
Concept explainers
Applying the Concepts 6–3
Times To Travel to School
Twenty students from a statistics class each collected a random sample of times on how long it took students to get to class from their homes. All the sample sizes were 30. The resulting means are listed.
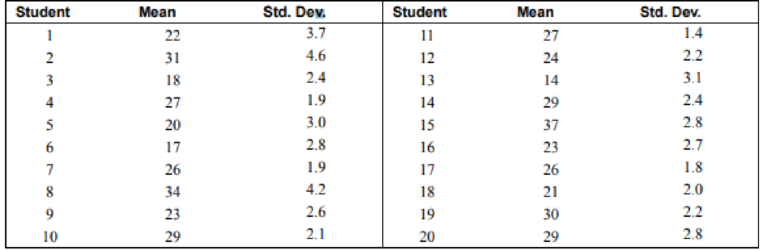
1. The students noticed that everyone had different answers. If you randomly sample over and over from any population, with the same
2. The students wondered whose results were right. How can they find out what the population
3. Input the means into the computer and check if the distribution is normal.
4. Check the mean and standard deviation of the means. How do these values compare to the students’ individual scores?
5. Is the distribution of the means a sampling distribution?
6. Check the sampling error for students 3, 7, and 14.
7. Compare the standard deviation of the sample of the 20 means. Is that equal to the standard deviation from student 3 divided by the square of the sample size? How about for student 7, or 14?
See page 368 for the answers.
1.
To check: Whether the result will be same when a random sample with same sample size is selected over and over from any population results in same mean.
Answer to Problem 1AC
No, the result will be same when a random sample with same sample size is selected over and over from any population results in same mean.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Twenty students each collected a random sample of times on how long it took students to get to class from their homes. Sample size is 30.
Justification:
Since, population is very large, and it’s very rare that the observations in each sample are same or close to each other. Also, it’s very rare event that samples from such a large population have same means. Therefore, the probability that different samples of same size have same means is approximately zero since that event is very rare. Thus, a random sample over and over from any population does not results in same mean.
2.
The method to find population mean and population standard deviation.
Answer to Problem 1AC
By taking average of all sample means and standard deviations.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Sample means and sample standard deviations of 20 samples.
Justification:
Since, sample means and sample standard deviations are given; therefore population mean can be estimated by taking average of all sample means.
Similarly, population standard deviation can be estimated by taking average of all given standard deviations.
3.
Whether the distribution is normal or not.
Answer to Problem 1AC
Given data is not normal.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Means of 30 samples are given.
Table:
| Students | Average time |
| 1 | 22 |
| 2 | 31 |
| 3 | 18 |
| 4 | 27 |
| 5 | 20 |
| 6 | 17 |
| 7 | 26 |
| 8 | 34 |
| 9 | 23 |
| 10 | 29 |
| 11 | 27 |
| 12 | 24 |
| 13 | 14 |
| 14 | 29 |
| 15 | 37 |
| 16 | 23 |
| 17 | 26 |
| 18 | 21 |
| 19 | 30 |
| 20 | 29 |
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the histogram using the MINITAB software:
- Enter the given data in columns.
- Choose Graph > select Histogram > select with fit > select ok.
- Select the column of average time.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From MINITAB output, the data of 20 means is not normal but is highly negatively skewed.
4.
To find the mean and standard deviation of the sample means.
Answer to Problem 1AC
Mean and standard deviation of sample means is 25.4 and 5.8 resp.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Sample means and sample standard deviations of 20 samples of size 30 each are given in table.
Table:
| Students | Average time | Standard deviation |
| 1 | 22 | 3.7 |
| 2 | 31 | 4.6 |
| 3 | 18 | 2.4 |
| 4 | 27 | 1.9 |
| 5 | 20 | 3 |
| 6 | 17 | 2.8 |
| 7 | 26 | 1.9 |
| 8 | 34 | 4.2 |
| 9 | 23 | 2.6 |
| 10 | 29 | 2.1 |
| 11 | 27 | 1.4 |
| 12 | 24 | 2.2 |
| 13 | 14 | 3.1 |
| 14 | 29 | 2.4 |
| 15 | 37 | 2.8 |
| 16 | 23 | 2.7 |
| 17 | 26 | 1.8 |
| 18 | 21 | 2 |
| 19 | 30 | 2.2 |
| 20 | 29 | 2.8 |
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display Descriptive Statistics.
- In Variables enter the columns Average time and StDev.
- Click OK.
Statistics

5.
Whether distribution of means is sampling distribution.
Answer to Problem 1AC
No.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Sample means and sample standard deviations of 20 samples of size 30 each.
Justification:
In given question each sample size is 30. Sampling distribution means that distribution of all possible samples of size 30 from the population. But, there are only 20 samples which are very less. Therefore, distribution of given sample means is not a sampling distribution.
6.
the standard error for 3rd, 7th and 14th students.
Answer to Problem 1AC
Standard errors of 3rd, 7th and 14th students are −7.4, 0.6 and 3.6 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Sample means for 3rd, 7th and 14th students are 18, 26, 29 respectively.
From part 4, mean of sample means is 25.4.
Calculation:
Let,
S represents mean of sample means.
S3 represents mean corresponding to 3rd student.
S7 represents mean corresponding to 7th student.
S14 represents mean corresponding to14th student.
Similarly,
The standard errors of 3rd, 7th and 14th students are −7.4, 0.6 and 3.6 respectively.
7.
Compare the standard deviation for 3rd, 7th and 14th students divided by sample size 30 with standard deviations of means.
Answer to Problem 1AC
Standard deviation of means is greater than standard deviation divided by square root of the sample size.
Explanation of Solution
Given Info:
Sample deviations for 3rd, 7th and 14th students.
From part 4, standard deviation of sample means is 5.8.
Sample size is 30.
Calculation:
SD represents the standard deviation of sample means.
SD3 represents the value obtained by dividing standard deviation of 3rd student divided by sample size.
SD7 represents the value obtained by dividing standard deviation of 7th student divided by sample size.
SD14 represents the value obtained by dividing standard deviation of 14th student divided by sample size.
So, SD3 is less than SD
So, SD7 is less than SD.
So, SD14 is less than SD.
Therefore, the standard deviations for 3rd, 7th and 14th student divided by sample sizes are less than the standard deviation of means.
Moreover, the standard deviation of means is greater than standard deviation divided by square root of the sample size.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
- Find the sample space for the experiment. You toss a coin twice and a six-sided die once.arrow_forwardShow the sample space of the experiment: toss a fair coin three times.arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between events and outcomes? Give an example of both using the sample space of tossing a coin 50 times.arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





