the given transactions:
| General Journal | Page - 1 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| November 1 | Accounts receivable (2) | 111 | $ 583 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 550 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (1) | 221 | $ 33 | ||
| (To record the sale on account to AC; Sales slip 101) | ||||
| November 2 | Accounts receivable (4) | 111 | $ 874.50 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 825.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (3) | 221 | $ 49.50 | ||
| (To record the sale on account to JP; Sales slip 102) |
Table (3)
| General Journal | Page - 2 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| November 7 | Accounts receivable (6) | 111 | $ 434.60 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 410.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (5) | 221 | $ 24.60 | ||
| (To record the sale on account to BH; Sales slip 103) | ||||
| November 12 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 421 | $ 95.00 | |
| Sales Tax Payable (7) | 221 | $ 5.70 | ||
| Accounts receivable (8) | 111 | $ 100.70 | ||
| (To record the sales returns from JP for the sales made on November 2 using sales slip 102, the credit memorandum is 101) | ||||
| November 15 | Cash (10) | 101 | $ 10,653 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 10,050 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (9) | 221 | $ 603 | ||
| (To record the cash sales) | ||||
| November 16 | Accounts receivable (12) | 111 | $ 583 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 550 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (11) | 221 | $ 33 | ||
| (To record the sale on account to GS; Sales slip 104) | ||||
| November 17 | Accounts receivable (14) | 111 | $ 1,457.50 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 1,375.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (13) | 221 | $ 82.50 | ||
| (To record the sale on account to DN; Sales slip 105) | ||||
| November 18 | Cash | 101 | $ 320 | |
| Accounts receivable | 111 | $ 320 | ||
| (To record the receipt of partial payment from AC) |
Table (4)
| General Journal | Page - 3 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| November 20 | Cash (15) | 101 | $ 773.80 | |
| Accounts receivable | 111 | $ 773.80 | ||
| (To record the receipt of payment from JP) | ||||
| November 24 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 421 | $ 120.00 | |
| Sales Tax Payable (16) | 221 | $ 7.20 | ||
| Accounts receivable (17) | 111 | $ 127.20 | ||
| (To record the sales returns from DN for the sales made on November 17 using sales slip 105, the credit memorandum is 102) | ||||
| November 28 | Cash | 101 | $ 434.60 | |
| Accounts receivable | 111 | $ 434.60 | ||
| (To record the receipt of payment from BH) | ||||
| November 29 | Accounts receivable (19) | 111 | $ 715.50 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 675.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (18) | 221 | $ 40.50 | ||
| (To record the sale on account to BH; Sales slip 103) | ||||
| November 30 | Cash (21) | 101 | $ 10,971 | |
| Sales | 401 | $ 10,350 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable (20) | 221 | $ 621 | ||
| (To record the cash sales) |
Table (5)
Working Notes (1):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 1.
Working Notes (2):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 1.
Working Notes (3):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 2.
Working Notes (4):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 4.
Working Notes (5):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 12.
Working Notes (6):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 12.
Working Notes (7):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 12.
Working Notes (8):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 12.
Working Notes (9):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 15.
Working Notes (10):
Calculate the value of Cash on November 15.
Working Notes (11):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 16.
Working Notes (12):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 16.
Working Notes (13):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 17.
Working Notes (14):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 17.
Working Notes (15):
Calculate the value of Cash on November 20.
Working Notes (16):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 24.
Working Notes (17):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 24.
Working Notes (18):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 29.
Working Notes (19):
Calculate the value of Accounts receivable on November 29.
Working Notes (20):
Calculate the value of Sales Tax Payable on November 30.
Working Notes (21):
Calculate the value of Cash on November 30.
3
Using the Schedule of Accounts Receivable compare the Accounts receivable balances with the total and identify the amount and percentage of sales decreased due to the defective goods.
Explanation of Solution
Schedule of accounts receivable: This is the schedule which reports all the debtors of a company during the given period and the balances to be recovered from them.
Prepare the Accounts receivable Subsidiary Ledger:
| ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE SUBSIDIARY LEDGER | |||||
| NAME: AC | |||||
| ADDRESS: | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance |
| 2019 | |||||
| November 1 | Sales Slip 101 | J1 | $ 583.00 | $ 583.00 | |
| November 18 | J2 | $ 320.00 | $ 263.00 | ||
| NAME: BH | |||||
| ADDRESS: | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance |
| 2019 | |||||
| November 7 | Sales Slip 103 | J2 | $ 434.60 | $ 434.60 | |
| November 28 | J3 | $ 434.60 | $ 0.00 | ||
| November 29 | Sales Slip 106 | J3 | $ 715.50 | $ 1,150.10 | |
| NAME: DN | |||||
| ADDRESS: | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance |
| 2019 | |||||
| November 17 | Sales Slip 105 | J2 | $ 1,457.50 | $ 1,457.50 | |
| November 24 | Credit Memorandum 102 | J3 | $ 127.20 | $ 1,330.30 | |
| NAME: JP | |||||
| ADDRESS: | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance |
| 2019 | |||||
| November 1 | Sales Slip 102 | J1 | $ 874.50 | $ 874.50 | |
| November 12 | Credit Memorandum 101 | J2 | $ 100.70 | $ 773.80 | |
| November 20 | J3 | $ 773.80 | $ 0.00 | ||
Table (6)
| ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE SUBSIDIARY LEDGER | |||||
| NAME: GS | |||||
| ADDRESS: | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit | Credit | Balance |
| 2019 | |||||
| November 16 | Sales Slip 104 | J2 | $ 583.00 | $ 583.00 | |
Table (7)
Prepare the Schedule of Accounts Receivable:
| Company AL | |
| Schedule of Accounts Receivable | |
| November 30, 2019 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| AC | $ 263.00 |
| BH | $ 715.50 |
| DN | $ 1,330.30 |
| JP | $ 0.00 |
| GS | $ 583.00 |
| Total accounts receivable | $ 2,891.80 |
Table (8)
The amount of sales decreased due to the defective goods is $215 and the percentage of sales decreased due to the defective goods is 0.9%.
Working notes (22):
Calculate the percentage of sales:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
GEN COMBO COLLEGE ACCOUNTING; CONNECT ACCESS CARD
- You returned damaged goods to C.C. Rogers Inc. and received a credit memo for $250. Which journal(s) would the company use to record this transaction? A. sales journal only B. purchases journal and the accounts payable subsidiary ledger C. cash receipts journal and the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger D. cash disbursements journal and the accounts payable subsidiary ledger E. general journal and the accounts payable subsidiary ledgerarrow_forwardWhich of the following accounts are used when recording the sales entry of a sale on credit? A. merchandise inventory, cash B. accounts receivable, merchandise inventory C. accounts receivable, sales D. sales, cost of goods soldarrow_forwardIf a customer pays with a credit card and the service has been provided, which of the following accounts will be used to record the sales entry for this transaction? A. Cost of Goods Sold, Merchandise Inventory, Sales Revenue B. Sales Revenue, Credit Card Expense, Accounts Receivable C. Accounts Receivable, Merchandise Inventory, Credit Card Expense D. Cost of Goods Sold, Credit Card Expense, Sales Revenuearrow_forward
- In the revenue cycle (for sales on credit), a customer places an order for a certain product. Which step does not occur before shipping the goods to the customer? Check inventory availabilityPick and pack the goodsCheck customer creditBill the customerObtain the customer orderarrow_forwardThe journal entry to record a credit sale ignoring cost of goods sold is ANSWER: Accounts Receivable Sales Revenue Explain to me why this is the answerarrow_forwardWhich of the following journal entries is recording merchandise inventory leaving the warehouse on a truck to be delivered to the customer? Question 4 options: debit Merchandise Inventory; credit Cash debit Cash; credit Sales debit Cost of Goods Sold; credit Merchandise Inventory debit Accounts Receivables; credit Salesarrow_forward
- If a customer purchases merchandise on credit and returns the defective merchandise beforepayment, what accounts would recognize this transaction?A. sales discount, cashB. sales returns and allowances, cashC. accounts receivable, sales discountD. accounts receivable, sales returns and allowancesarrow_forwardA customer returned damaged goods for credit. Under a perpetual system, which of the seller's accounts decreases? a. sales revenue b. sales returns c. accounts receivable d. purchase returnsarrow_forwardThe operating cycle of a merchandiser with credit sales includes the following five activities. With merchandise acquisition as the starting point, arrange the events in the correct order. a. Prepare merchandise for sale b. Collect cash from customers on account c. Make credit sales to customers d. Purchase merchandise e. Monitor and service accounts receivablearrow_forward
- Question 5 The General Ledger entry when Goods Issued is posted is DB: Cost of Goods Sold: CR: Inventory DB:Cost of Good Sold; CR Sales Revenue DB: Inventory, CR: Cost of Goods Sold DB: Sales Revenue, CR:Inventory Question 6 (1 If the wrong item is entered into a sales order, when will the mistake be caught? none of the answers when the warehouse ships the order when accounts receivable sends the invoice when the order is received by customerarrow_forwardcontrolling account Match the terms with the definitions, chapter 10 A summary account maintained in the general ledger for a subsidiary ledger (for example, the accounts receivable ledger). Merchandise returned by a customer for a refund. A transfer of merchandise from one sales return sale business or individual to another in exchange for cash or a promise to pay cash. Discounts to encourage prompt payment by cash discounts customers who buy merchandise on account. The seller's term for cash discounts. sales discounts A document issued when credit is given for merchandise returned or for an allowance. credit memo A document that is generated to bill the customer who made the purchase. sales invoice An alphabetical or numerical listing of customer accounts and balances, usually prepared at the end of the month. schedule of accounts receiva ✓ A document created as evidence of a sale in sales ticket a retail business. A separate ledger containing an individual account receivable for…arrow_forwardThe return of goods by a customer ( Sales Return ) should be credited in the ledger account of ? Select one: a. Sales account O b. Accounts receivable account O c. Purchase Return account O d. Sales Return accountarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning  College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub



