
Concept explainers
Scores from a questionnaire measuring social anxiety form a
- a. for a random sample of n = 4 people?
- b. for a random sample of n = 16 people?
- c. for a random sample of n = 25 people?
a.
Answer to Problem 11P
The probability of obtaining a sample mean greater than M=53 for given sample is 0.2743.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Numbers of people in a random sample are n=4.
Population mean is μ=50.
Population standard deviation is σ=10.
Sample mean is M=53.
Calculation:
If μ and σ represents the population mean and standard deviation respectively. Let n represents numbers of scores in each sample. Let M represents given sample mean. Then,
μ=50σ=10n=4M=53
Let ˉX represents the random sample mean from given distribution. Let μM and σM represents mean and standard error of ˉX Then, expected mean of ˉX will be same as population mean and standard error is calculated as:
μM=50σM=σ√n=10√4=5
Let p represents the probability that random mean is greater than M=53.
p=P(ˉX>53)=1−P(ˉX<53)
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P(ˉX<53) using the SPSS software:
- Click on first empty block of data view.
- Go to Transform>Choose Compute variable>Enter Probability in Target Variable.
- Choose CDF& Noncentral CDF under Function group> choose CDF.Normal> drag it to the numeric expression.
- Enter 53,50,5 in the braces of CDF.NORMAL
- Choose OK.
Output using the SPSS software is given below:
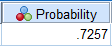
From the SPSS output, P(ˉX<53) is 0.7257.
Using (1) p is calculated as:
p=1−P(ˉX<53)=1−0.7257=0.2743
Thus, the probability of obtaining a mean greater than M=53 for given sample is 0.2743.
b.
Answer to Problem 11P
The probability of obtaining a sample mean greater than M=53 for given sample is 0.1151.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Numbers of people in a random sample are n=16.
Population mean is μ=50.
Population standard deviation is σ=10.
Sample mean is M=53.
Calculation:
If μ and σ represents the population mean and standard deviation respectively. Let n represents numbers of scores in each sample. Let M represents given sample mean. Then,
μ=50σ=10n=16M=53
Let ˉX represents the random sample mean from given distribution. Let μM and σM represents mean and standard error of ˉX Then, expected mean of ˉX will be same as population mean and standard error is calculated as:
μM=50σM=σ√n=10√16=2.5
Let p represents the probability that random mean is greater than M=53.
p=P(ˉX>53)=1−P(ˉX<53)
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P(ˉX<53) using the SPSS software:
- Click on first empty block of data view.
- Go to Transform>Choose Compute variable>Enter Probability in Target Variable.
- Choose CDF& Noncentral CDF under Function group> choose CDF.Normal> drag it to the numeric expression.
- Enter 53,50,2.5 in the braces of CDF.NORMAL
- Choose OK.
Output using the SPSS software is given below:
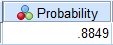
From the SPSS output, P(ˉX<53) is 0.8849.
Thus,
p=1−P(ˉX<53)=1−0.8849=0.1151
Hence, the probability of obtaining a mean greater than M=53 for given sample is 0.1151.
c.
Answer to Problem 11P
The probability of obtaining a sample mean greater than M=53 for given sample is 0.0668.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Numbers of people in a random sample are n=25.
Population mean is μ=50.
Population standard deviation is σ=10.
Sample mean is M=53.
Calculation:
If μ and σ represents the population mean and standard deviation respectively. Let n represents numbers of scores in each sample. Let M represents given sample mean. Then,
μ=50σ=10n=25M=53
Let ˉX represents the random sample mean from given distribution. Let μM and σM represents mean and standard error of ˉX Then, expected mean of ˉX will be same as population mean and standard error is calculated as:
μM=50σM=σ√n=10√25=2
Let p represents the probability that random mean is greater than M=53.
p=P(ˉX>53)=1−P(ˉX<53)
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P(ˉX<53) using the SPSS software:
- Click on first empty block of data view.
- Go to Transform>Choose Compute variable>Enter Probability in Target Variable.
- Choose CDF& Noncentral CDF under Function group> choose CDF.Normal> drag it to the numeric expression.
- Enter 53,50,2 in the braces of CDF.NORMAL
- Choose OK.
Output using the SPSS software is given below:
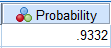
From the SPSS output, P(ˉX<53) is 0.9332.
Thus,
p=1−P(ˉX<53)=1−0.9332=0.0668
Hence, the probability of obtaining a mean greater than M=53 for given sample is 0.0668.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Essentials of Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap Course List)
- If, based on a sample size of 900,a political candidate finds that 509people would vote for him in a two-person race, what is the 95%confidence interval for his expected proportion of the vote? Would he be confident of winning based on this poll? Question content area bottom Part 1 A 9595% confidence interval for his expected proportion of the vote is (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardA population that is uniformly distributed between a=0and b=10 is given in sample sizes 50( ), 100( ), 250( ), and 500( ). Find the sample mean and the sample standard deviations for the given data. Compare your results to the average of means for a sample of size 10, and use the empirical rules to analyze the sampling error. For each sample, also find the standard error of the mean using formula given below. Standard Error of the Mean =sigma/Root Complete the following table with the results from the sampling experiment. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Sample Size Average of 8 Sample Means Standard Deviation of 8 Sample Means Standard Error 50 100 250 500arrow_forward
- A survey of 250250 young professionals found that two dash thirdstwo-thirds of them use their cell phones primarily for e-mail. Can you conclude statistically that the population proportion who use cell phones primarily for e-mail is less than 0.720.72? Use a 95% confidence interval. Question content area bottom Part 1 The 95% confidence interval is left bracket nothing comma nothing right bracket0.60820.6082, 0.72510.7251. As 0.720.72 is within the limits of the confidence interval, we cannot conclude that the population proportion is less than 0.720.72. (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardA survey of 250 young professionals found that two-thirds of them use their cell phones primarily for e-mail. Can you conclude statistically that the population proportion who use cell phones primarily for e-mail is less than 0.72? Use a 95% confidence interval. Question content area bottom Part 1 The 95% confidence interval is [ ], [ ] As 0.72 is ▼ above the upper limit within the limits below the lower limit of the confidence interval, we ▼ can cannot conclude that the population proportion is less than 0.72. (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward
- Questions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardFrom a sample of 26 graduate students, the mean number of months of work experience prior to entering an MBA program was 34.67. The national standard deviation is known to be18 months. What is a 90% confidence interval for the population mean? Question content area bottom Part 1 A 9090% confidence interval for the population mean is left bracket nothing comma nothing right bracketenter your response here,enter your response here. (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
