
Alopecia pattern baldness, and hirsutism
INTRODUCTION:
The hair is one of the descriptive characters of the mammals. The abnormalities of the hair are always results not only because of defect in the hair growth cycle but also loosening of the surrounding dermal layers. Also the hormonal imbalances will be acting as a triggering factor for the abnormalities.
EXPLANATION:
Alopecia:
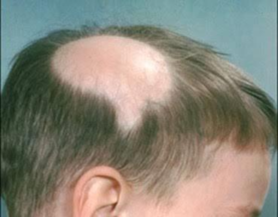
It is loss of hair from the body mainly from scalp. It is otherwise called as spot baldness. It may be results from autoimmune diseases. Usually it is round patchy loss of hair.
Pattern baldness:
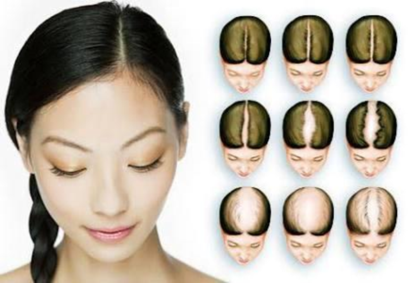
It is a permanent loss of hair from the scalp. Both males and females are affected equally. If it occurs in males, it is called as androgenic alopecia. In females, it is called as androgenetic alopecia. But hair loss rarely proceeds to baldness in females compare to males.
Hirsutism:
It is a term refers to an excessive body hair with increased size and pigmentation. It can be caused by an increased androgens level or hair follicle sensitivity to androgens.

CONCLUSION:
The hair is not only a subject of aesthetic sense. But it is also an indicator of overall health. Hence it is very important to rescue the hair from losing and monitoring for the hair problems.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
- AaBbCc X AaBbCc individuals are crossed. What is the probability of their offspring having a genotype AABBCC?arrow_forwardcircle a nucleotide in the imagearrow_forward"One of the symmetry breaking events in mouse gastrulation requires the amplification of Nodal on the side of the embryo opposite to the Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE). Describe one way by which Nodal gets amplified in this region." My understanding of this is that there are a few ways nodal is amplified though I'm not sure if this is specifically occurs on the opposite side of the AVE. 1. pronodal cleaved by protease -> active nodal 2. Nodal -> BMP4 -> Wnt-> nodal 3. Nodal-> Nodal, Fox1 binding site 4. BMP4 on outside-> nodal Are all of these occuring opposite to AVE?arrow_forward
- If four babies are born on a given day What is the chance all four will be girls? Use genetics lawsarrow_forwardExplain each punnet square results (genotypes and probabilities)arrow_forwardGive the terminal regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the first residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line : Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line: Give the second residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: a) B1 Solution b) B2 c)hybrid rate constant (λ1) d)hybrid rate constant (λ2) e) ka f) t1/2,absorb g) t1/2, dist h) t1/2, elim i)apparent central compartment volume (V1,app) j) total AUC (short cut method) k) apparent volume of distribution based on AUC (VAUC,app) l)apparent clearance (CLapp) m) absolute bioavailability of oral route (need AUCiv…arrow_forward
- You inject morpholino oligonucleotides that inhibit the translation of follistatin, chordin, and noggin (FCN) at the 1 cell stage of a frog embryo. What is the effect on neurulation in the resulting embryo? Propose an experiment that would rescue an embryo injected with FCN morpholinos.arrow_forwardParticipants will be asked to create a meme regarding a topic relevant to the department of Geography, Geomatics, and Environmental Studies. Prompt: Using an online art style of your choice, please make a meme related to the study of Geography, Environment, or Geomatics.arrow_forwardPlekhg5 functions in bottle cell formation, and Shroom3 functions in neural plate closure, yet the phenotype of injecting mRNA of each into the animal pole of a fertilized egg is very similar. What is the phenotype, and why is the phenotype so similar? Is the phenotype going to be that there is a disruption of the formation of the neural tube for both of these because bottle cell formation is necessary for the neural plate to fold in forming the neural tube and Shroom3 is further needed to close the neural plate? So since both Plekhg5 and Shroom3 are used in forming the neural tube, injecting the mRNA will just lead to neural tube deformity?arrow_forward
 Nutrition Through The Life CycleHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337919333Author:Brown, Judith E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Nutrition Through The Life CycleHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337919333Author:Brown, Judith E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,- Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:Cengage
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning





