
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 36P
Figure P7.36 shows two thin beams joined at right angles. The vertical beam is 15.0 kg and 1.00 m long and the horizontal beam is 25.0 kg and 2.00 m long.
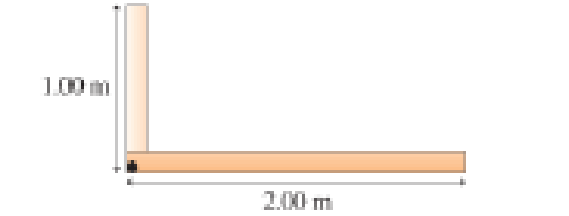
Figure P7.36
a. Find the center of gravity of the two joined beams. Express your answer in the form (x, y), taking the origin at the corner where the beams join.
b. Calculate the gravitational torque on the joined beams about an axis through the corner. The beams are seen from the side.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cm
Chapter 7 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 7 - The batter in a baseball game hits a home run. As...Ch. 7 - Viewed from somewhere in space above the north...Ch. 7 - Figure Q7.3 shows four pulleys, each with a heavy...Ch. 7 - If you are using a wrench to loosen a very...Ch. 7 - If you are using a wrench to loosen a very...Ch. 7 - A screwdriver with a very thick handle requires...Ch. 7 - If you have ever driven a truck, you likely found...Ch. 7 - A common type of door stop is a wedge made of...Ch. 7 - A student gives a steady push to a ball at the end...Ch. 7 - Prob. 10CQ
Ch. 7 - Prob. 11CQCh. 7 - If you grasp a hammer by its lightweight handle...Ch. 7 - Suppose you have two identical-looking metal...Ch. 7 - The moment of inertia of a uniform rod about an...Ch. 7 - The wheel in Figure Q7.15 is rolling to the right...Ch. 7 - With care, its possible to walk on top of a barrel...Ch. 7 - A nut needs to be tightened with a wrench. Which...Ch. 7 - Suppose a bolt on your car engine needs to be...Ch. 7 - Prob. 19MCQCh. 7 - A typical compact disk has a mass of 15 g and a...Ch. 7 - Suppose manufacturers increase the size of compact...Ch. 7 - Two horizontal rods are each held up by vertical...Ch. 7 - Prob. 23MCQCh. 7 - A particle undergoing circular motion in the...Ch. 7 - Questions 25 through 27 concern a classic...Ch. 7 - Questions 25 through 27 concern a classic...Ch. 7 - Questions 25 through 27 concern a classic...Ch. 7 - What is the angular position in radians of the...Ch. 7 - A child on a merry-go-round takes 3.0 s to go...Ch. 7 - What is the angular speed of the tip of the minute...Ch. 7 - An old-fashioned vinyl record rotates on a...Ch. 7 - The earths radius is about 4000 miles. Kampala,...Ch. 7 - A Ferris wheel rotates at an angular velocity of...Ch. 7 - A turntable rotates counterclockwise at 78 rpm. A...Ch. 7 - A fast-moving superhero in a comic book runs...Ch. 7 - Figure P7.9 shows the angular position of a...Ch. 7 - The angular velocity (in rpm) of the blade of a...Ch. 7 - The 1.00-cm-long second hand on a watch rotates...Ch. 7 - The earths radius is 6.37 106 m; it rotates once...Ch. 7 - To throw a discus, the thrower holds it with a...Ch. 7 - A computer hard disk starts from rest, then speeds...Ch. 7 - The crankshaft in a race car goes from rest to...Ch. 7 - Reconsider the situation in Example 7.10. If Luis...Ch. 7 - Balls are attached to light rods and can move in...Ch. 7 - Six forces, each of magnitude either F or 2F, are...Ch. 7 - What is the net torque about the axle on the...Ch. 7 - The tune-up specifications of a car call for the...Ch. 7 - A professors office door is 0.91 m wide, 2.0 m...Ch. 7 - In Figure P7.22, force F2, acts half as far from...Ch. 7 - Tom and Jerry both push on the 3.00-m-diameter...Ch. 7 - What is the net torque on the bar shown in Figure...Ch. 7 - What is the net torque on the bar shown in Figure...Ch. 7 - What is the net torque on the bar shown in Figure...Ch. 7 - Prob. 27PCh. 7 - Prob. 28PCh. 7 - Hold your arm outstretched so that it is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 30PCh. 7 - The 2.0 kg, uniform, horizontal rod in Figure...Ch. 7 - A 4.00-m-long, 500 kg steel beam extends...Ch. 7 - An athlete at the gym holds a 3.0 kg steel ball in...Ch. 7 - The 2.0-m-long, 15 kg beam in Figure P7.34 is...Ch. 7 - Two thin beams are joined end-to-end as shown in...Ch. 7 - Figure P7.36 shows two thin beams joined at right...Ch. 7 - A regulation table tennis ball is a thin spherical...Ch. 7 - Three pairs of balls are connected by very light...Ch. 7 - A playground toy has four seats, each 5.0 kg,...Ch. 7 - A solid cylinder with a radius of 4.0 cm has the...Ch. 7 - A bicycle rim has a diameter of 0.65 m and a...Ch. 7 - a. What is the moment of inertia of the door in...Ch. 7 - A small grinding wheel has a moment of inertia of...Ch. 7 - While sitting in a swivel chair, you push against...Ch. 7 - An objects moment of inertia is 2.0 kg m2. Its...Ch. 7 - A 200 g, 20-cm-diameter plastic disk is spun on an...Ch. 7 - The 2.5 kg object shown in Figure P7.47 has a...Ch. 7 - A frictionless pulley, which can be modeled as a...Ch. 7 - If you lift the front wheel of a poorly maintained...Ch. 7 - On page 207 there is a photograph of a girl...Ch. 7 - A toy top with a spool of diameter 5.0 cm has a...Ch. 7 - A bicycle with 0.80-m-diameter tires is coasting...Ch. 7 - Figure P7.55 shows the angular...Ch. 7 - The grap in Figure P7.56 shows the angular...Ch. 7 - A car with 58-cm-diameter tires accelerates...Ch. 7 - The cable lifting an elevator is wrapped around a...Ch. 7 - The 20-cm-diameter disk in Figure P7.59 can rotate...Ch. 7 - A combination lock has a 1.0-cm-diameter knob that...Ch. 7 - A 70 kg mans arm, including the hand, can be...Ch. 7 - The three masses shown in Figure P7.62 are...Ch. 7 - A reasonable estimate of the moment of inertia of...Ch. 7 - Starting from rest, a 12-cm-diameter compact disk...Ch. 7 - The ropes in Figure P7.65 are each wrapped around...Ch. 7 - Flywheels are large, massive wheels used to store...Ch. 7 - A 1.0 kg ball and a 2.0 kg ball are connected by a...Ch. 7 - A 1.5 kg block is connected by a rope across a...Ch. 7 - The two blocks in Figure P7.69 are connected by a...Ch. 7 - The 2.0 kg, 30-cm-diameter disk in Figure P7.70 is...Ch. 7 - A tradesman sharpens a knife by pushing it with a...Ch. 7 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems The Bunchberry The...Ch. 7 - The Bunchberry The bunchberry flower has the...Ch. 7 - The Bunchberry The bunchberry flower has the...Ch. 7 - The Bunchberry The bunchberry flower has the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 76MSPPCh. 7 - Prob. 77MSPPCh. 7 - Prob. 78MSPP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
53. This reaction was monitored as a function of time:
A plot of In[A] versus time yields a straight ...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
89. Classify each chemical reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, or double-displacement ...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Researchers cross a corn plant that is pure - breeding forthe dominant traits colored aleurone (C1), full kerne...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- a cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forwardFrom number 2 and 3 I just want to show all problems step by step please do not short cut look for formulaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Torque? | Physics | Extraclass.com; Author: Extraclass Official;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zXxrAJld9mo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY