
Concept explainers
a.
Explain if the problem meets the requirements of a binomial problem.
a.
Answer to Problem 35E
Yes, the problem qualifies as a binomial problem.
Explanation of Solution
In order to qualify as a binomial problem it must satisfy the following conditions:
- The number of trials is fixed that is 500 new members.
- There are only two mutually exclusive outcomes, overweight and not overweight.
- The
probability is constant for each trial that is 0.30. - The trials are independent to each other.
Since the problem satisfies all the conditions of a binomial distribution.
Hence, the problem is qualified as a binomial problem.
b.
Find the probability that 175 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight.
b.
Answer to Problem 35E
The probability that 175 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight is 0.0085.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that 30% of its new members are 15 pounds overweight and the total number of new members in a metropolitan area is 500.
That is,
The mean can be obtained as follows:
The standard deviation can be obtained as follows:
The probability that 175 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight can be obtained as follows:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability using Excel:
- Click on the Formulas tab in the top menu.
- Select Insert
function . Then from category box, select Statistical and below that NORM.S.DIST. - Click Ok.
- In the dialog box, Enter Z value as 2.39.
- Enter Cumulative as TRUE.
- Click Ok, the answer appears in the spreadsheet.
Output obtained using Excel is represented as follows:
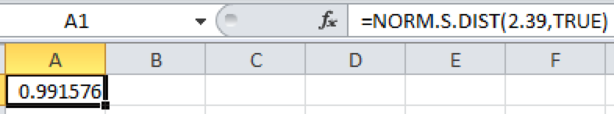
From the above output, the probability of Z less than 2.39 is 0.9915.
Now consider,
Therefore, the probability that 175 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight is 0.0085.
c.
Find the probability that 140 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight.
c.
Answer to Problem 35E
The probability that 140 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight is 0.8462.
Explanation of Solution
The probability that 140 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight can be obtained as follows:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability using Excel:
- Click on the Formulas tab in the top menu.
- Select Insert function, then from category box, select Statistical and below that NORM.S.DIST.
- Click Ok.
- In the dialog box, Enter Z value as –1.02.
- Enter Cumulative as TRUE.
- Click Ok, the answer appears in the spreadsheet.
Output obtained using Excel is represented as follows:
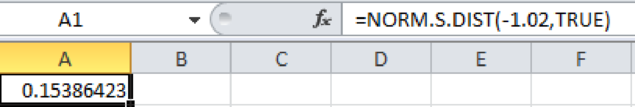
From the above output, the probability of Z less than –1.02 is 0.1538.
Consider,
Therefore, the probability that 140 or more of the new members are 15 pounds overweight is 0.8462.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- (c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward
- (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward29. State the Borel-Cantelli Lemmas without proof. What is the primary distinction between Lemma 1 and Lemma 2?arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning




